Abstract
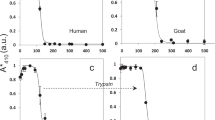
NMR measurements of the diffusional permeability of the human adult red blood cell (RBC) membrane to water (P d) and of the activation energy (E a,d) of the process furnished values of P d ~ 4 × 10−3 cm/s at 25 °C and ~6.1 × 10−3 cm/s at 37 °C, and E a,d ~ 26 kJ/mol. Comparative NMR measurements for other species showed: (1) monotremes (echidna and platypus), chicken, little penguin, and saltwater crocodile have the lowest P d values; (2) sheep, cow, and elephant have P d values lower than human P d values; (3) cat, horse, alpaca, and camel have P d values close to those of humans; (4) guinea pig, dog, dingo, agile wallaby, red-necked wallaby, Eastern grey kangaroo, and red kangaroo have P d values higher than those of humans; (5) mouse, rat, rabbit, and “small and medium size” marsupials have the highest values of P d (>8.0 × 10−3 cm/s at 25 °C and >10.0 × 10−3 cm/s at 37 °C). There are peculiarities of E a,d values for the RBCs from different species. The maximum inhibition of diffusional permeability of RBCs induced by incubation with p-chloromercuribenzene sulfonate varied between 0 % (for the chicken and little penguin) to ~50 % (for human, mouse, cat, sheep, horse, camel, and Indian elephant), and ~60–75 % (for rat, guinea pig, rabbit, dog, alpaca, and all marsupials). These results indicate that no water channel proteins (WCPs) or aquaporins are present in the membrane of RBCs from monotremes (echidna, platypus), chicken, little penguin and saltwater crocodile whereas WCPs from the membranes of RBCs from marsupials have peculiarities.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abu-Hamdah R, Cho WJ, Jeremic A, Kelly M, Ilie A, Jena BP (2004) Regulation of the water channel aquaporin-1: isolation and reconstitution of the regulatory complex. Cell Biol Int 28:1–17
Balaban AT, Haiduc I, Matasa CG, Sha’afi RI (2006) Who discovered the water channels (aquaporins)? Cell Mol Biol 52:6–7
Bârzu O, Benga G, Mureşan L, Dancea S, Tilinca R (1971) Stability and enzymatic properties of liver mitochondria in diluted suspensions. Enzyme 12:433–448
Bârzu O, Mureşan L, Benga G (1972) Spectrophotometric method for assay of oxygen uptake. IV. Study of the respiratory chain in small amounts of biological materials. Anal Biochem 46:374–387
Beilharz GR, Middlehurst CR, Kuchel PW, Hunt GE, Johnson GFS (1984) Determination of choline in erythrocytes using high resolution proton nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy: comparison with a choline oxidase method. Anal Biochem 137:324–328
Benga G (1983) Spin labelling. In: Wrigglesworth JM (ed) Biochemical research techniques. Wiley, London, pp 79–117
Benga G (1984) Molecular composition and functional properties of human liver mitochondria. In: Benga G, Baum H, Kummerow FA (eds) Membrane processes (molecular biology and medical applications). Springer, New York, pp 65–91
Benga G (1985) Protein–lipid interactions in biological membranes. In: Benga G (ed) Structure and properties of cell membranes, vol I. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 160–188
Benga G (1988a) Protein–lipid interactions in biological membranes—spin label studies and physiological implications. Mol Asp Med 10:201–222
Benga G (1988b) Water transport in human red blood cells. Prog Biophys Mol Biol 51:193–245
Benga G (1989a) Membrane proteins involved in the water permeability of human erythrocytes: binding of p-chloromercuribenzene sulfonate to membrane proteins correlated with nuclear magnetic resonance measurements. In: Benga G (ed) Water transport in biological membranes, vol 2. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 41–61
Benga G (1989b) Permeability through pores and holes. Curr Opin Cell Biol 1:771–774
Benga G (1989c) Water exchange through the erythrocyte membrane. Int Rev Cytol 114:273–316
Benga G (2001) Diffusional water permeability of red blood cells from various vertebrate species. B Mol Med 7–8:27–42
Benga G (2003) Birth of water channel proteins—the aquaporins. Cell Biol Int 27:701–709
Benga G (2004) The first water channel protein (later called aquaporin 1) was first discovered in Cluj-Napoca, Romania. Rom J Physiol 41:3–20
Benga G (2005) Water channel proteins: from their discovery in 1985 in Cluj-Napoca, Romania, to the 2003 Nobel prize in chemistry and their medical implications. In: The 9th world multi-conference on systemics, cybernetics and informatics, Orlando, Fl, vol 10, pp 99–104
Benga G (2006a) Water channel proteins: from their discovery in Cluj-Napoca, Romania, to the 2003 Nobel prize in chemistry and their implications in molecular medicine. Keio J Med 55(2):64–69
Benga G (2006b) Water channels (aquaporins and relatives): twenty years after their discovery in Cluj-Napoca, Romania. Acta Endocrinologica (Buc) 2:323–335
Benga G (2006c) Water channel proteins: from their discovery in 1985 in Cluj-Napoca, Romania, to the 2003 Nobel prize in chemistry. Cell Mol Biol 52:10–19
Benga G (2009) Water channel proteins (later called aquaporins) and relatives: past, present, and future. IUBMBLife 61(2):112–133
Benga G (2012a) The first discovered water channel protein, later called aquaporin 1: molecular characteristics, functions and medical implications. Mol Asp Med 33:518–534
Benga G (2012b) On the definition, nomenclature and classification of water channel proteins (aquaporins and relatives). Mol Asp Med 33:514–517
Benga G, Benga I (2005) Priorities in the discovery of the implications of water channels in epilepsy and Duchenne muscular dystrophy. In: Zinn D, Savoie M, Lin KC, El-Badawy ES, Benga G (eds) Proceedings of the 9th world multi-conference on systemics, cybernetics and informatics, vol 10, pp 111–115
Benga I, Benga O (2012) Implications of water channel proteins in selected neurological disorders: epilepsies, muscular dystrophies, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, neuromyelitis optica, Parkinson’s disease, and spongiform encephalopathies. Mol Asp Med 33:590–604
Benga G, Borza V (1975) Differences in reactivity of cytochrome oxidase from human liver mitochondria with horse and human cytochrome c. Arch Biochem Biophys 169:354–357
Benga G, Borza T (1995) Diffusional water permeability of mammalian red blood cells. Comp Biochem Physiol 112B:653–659
Benga Gh, Borza T, Matei H, Hodor P, Frentescu L, Ghiran I, Lupşe C (1995) Comparative nuclear magnetic resonance studies of diffusional water permeability of red blood cells from different species. VIII. Adult and fetal guinea pig (Cavia procellus). Comp Haematol Int 5:106–111
Benga G, Chapman D (1976) Protein–lipid interactions in biomembranes. I. Albumin–liposome model system—spin label studies. Rev Roum Biochim 13:251–261
Benga G, Ferdinand W (1977) Increased content of hydrophobic amino acid residues in lipid-rich mitochondrial membranes: a comparison of rat and human liver mitochondria. Int J Biochem 8:17–20
Benga G, Holmes RP (1984) Interactions between components in biological membranes and their implications for membrane function. Prog Biophys Mol Biol 43:195–257
Benga O, Huber VJ (2012) Brain water channel proteins in health and disease. Mol Asp Med 33:562–578
Benga G, Kuchel PW (2005) Physiological significance of water channel proteins in the red blood cell membranes: analysis at the level of the cell- and of the whole-body systems. In: The 9th world multi-conference on systemics, cybernetics and informatics, Orlando, Fl (USA), vol 10, pp 105–110
Benga G, Morariu VV (1977) Membrane defect affecting water permeability in human epilepsy. Nature 265:636–638
Benga G, Mureşan L (1974) Human liver mitochondria. III. ATP-ase activity as an index of mitochondrial damage. Biochem Med 10:131–145
Benga G, Strach SJ (1975) Interpretation of ESR spectra of nitroxide-maleimide-labelled proteins and the use of this technique in the study of albumin and biomembranes. Biochim Biophys Acta 400:69–79
Benga G, Ţărmure C, Hodârnău A (1971) The determination of proteins in lipid rich mitochondrial suspensions. Enzyme 12:574–577
Benga G, Mureşan L, Dancea S (1972) Conditions for isolation and study of enzymic properties of human liver mitochondria. Biochem Med 6:508–521
Benga G, Hodârnău A, Böhm B, Borza V, Tilinca R, Dancea S, Petrescu I, Ferdinand W (1978a) Human liver mitochondria: relation of a particular lipid composition to the mobility of spin-labelled lipids. Eur J Biochem 84:625–633
Benga G, Tilinca R, Hodârnău A, Băltescu V, Borza V, Acalovschi I (1978b) Fracţionarea subcelulară a ficatului uman. Determinarea activităţii adenilat-kinazei. Clujul Med 51:41–46
Benga G, Dancea S, Poruţiu D (1979a) Comparative electron microscopic aspects of human liver mitochondria in situ and isolated in suspensions. Morphol Embryol 25:205–208
Benga G, Hodârnău A, Tilinca R, Poruţiu D, Dancea S, Pop VI, Wrigglesworth J (1979b) Fractionation of human liver mitochondria: enzymic and morphological characterization of the inner and outer membranes as compared to rat liver mitochondria. J Cell Sci 35:417–429
Benga G, Popescu O, Pop VI (1979c) Protein-lipid interactions in biological membranes. Cytochrome oxidase-lipid complex: spin label studies. Rev Roum Biochim 16:175–181
Benga G, Porumb T, Frangopol PT (1979d) Evidence for various degrees of motional freedom of the ‘boundary’ lipid in cytochrome oxidase. Cell Biol Int Rep 3:651–657
Benga G, Petrescu I, Ţărmure C, Pop VI (1980) Species related functional properties of mitochondria: comparison between rat and human liver mitochondria. Rev Roum Biol Biol Anim 25:147–154
Benga G, Porumb T, Wrigglesworth JM (1981) Estimation of lipid regions in a cytochrome oxidase-lipid complex using spin labelling electron spin resonance: distribution effects on the spin label. J Bioenerg Biomembr 13:269–283
Benga G, Pop VI, Ionescu M, Holmes RP, Popescu O (1982) Irreversible inhibition of water transport in erythrocytes by fluorescein mercuric acetate. Cell Biol Int Rep 6:775–781
Benga G, Hodârnău A, Ionescu M, Pop VI, Frangopol PT, Strujan V, Holmes RP, Kummerow FW (1983a) A comparison of the effects of cholesterol and 25-hydroxy-cholesterol on egg yolk lecithin liposomes: spin label studies. In: Kummerow FA, Benga G, Holmes RP (eds) Biomembranes and cell function, vol 414. Ann NY Acad Sci, pp 140–152
Benga G, Ionescu M, Popescu O, Pop VI (1983b) Effect of chlorpromazine on proteins in human erythrocyte membranes as inferred from spin labeling and biochemical analyses. Mol Pharmacol 23:771–778
Benga G, Pop VI, Ionescu M, Hodârnău A, Tilinca R, Frangopol PT (1983c) Comparison of human and rat liver microsomes by spin label and biochemical analyses. Biochim Biophys Acta 750:194–199
Benga G, Pop VI, Popescu O, Ionescu M, Mihele V (1983d) Water exchange through erythrocyte membranes: nuclear magnetic resonance studies on the effects of inhibitors and of chemical modification of human membranes. J Membr Biol 76:129–137
Benga G, Popescu O, Holmes RP, Pop VI (1983e) NMR studies on the mechanism of water diffusion through human erythrocyte membranes. Bull Magn Reson 5(1–2):265
Benga G, Popescu O, Pop VI (1983f) Water exchange through erythrocyte membranes. V. Incubation with papain prevents the p-chloromercuribenzensulfonate inhibition of water diffusion studied by a nuclear magnetic resonance technique. Cell Biol Int Rep 7:807–818
Benga G, Travis BD, Pop VI, Popescu O, Toader S, Holmes RP (1984) The effect of the saturation and isomerization of dietary fatty acids on the osmotic fragility and water diffusional permeability of rat erythrocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta 775:255–259
Benga G, Popescu O, Pop VI (1985a) Water exchange through erythrocyte membranes: p-chloromercuribenzenesulfonate inhibition of water diffusion in ghosts studied by a nuclear magnetic resonance technique. Biosci Rep 5:223–228
Benga G, Popescu O, Pop VI, Holmes RP, Pavel T, Ionescu M (1985b) Modifications of human erythrocyte membranes and their effect on water permeability studied by a nuclear magnetic resonance technique. In: Pullman A, Vasilescu V, Packer L (eds) Water and ions in biological systems. Plenum Press, New York and London, pp 303–312
Benga G, Borza V, Popescu O, Pop VI, Muresan A (1986a) Water exchange through erythrocyte membranes: nuclear magnetic resonance studies on resealed ghosts compared to human erythrocytes. J Membr Biol 89:127–130
Benga G, Popescu O, Borza V, Pop VI, Mocsy I, Brain A, Wrigglesworth JM (1986b) Water permeability of human erythrocytes. Identification of membrane proteins involved in water transport. Eur J Cell Biol 41:252–262
Benga G, Popescu O, Pop VI, Holmes RP (1986c) p-(Chloromercuri)benzenesulfonate binding by membrane proteins and the inhibition of water transport in human erythrocytes. Biochemistry 25:1535–1538
Benga G, Pop VI, Popescu O, Hodârnău A, Borza V, Presecan E (1987) Effects of temperature on water diffusion in human erythrocyte and ghosts—nuclear magnetic resonance studies. Biochim Biophys Acta 905:339–348
Benga G, Popescu O, Borza V, Pop VI, Hodârnău A (1989a) Water exchange through erythrocyte membranes: biochemical and nuclear magnetic resonance studies re-evaluating the effects of sulfhydryl reagents and of proteolytic enzymes on human membranes. J Membr Biol 108:105–113
Benga G, Popescu O, Pop VI, Borza V, Hodârnău A, Popescu M, Serbu AM, Benga I (1989b) Studies on water permeability and protein erythrocyte membranes in patients with Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Muscle Nerve 12:294–301
Benga G, Pop VI, Popescu O, Borza V (1990a) On measuring the diffusional water permeability of human red blood cells and ghosts by nuclear magnetic resonance. J Biochem Biophys Methods 21(2):87–102
Benga G, Pop VI, Popescu O, Borza V (1990b) The basal permeability to water of human red blood cells evaluated by a nuclear magnetic resonance technique. Bioscience Rep 10:31–36
Benga G, Popescu O, Borza V, Pop VI, Wrigglesworth JM (1990c) Water transport in human red cells: effects of non-inhibitory sulfhydryl reagents on membrane proteins and water exchange. Rev Roum Biochim 27:189–199
Benga G, Brain A, Pop VI, Wrigglesworth JM (1990d) Freeze-fracture electron microscopic observation on the effects of sulphydryl group reagents on human erythrocyte membranes. In: Peacey LD, Williams DB (eds) Electron microscopy 1990, Proc XIIth int congr electron microscopy, Aug 12–18, 1990, Seattle, Wa., vol 3: Biological sciences, San Francisco Press, San Francisco, CA, pp 524–525
Benga G, Hodârnău A, Tilinca R, Borza V, Ferdinand W (1991a) Amino acid composition of human liver mitochondrial membranes in normal and pathological conditions Bioscience Rep 11:95–100
Benga G, Popescu O, Borza V, Pop VI, Hodârnău A, Pop VI, Wrigglesworth J (1991b) Water transport in human red cells: effects of ‘non-inhibitory’ sulfhydryl reagents. Biochim Biophys Acta 1061:309–312
Benga G, Popescu O, Pop VI, Hodor P, Borza T (1992a) Effects on water diffusion of inhibitors affecting various transport processes in human red blood cells. Eur J Cell Biol 59:219–223
Benga G, Poruţiu D, Hodârnău A, Ferdinand W (1992b) Ultrastructural aspects and amino acid composition of the purified inner and outer membranes of human liver mitochondria as compared to rat liver mitochondria. Comp Biochem Physiol 102B(1):123–128
Benga G, Poruţiu D, Ghiran I, Kuchel PW, Gallagher CH, Cox GC (1992c) Scanning electron microscopy of red blood cells from eleven species of marsupials. Comp Haematol Int 2:227–230
Benga G, Borza V, Popescu O, Poruţiu D, Matei H (1993a) Comparative nuclear magnetic resonance studies of diffusional water permeability of red blood cells from sheep and cow. Comp Biochem Physiol 104B:589–594
Benga G, Chapman BE, Gallagher C, Agar NS, Kuchel PW (1993b) NMR studies of diffusional water permeability of erythrocytes from eight species of marsupials. Comp Biochem Physiol 106A:515–518
Benga G, Chapman BE, Gallagher C, Cooper D, Kuchel PW (1993c) NMR studies of diffusional water permeability of red blood cells from macropodid marsupials (kangaroos and wallabies). Comp Biochem Physiol 104A:799–803
Benga G, Matei H, Borza T, Poruţiu D, Lupşe C (1993d) Comparative nuclear magnetic resonance studies on water diffusional permeability of red blood cells from mice and rats. Comp Biochem Physiol 104A:491–495
Benga G, Matei H, Borza T, Poruţiu D, Lupşe C (1993e) Comparative nuclear magnetic resonance studies of diffusional water permeability of red blood cells from different species. V—Rabbit (Oryctolagus cuniculus). Comp Biochem Physiol 106B:281–285
Benga G, Chapman BE, Hinds L, Kuchel PW (1994a) Comparative NMR studies of diffusional water permeability of erythrocytes from some animals introduced to Australia: rat rabbit and sheep. Comp Haematol Int 4:232–235
Benga G, Ralston GB, Borza T, Chapman BE, Gallagher CH, Kuchel PW (1994b) NMR studies of diffusional water permeability of red blood cells from the echidna (Tachyglossus aculeatus). Comp Biochem Physiol 107B:45–50
Benga G, Banner M, Wrigglesworth JM (1996a) Quantitation of the water channel protein aquaporin (CHIP28) from red blood cells by densitometry of silver stained polyacrylamide gels. Electrophoresis 17(4):715–719
Benga G, Matei H, Chapman BE, Bulliman BT, Gallagher CH, Agar NS, Kuchel PW (1996b) Comparative nuclear magnetic resonance studies of diffusional water permeability of red blood cells from different species. IX. Australian feral chicken and domestic chicken (Gallus domesticus). Comp Haematol Int 6:92–95
Benga G, Grieve SM, Chapman BE, Gallagher CD, Kuchel PW (1999) Comparative NMR studies of diffusional water permeability of red blood cells from different species. X. Camel (Camelus dromedarius) and alpaca (Lama pacos). Comp Haematol Int 9:43–48
Benga G, Kuchel PW, Chapman BE, Cox GC, Gallagher CH (2000a) Comparative cell shape and diffusional water permeability of red blood cells from indian elephant (Elephas maximus) and man (Homo sapiens). Comp Haematol Int 10:1–8
Benga G, Matei H, Frenţescu L, Chapman BE, Kuchel PW (2000b) Comparative nuclear magnetic resonance studies of diffusional water permeability of red blood cells from different species. XI. Horses introduced to Australia and European horses (Equus caballus). Comp Haematol Int 10:138–143
Benga G, Frenţescu L, Matei H, Ţigan Şt (2001) Comparative nuclear magnetic resonance studies of water permeability of red blood cells from the maternal venous blood and the newborn umbilical cord blood. Clin Chem Lab Med 39:606–611
Benga G, Chapman BE, Matei H, Gallagher CD, Blyde D, Kuchel PW (2002a) Effects of p-chloromercuribenzene sulfonate on water transport across the marsupial erythrocyte membrane. J Comp Physiol B 172:513–518
Benga G, Ghiran I, Matei H, Frenţescu L, Florea A (2002b) Comparative nuclear magnetic resonance studies of diffusional water permeability of red blood cells from different species. XII. Dog (Canis familiaris) and cat (Felis domestica) Comp Clin Path 11:246–255
Benga G, Chapman BE, Cox GC, Kuchel PW (2003a) Comparative NMR studies of diffusional water permeability of red blood cells from different species: XIV. Little penguin (Eudyptula minor). Cell Biol Int 27:921–928
Benga G, Chapman BE, Kuchel PW (2003b) NMR measurements of human red blood cell diffusional permeability to D2O and H2O. B Mol Med 15–16:35–41
Benga G, Chapman BE, Cox GC, Kuchel PW (2009) Comparative NMR studies of diffusional water permeability of red blood cells from different species XV. Agile wallaby (Macropus agilis), red-necked wallaby (Macropus rufogriseus) and Goodfellow`s tree kangaroo (Dendrolagus goodfellowi). Comp Biochem Physiol Part A 154:105–109
Benga G, Chapman BE, Cox GC, Kuchel PW (2010a) Comparative NMR studies of diffusional water permeability of red blood cells from different species XVIII. Platypus (Ornithorhynchus anatinus) and saltwater crocodile (Crocodylus porosus). Cell Biol Int 34:703–708
Benga G, Chapman BE, Matei H, Cox GC, Romeo T, Mironescu E, Kuchel PW (2010b) Comparative NMR studies of diffusional water permeability of red blood cells from different species XVI. Dingo (Canis familiaris dingo) and dog (Canis familiaris). Cell Biol Int 34:373–378
Brindle KM, Brown FF, Campbell ID, Grathwohl C, Kuchel PW (1979) Application of spin echo nuclear magnetic resonance to whole cell systems: membrane transport. Biochem J 180:37–44
Brown FF, Campbell ID, Kuchel PW, Rabenstein DL (1977) Human erythrocyte metabolism studies by 1H spin echo NMR. FEBS Lett 82:12–16
Bulliman BT, Kuchel PW (1988) A series expression for the surface area of an ellipsoid and its application to the computation of the surface area of avian erythrocytes. J Theor Biol 134:113–123
Căproiu MT (2006) The 2003 Nobel Prize in chemistry eluded the Romanian chemist Gheorghe Benga. Rev Chim 57(4):439–443
Chapman BE, Beilharz GR, York MJ, Kuchel PW (1982) Endogenous phospholipase and choline release in human erythrocytes: a study using 1H NMR spectroscopy. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 105:1280–1287
Chapman BE, Kuchel PW, Lovric VA, Raftos JE, Stewart IM (1985) Regeneration of phosphorylated metabolites in stored erythrocytes in an open perfusion system: studies using 31P NMR spectroscopy. Br J Haematol 61:385–392
Chapman BE, Kirk K, Kuchel PW (1986) Bicarbonate exchange kinetics at equilibrium across the human erythrocyte membrane by 13C NMR. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 136:266–272
Ciechanowicz A, Krzysztalowska M, Binczak-Kuleta A (2009) Akwaporyny—nowy element w regulacji gospodarki wodnej organizmu. Pol Merk Lek 27(158):144–147
Conlon T, Outhtred R (1972) Water diffusion permeability of erythrocytes using an NMR technique. Biochim Biophys Acta 288:354–361
Cucuianu M (2006) The discovery by Gh. Benga of the first water channel protein in 1985 in Cluj-Napoca, Romania, a few years before P. Agre (2003 Nobel Prize in chemistry). Rom J Int Med 44:323–334
Denker BM, Smith BL, Kuhajda FP, Agre P (1988) Identification, purification and partial characterization of a novel Mr 28,000 integral membrane protein from erythrocytes and renal tubules. J Biol Chem 263:15634–15642
Duţu A, Borza V, Mosora N, Motocu M, Benga G (1985) ATP-ase activity of mitochondria isolated from needle-biopsy liver samples of diabetic subjects. Rev Roum Med Med Int 23:201–206
Endre ZH, Kuchel PW (1986) Viscosity of concentrated solutions and of human erythrocyte cytoplasm determined from NMR measurement of molecular correlation times: the dependence of viscosity on cell volume. Biophys Chem 24:337–356
Endre ZH, Chapman BE, Kuchel PW (1984) Cell volume dependence of 1H spin echo NMR signals in human erythrocyte suspensions: the influence of in situ field gradients. Biochim Biophys Acta 803:137–144
Fischbarg J, Diecke FPJ, Iserovich P, Rubashkin A (2006) The role of the tight junction in paracellular fluid transport across corneal endothelium. Electro-osmosis as a driving force. J Membr Biol 210:117–130
Frangopol P, Gavrilǎ L (2005) Memorandum regarding the discovery of the first water channel protein by Gheorghe Benga in Romania, a few years before Peter Agre (2003 Nobel Prize in Chemistry). Rom J Genet 1:101–102
Gozariu L (2006) Comments on the discovery of water channels, selected for the 2003 Nobel Prize in chemistry, and the regrettable omission of Gheorghe Benga. Acta Endocrinologica (Buc) 2:377–380
Haris P, Chapman D, Benga G (1995) A Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopic investigation of the hydrogen–deuterium exchange and secondary structure of the 28-kDa channel-forming integral membrane protein (CHIP28). Eur J Biochem 233:659–664
Haulică I (2006) A regrettable mistake in the award of the 2003 Nobel Preize in chemistry: the omission of Gheorghe Benga, the first discoverer of the water channel protein in the red blood cell membrane. Cell Mol Biol 52:8–9
Hodârnău A, Travis BD, Benga G, Pop VI, Popescu O, Holmes RP (1989) The effect of dietary fatty acids on ATP-ase activities and fluidity of rat erythrocyte membranes. Rev Roum Biochim 26:33–39
Hume DI (1982) Digestive physiology and nutrition of marsupials. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Jones AJ, Kuchel PW (1980) Measurement of choline concentration and transport in human erythrocytes by 1H NMR: comparison of normal blood and from lithium-treated psychiatric patients. Clin Chim Acta 104:77–85
King GF, Kuchel PW (1984) A proton NMR study of imidodipeptide transport and hydrolysis in the human erythrocyte: possible physiological roles for the coupled system. Biochem J 220:553–560
Kirk K, Kuchel PW (1985) Red cell volume changes monitored using a new NMR procedure. J Magn Reson 62:568–572
Kirk K, Kuchel PW (1988a) Characterisation of the transmembrane chemical shift differences in the 31P NMR spectra of some phosphoryl compounds in erythrocyte suspensions. Biochemistry 27:8795–8802
Kirk K, Kuchel PW (1988b) The contribution of magnetic susceptibility effects to transmembrane chemical shift differences in the 31P NMR spectra of oxygenated erythrocyte suspensions. J Biol Chem 263:130–134
Kirk K, Raftos JE, Kuchel PW (1986) Triethyl phosphate as an internal 31P NMR reference in biological samples. J Magn Reson 70:484–487
Kirk K, Kuchel PW, Labotka RJ (1988) Hypophosphite ion as a 31P NMR probe of membrane potential in erythrocyte suspensions. Biophys J 54:241–248
Kuchel PW (2006) The story of the discovery of aquaporins: convergent evolution of ideas—but who got there first? Cell Mol Biol 52:2–5
Kuchel PW, Benga G (2003) Why is the transmembrane exchange of water in the red blood cell so fast? B Mol Med 15–16:29–34
Kuchel PW, Benga G (2005) Why does the mammalian red blood cell have aquaporins? Biosystems 82:189–196
Kuchel PW, Chapman BE (1983) NMR spin exchange kinetics at equilibrium in membrane transport and enzyme systems. J Theor Biol 105:569–589
Kuchel PW, Reynolds CH, Dalziel K (1980) Determination of the stability constants of Mn++ and Mg++ complexes of the components of the NADP-linked isocitrate dehydrogenase reaction by electron spin resonance. Eur J Biochem 110:465–473
Kuchel PW, Jarvie PE, Conyers RAJ (1982) Erythrocyte glycolysis: stimulation by nalidixic acid. Biochem Med 27:95–100
Kuchel PW, Chapman BE, Endre ZH, King GF, Thorburn DR, York MJ (1984) Monitoring metabolic reactions in human erythrocytes using NMR spectroscopy. Biomed Biochim Acta 43:719–726
Kuchel PW, Bulliman BT, Chapman BE, Kirk K (1987a) The use of transmembrane differences in saturation transfer for measuring fast membrane transport: H13CO3—exchange across the human erythrocyte. J Magn Reson 74:1–11
Kuchel PW, Bulliman BT, Chapman BE, Kirk K, Potts JR (1987b) Fast transmembrane exchange in red cells studied with NMR. Biomed Biochim Acta 46:S55–S59
Kuchel PW, Chapman BE, Potts JR (1987c) Glucose transport in human erythrocytes measured using 13C NMR spin transfer. FEBS Lett 219:5–10
Macey RI (1984) Transport of water and urea in red blood cells. Am J Physiol 246:195–203
McIntyre LM, Thorburn DR, Bubb WA, Kuchel PW (1989) Comparison of computer simulations of the F-type and L-type non-oxidative hexose monophosphate shunts with 31P NMR experimental data from human erythrocytes. Eur J Biochem 180:399–420
Morariu VV, Benga G (1977) Evaluation of a nuclear magnetic resonance technique for the study of water exchange through erythrocyte membranes in normal and pathological subjects. Biochim Biophys Acta 469:301–310
Morariu VV, Benga G (1984) Water diffusion through erythrocyte membranes in normal and pathological subjects: nuclear magnetic resonance investigations. In: Benga G, Baum H, Kummerow FA (eds) Membrane processes: molecular biology and medical applications. Springer Verlag, New York, pp 121–139
Morariu VV, Pop VI, Popescu O, Benga G (1981) Effects of temperature and pH on the water exchange through erythrocyte membranes: nuclear magnetic resonance studies. J Membr Biol 62:1–5
Pop VI, Popescu O, Smith T, Kummerow FA, Holmes R, Benga G (1990) Water diffusional permeability of rat erythrocytes is not influenced by the dietary fatty acids. Rev Roum Biochim 27:27–31
Potts JR, Kirk K, Kuchel PW (1989) Characterisation of the transport of the nonelectrolyte dimethyl methylphosphonate across the red-cell membrane. NMR Biomed 1:198–204
Preston GM, Carroll TP, Guggino WB, Agre P (1992) Appearance of water channels in Xenopus oocytes expressing red cell CHIP 28 protein. Science 256:385–387
Raftos JE, Kirk K, Kuchel PW (1988) Further investigation of the use of dimethyl methylphosphonate as a 31P-NMR probe of red cell volume. Biochim Biophys Acta 968:160–166
Reynolds CH, Kuchel PW, Dalziel K (1978) Equilibrium binding of co-enzymes and substrates to NADP-linked isocitrate dehydrogenase from bovine heart mitochondria. Biochem J 171:733–742
Robinson G, Chapman BE, Kuchel PW (1984) 31P NMR spin transfer in the phosphoglyceromutase reaction. Eur J Biochem 143:643–649
Schneider F (2005) Twenty years since the discovery of the first water channel protein by Gheorghe Benga’s group in Romania. Fiziologia-Physiology 15:29–30
Şerbu A-M, Marian A, Popescu O, Pop VI, Borza V, Benga I, Benga G (1986) Decreased water permeability of erythrocyte membranes in patients with Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Muscle Nerve 9:243–247
Sha’afi RI (2005) Opening address to the symposium “Water Channel Proteins: from their Discovery in 1985 in Romania to the 2003 Nobel Prize in Chemistry and their Implications in Molecular Medicine Systems”. In: Zinn D, Savoie M, Lin KC, El-Badawy ES, Benga G (eds) Proceedings of the 9th world multi-conference on systemics, cybernetics and informatics, vol 10, pp 128–129
Schafer JA, Andreoli TE (1980) Principles of water and non-electrolyte transport across membranes. In: Hoffman JF, Farnestil DD (eds) Membrane physiology. Plenum Press, New York, pp 177–190
Sholle VD, Kagan E, Michailov VJ, Rozantsev EG, Frangopol PT, Frangopol M, Pop VI, Benga G (1980) A new spin label for SH groups in proteins: the synthesis and some applications in labelling of albumin and erythrocyte membranes. Rev Roum Biochim 17:291–298
Strachan R (ed) (1983) Complete book of Australian mammals. Angus and Robertson, Sydney
Ţehaniuc A, Benga G (2011) Red blood cell water permeability in elderly people. Acta Endocrinologica (Buc) 7(3):299–310
Toader C, Acalovschi I, Toader I, Manta I, Hodârnău A, Benga G (1976) Factors influencing the establishment of the normal values of the respiratory activities of human liver mitochondria. Enzyme 21:232–242
Vandenberg JI, King GF, Kuchel PW (1985a) Enkephalin degradation by human erythrocytes and haemolysates studied using 1H NMR spectroscopy. Arch Biochem Biophys 242:515–522
Vandenberg JI, King GF, Kuchel PW (1985b) The assimilation of tri- and tetrapeptides by human erythrocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta 846:127–134
Vandenberg JI, Kuchel PW (2003) Nobel prizes for magnetic resonance imaging and channel proteins. Med J Aust 179:611–613
Vandenberg JI, Kuchel PW, King GF (1986) Application of progress curve analysis to in situ enzyme kinetics using 1H NMR spectroscopy. Anal Biochem 155:38–44
Wolburg H, Wolburg-Bucholz K, Fallier-Becker P, Noell S, Mack A (2011) Structure and functions of aquaporin-4-based orthogonal arrays of particles. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol 287:1–41
Wolburg H, Noell S, Fallier-Becker P, Mack A, Wolburg-Bucholz K, Wolburg-Bucholz K (2012) The disturbed blood–brain barrier in human glioblastoma. Mol Asp Med. doi:10.1016/j.mam.2012.02.003
York MJ, Kuchel PW, Chapman BE, Jones AJ (1982) Incorporation of labelled glycine into glutathione of intact human erythrocytes by enzyme catalysed exchange—an NMR study. Biochem J 207:65–72
Acknowledgments
The author is very grateful to Philip Kuchel for his essential contribution to making our program of collaboration for over 20 years possible and fruitful. The author also thanks the co-authors of papers mentioned in the references, for their competent help in the program of research on the water permeability of red blood cells, started in 1976 with Vasile Morariu (Cluj-Napoca, Romania), which led to the discovery in 1977 of the implications of WCPs in epilepsy, with Vasile Morariu, Ileana Benga, and Cornelia Morariu (Cluj-Napoca, Romania), and later to the discovery in 1985 of the first water channel protein, later called AQP1 (for which special thanks are due to Octavian Popescu, Victor I. Pop, Victoria Borza, Ana Muresan, Ildiko Mocsy (Cluj-Napoca, Romania), Ross Holmes (USA), and John Wrigglesworth and Anthony Brain (UK)). Special thanks to Radu Mureşan, Adrian Florea, and Ciprian Mihali (for important help in achieving the final form of this paper). Financial support from the Ministry of Education and Research of The “Iuliu Hatieganu” University of Medicine and Pharmacy Cluj-Napoca, from the Academy of Medical Sciences, from the National Council for Science and Technology, from the National Council for Higher University Scientific Research (Romania), from Taronga Zoo, from The University of Sydney (Australia), from the Wellcome Trust (UK), and from the National Science Foundation (USA) is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Special Issue: From kinetics to imaging: An NMR odyssey.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Benga, G. Comparative studies of water permeability of red blood cells from humans and over 30 animal species: an overview of 20 years of collaboration with Philip Kuchel. Eur Biophys J 42, 33–46 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00249-012-0868-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00249-012-0868-7