Abstract
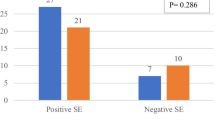
A strong association between rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and human leukocyte antigen (HLA) has been observed in many different populations and that accounts for approximately one-third of the genetic component of RA susceptibility. The greatest effect comes from DRβ1 gene where the strongest association has been found with DRβ1*04 (DR4) allele. As serology has some disadvantages over polymerase chain reaction (PCR)-based techniques and commercially available PCR-based kits are expensive, this study was aimed to standardize simple in-house PCR-SSP technique. Accuracy of this test was further checked with standard PCR-SSOP (RLS) results. The frequency HLA-DRβ1*04 was significantly increased among RA patients when compared with normal controls. In this study, a very simple, convenient and more cost-effective in-house PCR-SSP technique was standardized for HLA-DRβ1*04 typing that is helpful to RA diagnosis in developing countries like India, which can be used as a good screening test.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Laivoranta-Nyman S, Mottonen T, Luukkainen R, Hakala M, Yli-Kerttula U, Hannonen P, Tuokko J, Toivanen A, Ilonen J (2000) Immunogenetic differences between patients with familial and non-familial rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 59:173–177
Lefevre S, Knedla A, Tennie C, Kampmann A, Wunrau C, Dinser R (2009) Synovial fibroblasts spread rheumatoid arthritis to unaffected joints. Nat Med 15(12):1414–1422
Thorsby E (1997) Invited anniversary review: HLA associated diseases. Hum Immunol 53:1–11
Turesson C, Matteson EL (2006) Genet Rheum Arthr. Mayo Clin Proc 81:94–101
Stastny P (1978) Association of the B-cell alloantigen DRw4 with rheumatoid arthritis. N Engl J Med 298(16):869–871
Singwe-Ngandeu M, Finckh A, Bas S, Tiercy JM, Gabay C (2010) Diagnostic value of anti-cyclic citrullinated peptides and association with HLA-DRB1 shared epitope alleles in African rheumatoid arthritis patients. Arthr Res Therapy 12:R36
Wordsworth BP, Lanchburyt JSS, Sakkast LI, Welsht KI, Panayit GS, Bell JI (1989) HLA-DR4 Subtype frequencies in rheumatoid arthritis indicate that DRB1 is the major susceptibility locus within the HLA class II region. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86:10049–10053
Kim TG, Choi HB, Park SH, Kim HY, Han H (1999) DQCAR 113 and DQCAR 115 in combination with HLA-DRB1 alleles are significant markers of susceptibility to rheumatoid arthritis in the Korean population. Tissue Antigens 54:552–559
Hong GH, Park MH, Takeuchi F, Oh MD, Song YW, Nabeta H, Nakano K, Ito K, Park KS (1996) Association of specific amino acid sequence of HLA-DR with rheumatoid arthritis in Koreans and its diagnostic value. J Rheumatol 23:1699–1703
Takeuchi F, Nakano K, Matsuta K, Nabeta H, Bannai M, Tanimoto K (1996) Positive and negative association of DRB genotypes with Japaneese patients with early rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol 14:17–22
Higami K, Hakoda M, Matsuda Y, Ueda H (1997) Lack of association of DRB1 genotype with radiologic progression in Japanese patients with early rheumatoid arthritis. Arthr Rheum 40:2241–2247
Laivoranta-Nyman S, Mottonen T, Hermann R, Tuokko J, Luukkainen R, Hakala M, Honnonen P (2004) HLA-DR-DQ haplotypes and genotypes in Finnish patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 63:1406–1412
Mehra NK, Vaidya MC, Taneja V, Agarwal A, Malaviya AN (1996) HLA-DR antigens in rheumatoid arthritis in North India. Hum Immunol 46:35–41
Taneja V, Mehra NK, Kailash S, Anand C, Malaviya AN (1992) Protective and risk DR phenotypes in Asian Indian patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Ind J Med Res 96:16–23
Jun KR, Choi SE, Cha C-H, Oh H-B, Heo Y-S, Lee K-j, Ahn H-y (2007) Meta-analysis of the association between HLA-DRB1 allele and rheumatoid arthritis susceptibility in Asian populations. J Korean Med Sci 22:973–980
Jaini R, Kaur G, Mehra NK (2002) Heterogeneity of HLA-DRB1*04 and its associated haplotypes in the North Indian population. Hum Immunol 63(1):24–29
Jun KR, Choi SE, Cha CH, Oh HB, Heo YS (2007) Meta analysis of the association between HLA-DRB1 allele and rheumatoid arthritis susceptibility in Asian populations. J Korean Med Sci 22:973–980
Gregersen PK, Silver J, Winchester RJ (1987) The shared epitope hypothesis. An approach to understanding the molecular genetics of susceptibility to rheumatoid arthritis. Arthr Rheum 30:1205–1213
de Vries N, Tijssen H, van Reil PL, van de Putte LB (2002) Reshaping the shared epitope hypothesis: HLA-associated risk for rheumatoid arthritis is encoded by amino acid substitution at position 67-74 of the HLA-DRB1 molecule. Arthr Rheum 46:921–928
Gorman JD, Lum RF, Chen JJ, Suarez-Almazor ME, Thomson G, Criswell LA (2004) Impact of shared epitope genotype and ethnicity on erosive disease: a meta-analysis of 3,240 rheumatoid arthritis patients. Arthr Rheum 50:400–412
Tiwari JL, Terasaki PI (1985) HLA and disease associations. Springer, New York
Terasaki PI, McClelland JD (1964) Micro droplet assay for human cytotoxins. Nature 204:998–1000
Olerup O, Zetterquist H (1992) HLA-DR typing by PCR amplification with sequence-specific primers (PCR-SSP) in 2 hours. An alternative to serological DR typing in clinical practice including donor-recipient matching in cadaveric transplantations. Tissue Antigens 39:225–235
Aletaha D, Neogi T, Silman A, Hobbs K, Symmons D (2010) Rheumatoid arthritis classification criteria, an American college of rheumatology/European league against rheumatism collaborative initiative. Arthr Rheum 62:2569–2581
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Parasannanavar, D.J., Yeola, A., Pradhan, V. et al. HLA-DRβ1*04 typing by simple in-house PCR-SSP technique for rheumatoid arthritis patients. Rheumatol Int 33, 867–870 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-012-2448-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-012-2448-7