Abstract
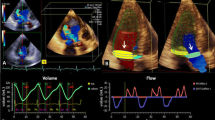
Recent studies have suggested that both cardiac magnetic resonance (MR) and multidetector computed tomography (MDCT) can quantify aortic regurgitation (AR) by planimetry of the anatomical regurgitant orifice (ARO). However, this measurement was not compared with quantitative assessment of AR such as the effective regurgitant orifice (ERO) by proximal isosurface area (PISA) transthoracic echocardiography (TTE) or phase contrast MR. In 42 patients (34 men, age 54 ± 11 years) we compared planimetered ARO by MDCT and MR with ERO and regurgitant volume by PISA TTE and phase contrast MR. ARO by MDCT (r = 0.87, p < 0.001) and MR (r = 0.81, p < 0.001) correlated highly with ERO by TTE. However, ARO by MDCT (27 ± 15 mm2, p < 0.001), but not by MR (23 ± 13 mm2, p = 0.58), were larger than PISA ERO (22 ± 11 mm2). ARO by MDCT (r = 0.78, p < 0.001; r = 0.85, p < 0.001) and MR (r = 0.85, p < 0.001; r = 0.87 p < 0.001) correlated well with regurgitant volume by PISA and phase contrast MR. Both MDCT (к = 0.80, p < 0.001) and MR (к = 0.84, p < 0.001) demonstrated excellent agreement in correctly assessing the mechanisms of AR, i.e. aortic root dilatation (type I), cusp prolapse (type II) and restrictive cusp motion (type III), using surgical inspection as a reference. Measurement of ARO by both MDCT and MR allows accurate quantitative assessment of AR. Both techniques can also accurately determine the mechanism of AR.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AR:
-
aortic regurgitation
- ARO:
-
anatomical regurgitant orifice
- AUC:
-
area under the ROC curve
- ERO:
-
efficient regurgitant orifice
- MR:
-
cardiac magnetic resonance
- MDCT:
-
multidetector row computed tomography
- PISA:
-
proximal isosurface area
- ROC:
-
receiver operating characteristics
- TTE:
-
transthoracic echocardiography
- TEE:
-
transoesophageal echocardiography
References
Bonow RO, Carabello BA, Kanu C, de LA Jr, Faxon DP, Freed MD, Gaasch WH, Lytle BW, Nishimura RA, O’Gara PT, O’Rourke RA, Otto CM, Shah PM, Shanewise JS, Smith SC Jr, Jacobs AK, Adams CD, Anderson JL, Antman EM, Faxon DP, Fuster V, Halperin JL, Hiratzka LF, Hunt SA, Lytle BW, Nishimura R, Page RL, Riegel B (2006) ACC/AHA 2006 guidelines for the management of patients with valvular heart disease: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines (writing committee to revise the 1998 Guidelines for the Management of Patients With Valvular Heart Disease): developed in collaboration with the Society of Cardiovascular Anesthesiologists: endorsed by the Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions and the Society of Thoracic Surgeons. Circulation 114:e84–e231
Enriquez-Sarano M, Tajik AJ (2004) Clinical practice. Aortic regurgitation. N Engl J Med 351:1539–1546
Bekeredjian R, Grayburn PA (2005) Valvular heart disease: aortic regurgitation. Circulation 112:125–134
Vahanian A, Baumgartner H, Bax J, Butchart E, Dion R, Filippatos G, Flachskampf F, Hall R, Iung B, Kasprzak J, Nataf P, Tornos P, Torracca L, Wenink A (2007) Guidelines on the management of valvular heart disease: The Task Force on the Management of Valvular Heart Disease of the European Society of Cardiology. Eur Heart J 28:230–268
Zoghbi WA, Enriquez-Sarano M, Foster E, Grayburn PA, Kraft CD, Levine RA, Nihoyannopoulos P, Otto CM, Quinones MA, Rakowski H, Stewart WJ, Waggoner A, Weissman NJ (2003) Recommendations for evaluation of the severity of native valvular regurgitation with two-dimensional and Doppler echocardiography. J Am Soc Echocardiogr 16:777–802
Ambrosi P, Faugere G, Desfossez L, Habib G, Bory M, Luccioni R, Bernard P (1995) Assessment of aortic regurgitation severity by magnetic resonance imaging of the thoracic aorta. Eur Heart J 16:406–409
Dulce MC, Mostbeck GH, O’Sullivan M, Cheitlin M, Caputo GR, Higgins CB (1992) Severity of aortic regurgitation: interstudy reproducibility of measurements with velocity-encoded cine MR imaging. Radiology 185:235–240
Sondergaard L, Lindvig K, Hildebrandt P, Thomsen C, Stahlberg F, Joen T, Henriksen O (1993) Quantification of aortic regurgitation by magnetic resonance velocity mapping. Am Heart J 125:1081–1090
Recusani F, Bargiggia GS, Yoganathan AP, Raisaro A, Valdes-Cruz LM, Sung HW, Bertucci C, Gallati M, Moises VA, Simpson IA (1991) A new method for quantification of regurgitant flow rate using color Doppler flow imaging of the flow convergence region proximal to a discrete orifice. An in vitro study. Circulation 83:594–604
Tribouilloy CM, Enriquez-Sarano M, Fett SL, Bailey KR, Seward JB, Tajik AJ (1998) Application of the proximal flow convergence method to calculate the effective regurgitant orifice area in aortic regurgitation. J Am Coll Cardiol 32:1032–1039
Vanhoenacker PK, Heijenbrok-Kal MH, Van Heste R, Decramer I, Van Hoe LR, Wijns W, Hunink MG (2007) Diagnostic performance of multidetector CT angiography for assessment of coronary artery disease: meta-analysis. Radiology 244:419–428
Miller JM, Rochitte CE, Dewey M, Arbab-Zadeh A, Niinuma H, Gottlieb I, Paul N, Clouse ME, Shapiro EP, Hoe J, Lardo AC, Bush DE, de Roos A, Cox C, Brinker J, Lima JA (2008) Diagnostic performance of coronary angiography by 64-row CT. N Engl J Med 359:2324–2336
Sun Z, Jiang W (2006) Diagnostic value of multislice computed tomography angiography in coronary artery disease: a meta-analysis. Eur J Radiol 60:279–286
Hausleiter J, Meyer T, Hadamitzky M, Zankl M, Gerein P, Dorrler K, Kastrati A, Martinoff S, Schomig A (2007) Non-invasive coronary computed tomographic angiography for patients with suspected coronary artery disease: the Coronary Angiography by Computed Tomography with the Use of a Submillimeter resolution (CACTUS) trial. Eur Heart J
Budoff MJ, Dowe D, Jollis JG, Gitter M, Sutherland J, Halamert E, Scherer M, Bellinger R, Martin A, Benton R, Delago A, Min JK (2008) Diagnostic performance of 64-multidetector row coronary computed tomographic angiography for evaluation of coronary artery stenosis in individuals without known coronary artery disease: results from the prospective multicenter ACCURACY (Assessment by Coronary Computed Tomographic Angiography of Individuals Undergoing Invasive Coronary Angiography) trial. J Am Coll Cardiol 52:1724–1732
Mowatt G, Cook JA, Hillis GS, Walker S, Fraser C, Jia X, Waugh N (2008) 64-Slice computed tomography angiography in the diagnosis and assessment of coronary artery disease: systematic review and meta-analysis. Heart 94:1386–1393
Juergens KU, Fischbach R (2005) Left ventricular function studied with MDCT. Eur Radiol 16:342–357
Alkadhi H, Wildermuth S, Plass A, Bettex D, Baumert B, Leschka S, Desbiolles LM, Marincek B, Boehm T (2006) Aortic stenosis: comparative evaluation of 16-detector row CT and echocardiography. Radiology 240:47–55
Feuchtner GM, Dichtl W, Friedrich GJ, Frick M, Alber H, Schachner T, Bonatti J, Mallouhi A, Frede T, Pachinger O, Zur ND, Muller S (2006) Multislice computed tomography for detection of patients with aortic valve stenosis and quantification of severity. J Am Coll Cardiol 47:1410–1417
Pouleur AC, le Polain de Waroux JB, Pasquet A, Vanoverschelde JL, Gerber BL (2007) Aortic valve area assessment: multidetector CT compared with cine MR imaging and transthoracic and transesophageal echocardiography. Radiology 244:745–754
Lembcke A, Thiele H, Lachnitt A, Enzweiler CN, Wagner M, Hein PA, Eddicks S, Kivelitz DE (2008) Precision of forty slice spiral computed tomography for quantifying aortic valve stenosis: comparison with echocardiography and validation against cardiac catheterization. Invest Radiol 43:719–728
Alkadhi H, Desbiolles L, Husmann L, Plass A, Leschka S, Scheffel H, Vachenauer R, Schepis T, Gaemperli O, Flohr TG, Genoni M, Marincek B, Jenni R, Kaufmann PA, Frauenfelder T (2007) Aortic regurgitation: assessment with 64-section CT. Radiology 245:111–121
Feuchtner GM, Dichtl W, Schachner T, Muller S, Mallouhi A, Friedrich GJ, Nedden DZ (2006) Diagnostic performance of MDCT for detecting aortic valve regurgitation. AJR Am J Roentgenol 186:1676–1681
Jassal DS, Shapiro MD, Neilan TG, Chaithiraphan V, Ferencik M, Teague SD, Brady TJ, Isselbacher EM, Cury RC (2007) 64-slice multidetector computed tomography (MDCT) for detection of aortic regurgitation and quantification of severity. Invest Radiol 42:507–512
Feuchtner GM, Dichtl W, Muller S, Jodocy D, Schachner T, Klauser A, Bonatti JO (2008) 64-MDCT for diagnosis of aortic regurgitation in patients referred to CT coronary angiography. AJR Am J Roentgenol 191:W1–W7
Debl K, Djavidani B, Buchner S, Heinicke N, Fredersdorf S, Haimerl J, Poschenrieder F, Feuerbach S, Riegger GA, Luchner A (2008) Assessment of the anatomic regurgitant orifice in aortic regurgitation: a clinical magnetic resonance imaging study. Heart 94:e8
le Polain de Waroux JB, Pouleur AC, Goffinet C, Vancraeynest D, Van Dyck M, Robert A, Gerber BL, Pasquet A, El Khoury G, Vanoverschelde JL (2007) Functional anatomy of aortic regurgitation: accuracy, prediction of surgical repairability, and outcome implications of transesophageal echocardiography. Circulation 116:I264–I269
Pouleur AC, le Polain de Waroux JB, Pasquet A, Vancraeynest D, Vanoverschelde JL, Gerber BL (2007) Planimetric and continuity equation assessment of aortic valve area: head to head comparison between cardiac magnetic resonance and echocardiography. J Magn Reson Imaging 26:1436–1443
Pouleur AC, le Polain de Waroux J, Goffinet C, Vancraeynest D, Pasquet A, Gerber BL, Vanoverschelde JL (2008) Accuracy of the flow convergence method for quantification of aortic regurgitation in patients with central versus eccentric jets. Am J Cardiol 102:475–480
Feuchtner GM, Dichtl W, Muller S, Jodocy D, Schachner T, Klauser A, Bonatti JO (2008) 64-MDCT for diagnosis of aortic regurgitation in patients referred to CT coronary angiography. AJR Am J Roentgenol 191:W1–W7
Einstein AJ, Henzlova MJ, Rajagopalan S (2007) Estimating risk of cancer associated with radiation exposure from 64-slice computed tomography coronary angiography. JAMA 298:317–323
Katzberg RW, Barrett BJ (2007) Risk of iodinated contrast material-induced nephropathy with intravenous administration. Radiology 243:622–628
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Fonds National de la Recherche Scientifique of the Belgian Government (FNRS). Dr. Goffinet is aspirant of the Fonds National de la Recherche Scientifique of the Belgian Government.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Goffinet, C., Kersten, V., Pouleur, AC. et al. Comprehensive assessment of the severity and mechanism of aortic regurgitation using multidetector CT and MR. Eur Radiol 20, 326–336 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-009-1544-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-009-1544-x