Abstract
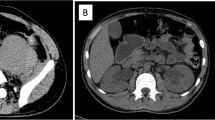
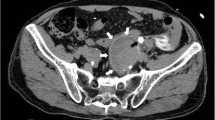
Iatrogenic pseudoaneurysm formation is an uncommon but potentially serious complication of cardiac catheterization. This case report describes diagnosis and treatment of a large left external iliac artery pseudoaneurysm in a 3-month-old boy following cardiac catheterization and aortic balloon dilatation for aortic coarctation. A 4-cm pulsatile mass in the left hemipelvis was discovered on MRI performed 6 weeks later for possible tethered spinal cord. Sonography and angiography showed a large pseudoaneurysm of the left external iliac artery just distal to the iliac bifurcation with no flow in the external iliac artery distal to the pseudoaneurysm. Percutaneous US-guided thrombin injection was performed twice, with partial recanalization after each treatment. The residual portion of the pseudoaneurysm was then successfully embolized with percutaneous coils deployed under US and fluoroscopic guidance.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kapoor BS, Haddad HL, Saddekni S et al (2009) Diagnosis and management of pseudoaneurysms: an update. Curr Probl Diagn Radiol 38:170–188
Frush DP, Paulson EK, O'Laughlin MP (2000) Successful sonographically guided thrombin injection in an infant with a femoral artery pseudoaneurysm. AJR Am J Roentgenol 175:485–487
Pelchovitz DJ, Cahill AM, Baskin KM et al (2005) Pseudoaneurysm in children: diagnosis and interventional management. Pediatr Radiol 35:434–439
Cope C, Zeit R (1986) Coagulation of aneurysms by direct percutaneous thrombin injection. AJR Am J Roentgenol 147:383–387
Krueger K, Zaehringer M, Strohe D et al (2005) Post-catheterization pseudoaneurysm: results of US-guided percutaneous thrombin injection in 240 patients. Radiology 236:1104–1110
Paulson EK, Sheafor DH, Kliewer MA et al (2000) Treatment of iatrogenic femoral arterial pseudoaneurysms: comparison of US-guided thrombin injection with compression repair. Radiology 215:403–408
Vitiello R, McCrindle BW, Nykanen D et al (1998) Complications associated with pediatric cardiac catheterization. J Am Coll Cardiol 32:1433–1440
Kobeiter H, Lapeyre M, Becquemin JP et al (2002) Percutaneous coil embolization of postcatheterization arterial femoral pseudoaneurysms. J Vasc Surg 36:127–131
Conflicts of interest
None
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lillis, A.P., Shaikh, R., Alomari, A.I. et al. Percutaneous coil embolization of massive pelvic pseudoaneurysm in an infant. Pediatr Radiol 45, 931–935 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-014-3183-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-014-3183-x