Abstract
Purpose
The aim of this study was to present our technique to implant unicompartmental knee arthroplasty (UKA) using navigation and to give our first results regarding the accuracy of the device.
Methods
A total of 33 patients with medial femorotibial osteoarthritis (31) or avascular necrosis (2) were included in this study. The mean preoperative hip-knee-ankle (HKA) angle was 172.7 ± 2.2° (range 167–177°) and the preoperative planning aimed to reach an HKA angle between 175 and 179° (177 ± 2°), a tibial varus at 3 ± 1°, which means a tibial mechanical angle (TMA) close to 87 ± 1°, and posterior tibial slope at 3 ± 2°. In all cases, we used the OrthoPilot® device with dedicated software allowing us to navigate only the tibial plateau.
Results
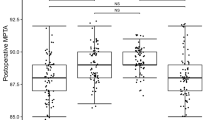
The preoperative plan was reached in 93.9 % of cases for HKA angle, 84.8 % for TMA and 100 % for the posterior slope.
Conclusions
Unicompartmental knee navigation is reliable. The navigation of only the tibial bone cut is a reasonable option as has been shown in this study. Its role is invaluable in the positioning of mobile-bearing UKA, where the risk of overcorrection should not be underestimated.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Borus T, Thornhill T (2008) Unicompartmental knee arthroplasty. J Am Acad Orthop Surg 16:9–18
Marmor L (1982) The Marmor knee replacement. Orthop Clin North Am 13:55–64
Cartier P, Cheaib S (1987) Unicondylar knee arthroplasty. 2-10 years of follow-up evaluation. J Arthroplasty 2:157–162
Hernigou P, Deschamps G (1996) Prothèses unicompartimentales du genou. Rev Chir Orthop Reparatrice Appar Mot 82(Suppl 1):23–60
Hernigou P, Deschamps G (2004) Alignment influences wear in the knee after medial unicompartmental arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 423:161–165
Scott RD (2006) Three decades of experience with unicompartmental arthroplasty: mistakes made and lessons learned. Orthopedics 29:829–831
Mercier N, Wimsey S, Saragaglia D (2010) Long-term clinical results of the Oxford medial unicompartmental knee arthroplasty. Int Orthop 34:1137–1143
Neyret P, Chatain F, Deschamps G (1996) Matériel et options dans les prothèses unicompartimentales du genou. Rev Chir Orthop Reparatrice Appar Mot 82(Suppl 1):48–52
Jenny JY, Boeri C (2001) Implantation d’une prothèse totale de genou assistée par ordinateur. Etude comparative cas-témoin avec une instrumentation traditionnelle. Rev Chir Orthop Reparatrice Appar Mot 87:645–652
Saragaglia D, Picard F, Chaussard C, Montbarbon E, Leitner F, Cinquin P (2001) Mise en place des prothèses totale du genou assistée par ordinateur: comparaison avec la technique conventionnelle. A propos d’une étude prospective randomisée de 50 cas. Rev Chir Orthop Reparatrice Appar Mot 87:18–28
Saragaglia D, Chaussard C, Rubens-Duval B (2006) Navigation as a predictor of soft tissue release during 90 cases of computer-assisted total knee arthroplasty. Orthopedics 29(10 Suppl):S137–S138
Ayach A, Plaweski S, Saragaglia D (2009) Computer-assisted uni knee arthroplasty for genu varum deformity. Results of axial correction in a case-control study of 40 cases. In 9th annual meeting of CAOS-International proceedings. Wingspan, Livermore, pp 4–7
Cossey AJ, Spriggins J (2005) The use of computer-assisted surgical navigation to prevent malalignment in unicompartmental knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 20:29–34
Jenny JY, Boeri C (2003) Unicompartmental knee prosthesis implantation with a non-image-based navigation system: rationale, technique, case-control comparative study with a conventional instrumented implantation. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 11:40–45
Jenny JY (2008) Navigated unicompartmental knee replacement. Sports Med Arthrosc 16:103–107
Jung KA, Kim SJ, Lee SC, Hwang SH, Ahn NK (2010) Accuracy of implantation during computer-assisted minimally invasive Oxford unicompartmental knee arthroplasty: a comparison with a conventional instrumented technique. Knee 17:387–391
Perlick L, Bäthis H, Tingart M, Perlick C, Lüring C, Grifka J (2004) Minimally invasive unicompartmental knee replacement with a nonimage-based navigation system. Int Orthop 28:193–197
Rosenberger RE, Fink C, Quirbach S, Attal R, Tecklenburg K, Hoser C (2008) The immediate effect of navigation on implant accuracy in primary mini-invasive unicompartmental knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 16:1133–1140
Jenny JY, Boeri C (2002) Accuracy of implantation of a unicompartmental knee arthroplasty with 2 different instrumentations: a case-controlled comparative study. J Arthroplasty 17:1016–1020
Larsson SE, Larsson S, Lundkvist S (1988) Unicompartmental knee arthroplasty. A prospective consecutive series followed for six to 11 years. Clin Orthop Relat Res 232:174–181
Ridgeway SR, McAuley JP, Ammeen DJ, Engh GA (2002) The effect of alignment of the knee on the outcome of unicompartmental knee replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Br 84:351–355
Seon JK, Song EK, Park SJ, Yoon TR, Lee KB, Jung ST (2009) Comparison of minimally invasive unicompartmental knee arthroplasty with or without a navigation system. J Arthroplasty 24:351–357
Lim MH, Tallay A, Bartlett J (2009) Comparative study of the use of computer assisted navigation system for axial correction in medial unicompartmental knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 17:341–346
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saragaglia, D., Picard, F. & Refaie, R. Navigation of the tibial plateau alone appears to be sufficient in computer-assisted unicompartmental knee arthroplasty. International Orthopaedics (SICOT) 36, 2479–2483 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-012-1679-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-012-1679-2