Abstract
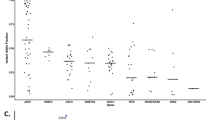
Transforming mutations in RAS genes are commonly found in human malignancies, including myeloid leukemias. To investigate the incidence, spectrum, and distribution of activating K- and N-RAS mutations in cytogenetically normal acute myeloid leukemia (CN-AML) patients, 204 CN-AML patients were screened. Activating K- and N-RAS mutations were detected in 3 of 204 (1.5 %) and 22 of 204 (10.8 %) CN-AML samples, respectively. RAS mutated patients presented with a lower percentage of bone marrow blasts (65 vs 80 %, P = 0.022). RAS mutations tended to occur with nucleophosmin-1 (NPM1) mutations (P = 0.079), and all three samples containing K-RAS mutations had concomitant NPM1 mutations. There was no significant overlap between K-RAS mutations and N-RAS, FLT3, CEBPA, IDH1/2, WT1 or MLL mutations. RAS mutation status did not impact relapse-free or overall survival of CN-AML patients. In contrast to reports of noncanonical RAS mutations in other cancers, including some leukemia subtypes, we only observed K- and N-RAS mutations in codons 12, 13, or 61 in CN-AML samples. Our findings suggest that while K-RAS mutations are infrequent in CN-AML, activating K-RAS mutations may cooperate with mutated NPM1 to induce leukemia.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bos JL (1989) Ras oncogenes in human cancer: a review. Cancer Res 49:4682–4689
Reuter CW, Morgan MA, Bergmann L (2000) Targeting the Ras signaling pathway: a rational, mechanism-based treatment for hematologic malignancies? Blood 96:1655–1669
Thiede C (2012) Mutant DNMT3A: teaming up to transform. Blood 119:5615–5617
Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network (2013) Genomic and epigenomic landscapes of adult de novo acute myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med 368:2059–2074
Shlush LI, Zandi S, Mitchell A, Chen WC, Brandwein JM, Gupta V et al (2014) Identification of pre-leukaemic haematopoietic stem cells in acute leukaemia. Nature 506:328–333
Schlenk RF, Döhner K, Krauter J, Fröhling S, Corbacioglu A, Bullinger L et al (2008) Mutations and treatment outcome in cytogenetically normal acute myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med 358:1909–1918
Paschka P, Marcucci G, Ruppert AS, Whitman SP, Mrózek K, Maharry K et al (2008) Wilms’ tumor 1 gene mutations independently predict poor outcome in adults with cytogenetically normal acute myeloid leukemia: a cancer and leukemia group B study. J Clin Oncol 26:4595–4602
Damm F, Heuser M, Morgan M, Yun H, Grosshennig A, Göhring G et al (2010) Single nucleotide polymorphism in the mutational hotspot of WT1 predicts a favorable outcome in patients with cytogenetically normal acute myeloid leukemia. J Clin Oncol 28:578–585
Bowen DT, Frew ME, Hills R, Gale RE, Wheatley K, Groves MJ et al (2005) RAS mutation in acute myeloid leukemia is associated with distinct cytogenetic subgroups but does not influence outcome in patients younger than 60 years. Blood 106:2113–2119
Bacher U, Haferlach T, Schoch C, Kern W, Schnittger S (2006) Implications of NRAS mutations in AML: a study of 2502 patients. Blood 107:3847–3853
Neubauer A, Maharry K, Mrózek K, Thiede C, Marcucci G, Paschka P et al (2008) Patients with acute myeloid leukemia and RAS mutations benefit most from postremission high-dose cytarabine: a Cancer and Leukemia Group B study. J Clin Oncol 26:4603–4609
Tyner JW, Erickson H, Deininger MW, Willis SG, Eide CA, Levine RL et al (2009) High-throughput sequencing screen reveals novel, transforming RAS mutations in myeloid leukemia patients. Blood 113:1749–1755
Damm F, Heuser M, Morgan M, Wagner K, Görlich K, Grosshennig A et al (2011) Integrative prognostic risk score in acute myeloid leukemia with normal karyotype. Blood 117:4561–4568
Morgan MA, Sebil T, Aydilek E, Peest D, Ganser A, Reuter CW (2005) Combining prenylation inhibitors causes synergistic cytotoxicity, apoptosis and disruption of RAS-to-MAP kinase signalling in multiple myeloma cells. Br J Haematol 130:912–925
Frohling S, Schlenk RF, Stolze I, Bihlmayr J, Benner A, Kreitmeier S et al (2004) CEBPA mutations in younger adults with acute myeloid leukemia and normal cytogenetics: prognostic relevance and analysis of cooperating mutations. J Clin Oncol 22:624–633
Döhner K, Schlenk RF, Habdank M, Scholl C, Rücker FG, Corbacioglu A et al (2005) Mutant nucleophosmin (NPM1) predicts favorable prognosis in younger adults with acute myeloid leukemia and normal cytogenetics: interaction with other gene mutations. Blood 106:3740–3746
Döhner K, Tobis K, Ulrich R, Fröhling S, Benner A, Schlenk RF et al (2002) Prognostic significance of partial tandem duplications of the MLL gene in adult patients 16 to 60 years old with acute myeloid leukemia and normal cytogenetics: a study of the Acute Myeloid Leukemia Study Group Ulm. J Clin Oncol 20:3254–3261
Thiede C, Steudel C, Mohr B, Schaich M, Schäkel U, Platzbecker U et al (2002) Analysis of FLT3-activating mutations in 979 patients with acute myelogenous leukemia: association with FAB subtypes and identification of subgroups with poor prognosis. Blood 99:4326–4335
Wagner K, Damm F, Göhring G, Görlich K, Heuser M, Schäfer I et al (2010) Impact of IDH1 R132 mutations and an IDH1 single nucleotide polymorphism in cytogenetically normal acute myeloid leukemia: SNP rs11554137 is an adverse prognostic factor. J Clin Oncol 28(14):2356–2364
Thol F, Damm F, Wagner K, Gohring G, Schlegelberger B, Hoelzer D et al (2010) Prognostic impact of IDH2 mutations in cytogenetically normal acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 116:614–616
Cheson BD, Bennett JM, Kopecky KJ, Büchner T, Willman CL, Estey EH et al (2003) Revised recommendations of the international working group for diagnosis, standardization of response criteria, treatment outcomes, and reporting standards for therapeutic trials in acute myeloid leukemia. J Clin Oncol 21:4642–4649
Korn EL (1986) Censoring distributions as a measure of follow-up in survival analysis. Stat Med 5:255–260
Kiyoi H, Naoe T, Nakano Y, Yokota S, Minami S, Miyawaki S et al (1999) Prognostic implication of FLT3 and N-RAS gene mutations in acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 93:3074–3080
Neubauer A, Dodge RK, George SL, Davey FR, Silver RT, Schiffer CA et al (1994) Prognostic importance of mutations in the ras proto-oncogenes in de novo acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 83:1603–1611
Gelsi-Boyer V, Trouplin V, Adélaïde J, Aceto N, Remy V, Pinson S et al (2008) Genome profiling of chronic myelomonocytic leukemia: frequent alterations of RAS and RUNX1 genes. BMC Cancer 8:299
Schnittger S, Schoch C, Kern W, Mecucci C, Tschulik C, Martelli MF et al (2005) Nucleophosmin gene mutations are predictors of favorable prognosis in acute myelogenous leukemia with a normal karyotype. Blood 106:3733–3739
Zhang J, Wang J, Liu Y, Sidik H, Young KH, Lodish HF et al (2009) Oncogenic Kras-induced leukemogenesis: hematopoietic stem cells as the initial target and lineage-specific progenitors as the potential targets for final leukemic transformation. Blood 113:1304–1314
Koo HM, Monks A, Mikheev A, Rubinstein LV, Gray-Goodrich M, McWilliams MJ et al (1996) Enhanced sensitivity to 1-beta-d-arabinofuranosylcytosine and topoisomerase II inhibitors in tumor cell lines harboring activated ras oncogenes. Cancer Res 56:5211–5216
Illmer T, Thiede C, Fredersdorf A, Stadler S, Neubauer A, Ehninger G et al (2005) Activation of the RAS pathway is predictive for a chemosensitive phenotype of acute myelogenous leukemia blasts. Clin Cancer Res 11:3217–3224
Zhao S, Zhang Y, Sha K, Tang Q, Yang X, Yu C et al (2014) KRAS (G12D) Cooperates with AML1/ETO to initiate a mouse model mimicking human acute myeloid leukemia. Cell Physiol Biochem 33(1):78–87
Kong G, Du J, Liu Y, Meline B, Chang YI, Ranheim EA, Wang J, Zhang J (2013) Notch1 gene mutations target KRAS G12D-expressing CD8+ cells and contribute to their leukemogenic transformation. J Biol Chem 288(25):18219–18227
Ley TJ, Mardis ER, Ding L, Fulton B, McLellan MD, Chen K et al (2008) DNA sequencing of a cytogenetically normal acute myeloid leukaemia genome. Nature 456:66–72
Acknowledgments
The authors thank E. Lux and K. Görlich for excellent technical support. This work was supported by grants to C.R. from the German José Carreras Leukemia Stiftung (DJCLS R 05/21 and DJCLS R 07/32f).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Christoph W. M. Reuter and Jürgen Krauter contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Reuter, C.W.M., Krauter, J., Onono, F.O. et al. Lack of noncanonical RAS mutations in cytogenetically normal acute myeloid leukemia. Ann Hematol 93, 977–982 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-014-2061-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-014-2061-9