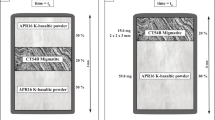
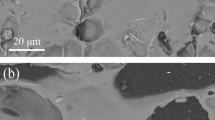
Abstract
High pressure melting behavior of three Fe-alloys containing 5 wt% Ni and (1) 10 wt% Si, (2) 15 wt% Si or (3) 12 wt% S was investigated up to megabar pressures by in situ X-ray diffraction and laser-heated diamond anvil cell techniques. We observe a decrease in melting temperature with increasing Si content over the entire investigated pressure range. This trend is used to discuss the melting curve of pure Fe. Moreover, our measurements of eutectic melting in the Fe–Fe3S system show a change in slope around 50 GPa concomitant with the fcc–hcp phase transition in pure solid iron. Extrapolations of our melting curve up to the core–mantle boundary pressure yield values of 3,600–3,750 K for the freezing temperature of plausible outer core compositions.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alfè D, Gillan MJ, Price GD (2002a) Composition and temperature of the Earth’s core constrained by combining ab initio calculations and seismic data. Earth Planet Sci Lett 195:91–98
Alfè D, Price GD, Gillan MJ (2002b) Iron under Earth’s core conditions: liquid-state thermodynamics and high-pressure melting curve from ab initio calculations. Phys Rev B 65:165118
Allègre CJ, Poirier JP, Humler E, Hofmann AW (1995) The chemical composition of the earth. Earth Planet Sci Lett 134:515–526
Anderson OL, Isaak DG (2002) Another look at the core density deficit of Earth’s outer core. Phys Earth Plan Int 131:19–27
Andrault D, Fiquet G, Itié JP, Richet P, Gillet P, Häusermann D, Hanfland H (1998) Thermal pressure in the laser heated diamond anvil cell: an X-ray diffraction study. Eur J Mineral 10:931–940
Andrault D, Morard G, Bolfan-Casanova N, Ohtaka O, Fukui H, Arima H, Guignot N, Funakoshi K, Lazor P, Mezouar M (2006) Study of partial melting at high pressure using in situ X-ray diffraction. High Press Res 26:267–276
Andrault D, Bolfan-Casanova N, Ohtaka O, Fukui H, Arima H, Fialin M, Funakoshi K (2009) Melting diagrams of Fe-rich alloys determined from synchrotron in situ measurements in the 15–23 GPa pressure range. Phys Earth Plan Int 174:181–191
Andrault D, Bolfan-Casanova N, Lo Nigro G, Bouhifd MA, Garbarino G, Mezouar M (2011) Solidus and liquidus profiles of chondritic mantle: implication for melting of the Earth across its history. Earth Planet Sci Lett 304:251–259
Asanuma H, Ohtani E, Sakai T, Terasaki H, Kamada S, Kondo T, Kikegawa T (2010) Melting of iron–silicon alloy up to the core–mantle boundary pressure: implications to the thermal structure of the Earth’s core. Phys Chem Minerals 37:353–359
Badro J, Fiquet G, Guyot F, Gregoryanz E, Occelli F, Antonangeli D, D’Astuto M (2007) Effect of light elements on the sound velocities in solid iron: Implications for the composition of Earth’s core. Earth Planet Sci Lett 254:233–238
Belonoshko AB, Ahuja R, Johansson B (2000) Quasi–Ab initio molecular dynamic study of Fe melting. Phys Rev Lett 84:3638–3641
Boehler R (1993) Temperatures in the earth’s core from melting point measurements of iron at high static pressures. Nature 363:534–536
Boehler R, De Hantsetters K (2004) New anvils design in diamond-cells. High Press Res 24:391–394
Brazhkin VV, Popova SV, Voloshin RN (1997) High pressure transformations in simple melts. High Press Res 15:267–305
Breuer D, Labrosse S, Spohn T (2010) Thermal evolution and magnetic field generation in terrestrial planets and satellites. Space Sci Rev 152:449–500
Brosh E, Makov G, Shneck RZ (2009) Thermodynamic analysis of high-pressure phase equilibria in Fe–Si alloys, implications for the inner-core. Phys Earth Plan Int 172:289–298
Brown JM, McQueen RG (1986) Phase Transitions, Grüneisen parameter, and elasticity for shocked iron between 77 GPa and 400 GPa. J Geophys Res 91:7485–7494
Campbell AJ, Seagle CT, Heinz DL, Shen G, Prakapenka VB (2007) Partial-melting in the iron-sulfur system at high pressure: a synchrotron X-ray diffraction study. Phys Earth Planet Inter 162:119–128
Chen B, Li J, Hauck SAI (2008) Non-ideal liquidus curve in the Fe-S system and Mercury’s snowing core. Geophys Res Lett 35:L07201
Chudinovskikh L, Boehler R (2007) Eutectic melting in the Fe-S system to 44 GPa. Earth Planet Sci Lett 257:97–103
Dewaele A, Mezouar M, Guignot N, Loubeyre P (2007) Melting of lead under high pressure studied using second-scale time-resolved x-ray diffraction. Phys Rev B 76:144106
Errandonea D (2010) The melting curve of ten metals up to 12 GPa and 1600 K. J Appl Phys 108:033517
Fei Y, Bertka CM, Finger LW (1997) High pressure iron sulfur compound, Fe3S2, and melting relations in the Fe–FeS system. Science 275:1621–1623
Fei Y, Li J, Bertka CM, Prewitt CT (2000) Structure type and bulk modulus of Fe3S, a new iron-sulfur compound. Am Mineral 85:1830–1833
Fiquet G, Auzende AL, Siebert J, Corgne A, Bureau H, Ozawa H, Garbarino G (2010) Melting of peridotite ay 140 Gigapascals. Science 329:1516–1518
Funamori N, Yagi T, Uchida T (1996) High-pressure and high-temperature in situ X-ray diffraction study of iron to above 30 GPa using MA8-type apparatus. Geophys Res Lett 23:953–956
Hirao N, Ohtani E, Kondo T, Kikegawa T (2004) Equation of state of iron-silicon alloys to megabar pressure. Phys Chem Minerals 31:329–336
Javoy M (1995) The integral enstatite chondrite model of the Earth. Geophys Res Lett 22:2219–2222
Kamada S, Terasaki H, Ohtani E, Sakai T, Kikegawa T, Ohishi Y, Hirao N, Sata N, Kondo T (2010) Phase relationships of the Fe–FeS system in conditions up to the Earth’s outer core. Earth Planet Sci Lett 294:94–100
Komabayashi T, Fei Y, Meng Y, Prakapenka VB (2009) In situ X-ray diffraction measuremetns of the γ-ε transition boundary of iron in an internally-heated diamond anvil cell. Earth Planet Sci Lett 282:252–257
Kubaschewski O (1982) Iron-binary phase diagrams, vol 1. Springer
Kuwayama Y, Hirose K (2004) Phase relations in the system Fe-FeSi at 21 GPa. Am Mineral 89:273–276
Kuwayama K, Sawai T, Hirose K, Sata N, Ohishi Y (2009) Phase relations of iron–silicon alloys at high pressure and high temperature. Phys Chem Minerals 36:511–518
Labrosse S, Hernlund JW, Coltice N (2007) A crystallizing dense magma ocean at the base of the Earth’s mantle. Nature 450:866–869
Lay T, Garnero EJ, Williams Q (2004) Partial melting in a thermo-chemical boundary layer at the base of the mantle. Phys Earth Plan Int 146:441–467
Lay T, Hernlund JW, Buffet BA (2008) Core–mantle boundary heat flow. Nat Geosci 1:25–32
Ma Y, Somayazulu M, Shen G, Mao HK, Shu J, Hemley RJ (2004) in situ X-ray diffraction studies of iron to earth-core conditions. Phys Earth Plan Int 143–144:455–467
Mezouar M, Crichton WA, Bauchau S, Thurel F, Witsch H, Torrecillas F, Blattman G, Marion P, Dabin Y, Chavanne J, Hignette O, Morawe C, Borel C (2005) Development of a new state-of-the-art beamline optimized for monochromatic single crystal and powder X-ray diffraction under extreme conditions at the ESRF. J Synch Rad 12:659–664
Morard G, Sanloup C, Fiquet G, Mezouar M, Rey N, Poloni R, Beck P (2007) Structure of eutectic Fe-FeS melts up to 17 GPa: Implications for planetary cores. Earth Planet Sci Lett 263:128–139
Morard G, Andrault D, Guignot N, Sanloup C, Mezouar M, Petitgirard S, Fiquet G (2008a) In situ determination of Fe-Fe3S phase diagram and liquid structural properties up to 65 GPa. Earth Planet Sci Lett 272:620–626
Morard G, Sanloup C, Guillot B, Fiquet G, Mezouar M, Perrillat JP, Garbarino G, Mibe K, Komabayashi T, Funakoshi K (2008b) in situ structural investigation of Fe–S–Si immiscible liquid system and evolution of Fe–S bond properties with pressure. J Geophys Res 113:B10205
Morard G, Bouchet J, Valencia D, Mazevet S, Guyot F (2011) The melting curve of iron at extreme pressures: implications for planetary cores. High Energy Dens Phys 7:141–144
Nguyen JH, Holmes NC (2004) Melting of iron at the physical conditions of the Earth’s core. Nature 427:339–342
Ozawa H, Hirose K, Mitome M, Bando Y, Sata N, Ohishi Y (2008) Chemical equilibrium between ferropericlase and molten iron to 134 GPa and implications for iron content at the bottom of the mantle. Geophys Res Lett 35:05308
Poirier JP (1994) Light elements in the Earth’s outer core: a critical review. Phys Earth Planet Inter 85:319–337
Raghavan V (2003) Fe–Ni–Si (iron-nickel-silicon). J Phase Equilibria 24:269–271
Schultz E, Mezouar M, Crichton WA, Bauchau S, Blattman G, Andrault D, Fiquet G, Boehler R, Rambert N, Sitaud B, Loubeyre P (2005) Double-sided laser heating system for in situ high-pressure and high temperature monochromatic X-ray diffraction at the ESRF. High Press Res 25:71–83
Seagle CT, Heinz DL, Campbell AJ, Prakapenka VB, Wanless ST (2008) Melting and thermal expansion in the Fe-FeO system at high pressure. Earth Planet Sci Lett 265:655–665
Shen G, Mao HK, Hemley RJ, Duffy TS, Rivers ML (1998) Melting and crystal structure of iron at high pressures and temperatures. Geophys Res Lett 25:373–376
Shen G, Prakapenka VB, Rivers ML, Sutton SR (2004) Structure of liquid iron up to 58 GPa. Phys Rev Lett 92:185701
Simon F, Glatzel G (1929) Remarks on fusion pressure curve. Z Anorg Allg Chem 178:309–316
Stewart AJ, Schmidt MW, van Westrenen W, Liebske C (2007) Mars: a new core-crystallisation regime. Science 316:1323–1325
Walker D, Cranswick LMD, Verma PK, Clark SM, Buhre S (2002) Thermal equations of state for B1 and B2 KCl. Am Mineral 87:805–812
Williams Q, Garnero EJ (1996) Seismic evidence for partial melt at the base of earth’s mantle. Science 273:1528–1530
Williams Q, Knittle E, Jeanloz R (1991) The high pressure melting curve of iron: a technical discussion. J Geophys Res 96:2171–2184
Yoo CS, Holmes NC, Ross M, Webb DJ, Pike C (1993) Shock temperatures and melting of iron at earth core conditions. Phys Rev Lett 70:3931–3934
Acknowledgments
GM acknowledges the SECHEL program of the Agence Nationale de la Recherche (Grant ANR-07-BLAN-185577) and the European Community’s Seventh Framework Programme (FP7/2007-2013)/ERC Grant Agreement No. 207467. The authors would like to thank the ESRF staff of the High Pressure Beamline ID27 (S. Bauchau) for the X-ray experiments. We would like also to thank G.Fiquet for fruitful discussions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Morard, G., Andrault, D., Guignot, N. et al. Melting of Fe–Ni–Si and Fe–Ni–S alloys at megabar pressures: implications for the core–mantle boundary temperature. Phys Chem Minerals 38, 767–776 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00269-011-0449-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00269-011-0449-9