Abstract
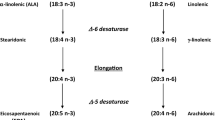
Sudden cardiac death remains one of the most serious medical challenges in Western countries. Increasing evidence in recent years has demonstrated that the n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) can prevent fatal ventricular arrhythmias in experimental animals and probably in humans. Dietary supplement of fish oils or intravenous infusion of the n-3 PUFAs prevents ventricular fibrillation caused by ischemia/reperfusion. Similar antiarrhythmic effects of these fatty acids are also observed in cultured mammalian cardiomyocytes. Based on clinical observations and experimental studies in vitro and in vivo, several mechanisms have been postulated for the antiarrhythmic effect of the n-3 PUFAs. The data from our laboratory and others have shown that the n-3 PUFAs are able to affect the activities of cardiac ion channels. The modulation of channel activities, especially voltage-gated Na+ and L-type Ca2+ channels, by the n-3 fatty acids may explain, at least partially, the antiarrhythmic action. It is not clear, however, whether one or more than one mechanism involves the beneficial effect of the n-3 PUFAs on the heart. This article summarizes our recent studies on the specific effects of the n-3 PUFAs on cardiac ion channels. In addition, the effect of the n-3 PUFAs on the human hyperpolarization-activated cyclic-nucleotide-modulated channel is presented.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albert C.M., Hennekens C.H., O’Donnell C.J., Ajani U.A., Carey V.J., Willett W.C., Ruskin J.N., Manson J.E. 1998. Fish consumption and risk of sudden cardiac death. JAMA 279:23–28
Albert C.M., Campos H., Stampfer M.J., Ridker P.M., Manson I.E., Willett W.C., Ma J. 2002. Blood levels of long-chain n-3 fatty acids and the risk of sudden death. N. Engl. J. Med. 346:1113–1118
An R.H., Wang X.L., Kerem B., Benhorin J., Medina A., Goldmit M., Kass R.S. 1998. Novel LQT-3 mutation affects Na+ channel activity through interactions between alpha- and betal-subunits. Circ. Res. 83:141–146
Ander B.P., Weber A.R., Rampersad P.P, Gilchrist J.S.C., Pierce G.N., Lukas A. 2004. Dietary flaxseed protects against ventricular fibrillation induced by ischemia-reperfusion in normal and hypercholesterolemic rabbits. J. Nutr. 134:3250–3256
Andersen O.S., Nielsen C., Maer A.M., Lundbaek J.A., Goulian M., Koeppe II, R.E. 1999. Ion channels as tools to monitor lipid bilayer-mernbrane protein interactions: gramicidin channels as molecular force transducers. Meth. Enzymol. 294:208–224
Bang H.O., Dyerberg J., Nielsen A. 1971. Plasma lipid and lipoprotein pattern in Greenlandic West-coast Eskimos. Lancet. 1:1143–1145
Billman G.E., Kang J.X., Leaf A. 1999. Prevention of sudden cardiac death by dietary pure {omega}-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids in dogs. Circulation 99:2452–2457
Billman G.E., Hallaq H., Leaf A. 1994. Prevention of ischemia-induced arrhythmias by n-3 fatty acids. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 91:4427–4430
Bogdanov K.Y., Spurgeon H.A., Vinogradova T.M., Lakatta E.G. 1998. Modulation of the transient outward current in adult rat ventricular myocytes by polyunsaturated fatty acids. Am. J. Physiol. 274:H571–H579
Calo L., Bianconi L., Colivicchi F., Lamberti F., Loricchio M.L., de Ruvo E., Meo A., Pandozi C., Staibano M., Santini M. 2005. N-3 Fatty acids for the prevention of atrial fibrillation after coronary artery bypass surgery: a randomized, controlled trial. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 45:1723–1728
Catterall W.A. 1989. Structure and function of voltage-sensitive ion channels. Science 242:50–61
Catterall W.A. 1992. Cellular and molecular biology of voltage-gated sodium channels. Physiol. Rev. 72:S15–S48
Cheng T.O., Dallongeville J., Montaye M., Amouyel P., Yarnell J., Evans A., Ducimetiere P., Bingham A., Luc G., Arveiler D., Mass B., Ferrieres J., Ruidavets J.-B. 2004. Fish consumption and coronary artery disease in China * Response. Circulation 109:e155–e156
Chung S., Jung W., Lee M.Y. 1999. Inward and outward rectifying potassium currents set membrane potentials in activated rat microglia. Neurosci. Lett. 262:121–124
Clarkson C.W., Hondeghem L.M. 1985. Mechanism for bupivacaine depression of cardiac conduction: fast block of sodium channels during the action potential with slow recovery from block during diastole. Anesthesiology 62:396–405
De Lorgeril M., Renaud S., Mamelle N., Salen P., Martin J.L., Monjaud L, Guidollet J., Touboul P., Delaye J. 1994. Mediterranean alpha-linolenic acid-rich diet in secondary prevention of coronary heart disease. Lancet 343:1454–1459
Dyerberg J., Bang H.O., Hjorne N. 1975. Fatty acid composition of the plasma lipids in Greenland Eskimos. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 28:958–966
Evans S.M., Cone E.J., Henningfield J.E. 1996. Arterial and venous cocaine plasma concentrations in humans: relationship to route of administration, cardiovascular effects and subjective effects. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 279:1345–1356
Girshman J., Greathouse D.V., Koeppe II R.E., Andersen O.S. 1997. Gramicidin channels in phospholipid bilayers with unsaturated acyl chains. Biophys. J. 73:1310–1319
GISSI-Prevention Investigators. 1999. Dietary supplementation with n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids and vitamin E after myocardial infarction: results of the GISSI-Prevenzione trial. Gruppo Italiano per lo Studio della Soprawivenza nell'Infarto miocardico. Lancet 354:447–455
Gomez A.M., Cheng H., Lederer W.J., Bers D.M. 1996. Ca2+ diffusion and sarcoplasmic reticulum transport both contribute to [Ca2+]i decline during Ca2+ sparks in rat ventricular myocytes. J. Physiol. 496:575–581
Hallaq H., Smith T. W., Leaf A. 1992. Modulation of dihydropyridine-sensitive calcium channels in heart cells by fish oil fatty acids. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 89:1760–1764
Honore E., Barhanin J., Attali B., Lesage R, Lazdunski M. 1994. External blockade of the major cardiac delayed-reetifier K+ (Kv1.5) by polyunsaturated fatty acids. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 91:1937–1941
Kang J.X., Leaf A. 1994. Effects of long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids on the contraction of neonatal rat cardiac myocytes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 91:9886–9890
Kang J.X., Leaf A. 1996. Prevention and termination of arrhythmias induced by lysophosphatidyl choline and acylcarnitine in neonatal rat cardiac myocytes by free omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 297:97–106
Kang J.X., Xiao Y.-F., Leaf A. 1995. Free long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids reduce membrane electrical excitability in neonatal rat cardiac myocytes. Proc. Natl. Acad Sci. USA 92:3997–4001
Kang J.X., Leaf A. 1996. Evidence that free polyunsaturated fatty acids modify Na+ channels by directly binding to the channel protein. Proc. Natl. Acad Sci. USA 93:3542–3546
Klausner R.D., Kleinfeld A.M., Hoover R.L., Karnovsky M.J. 1980. Lipid domains in membranes. J. Biol. Chem. 255:1286–1295
Leaf A., Kang J.X., Xiao Y.-F., Billman G.E. 2003. Clinical prevention of sudden cardiac death by n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids and mechanism of prevention of arrhythmias by n-3 fish oils. Circulation 107:2646–2652
Leaf A., Xiao Y.-F., Kang J.X., Billman G.E. 2003. Prevention of sudden cardiac death by n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids. Pharmacol. Ther. 98:355–377
Leaf A., Xiao Y.-F. 2001. The modulation of ionic currents in excitable tissues by n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids. J. Membrane Biol. 184:263–271
Ludwig A., Zong X., Jeglitsch M., Hofmann F., Biel M. 1998. A family of hyperpolarization-activated mammalian cation channels. Nature 393:587–591
Lundbaek J.A., Maer A.M., Andersen O.S. 1997. Lipid bilayer energy, curvature stress and assembly of gramicidin channels. Biochemistry 36:5695–5701
Lundbaek J.A., Birn P., Hansen A.J., Sogaard R., Nielsen C., Girshman J., Bruno M.J., Tape S.E., Egebjerg J., Greathouse D.V., Mattice G.L., Koeppe II, R.E., Andersen O.S. 2004. Regulation of sodium channel function by bilayer elasticity: The importance of hydrophobic coupling. effects of micelle-forming amphiphiles and cholesterol. J. Gen. Physiol 123:599–621
Makielski J.C., Limberis J.T., Chang S.Y., Fan Z., Kyle J.W. 1996. Coexpression of β1 with cardiac sodium channel α subunits in oocytes decreases lidocaine block. Mol. Pharmacol. 49:30–39
Marchioli R., Valagussa F., et al. on behalf of GISSI-Prevenzione investigators. 2000. The results of the GISSI-Prevenzione trial in the general framework of secondary prevention. Eur. Heart J. 21:949–952
McLennan P.L. 1993. Relative effects of dietary saturated, monounsaturated, and polyunsaturated fatty acids on cardiac arrhythmias in rats. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 57:207–212
McLennan P.L., Bridle T.M, Abeywardena M.Y., Charnock J.S. 1993. Comparative efficacy of n-3 and n-6 polyunsaturated fatty acids in modulating ventricular fibrillation threshold in marmoset monkeys. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 58:666–669
Mouhaffel A.H., Madu E.C., Satmary W.A., Fraker T.D. 1995. Cardiovascular complications of cocaine: review. Chest 107:1426–1434
Mozaffarian D., Ascherio A., Hu F.B., Stampfer M.J., Willett W.C., Siscovick D.S., Rimm E.B. 2005. Interplay between different polyunsaturated fatty acids and risk of coronary heart disease in men. Circulation 111:157–164
Mubagwa K., Flameng W., Carmeliet E. 1994. Resting and action potentials of nonischemic and chronically ischemic human ventricular muscle. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol 5:659–671
Negretti N., Pérez M.R., Walker D., O’Neill S.C. 2000. Inhibition of sarcoplasmic reticulum function by polyunsaturated fatty acids in intact, isolated myocytes from rat ventricular muscle. J. Physiol. 523:367–375
Noma A., Nakayama T., Kurachi Y, Irisawa H. 1984. Resting K conductances in pacemaker and non-pacemaker heart cells of the rabbit. Jpn. J. Physiol. 34:245–254
Pancrazio J.J., Frazer M.J., Lynch C. 1993. Barbiturate anesthetics depress the resting K+ conductance of myocardium. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 265:358–365
Pepe S., Bogdanov K., Hallaq H., Spurgeon H., Leaf A., Lakatta E 1994. ω3 Polyunsaturated fatty acid modulates dihydropyridine effects on L-type Ca2+ channels, cytosolic Ca2+, and contraction in adult rat cardiac myocytes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 91:8832–8836
Pound E.M., Kang J.X., Leaf A. 2001. Partition of polyunsaturated fatty acids, which prevent arrhythmias, into phospholipids cell membranes. J. Lipid Research 42:346–351
Qu Y., Isom L.L., Westenbroek R.E., Rogers J.C., Tanada T.N., McCormick K.A., Scheuer T., Catterall W.A. 1995. Modulation of cardiac Na+ channel expression in Xenopus oocytes by β1 subunit. J. Biol. Chem. 270:25696–25701
Santoro B., Liu D.T., Yao H., Bartsch D., Kandel E.R., Siegelbaum S.A., Tibbs G.R. 1998. Identification of a gene encoding a hyperpolarization-activated pacemaker channel of brain. Cell 93:717–729
Schrepf R., Limmer, t., Claus Weber P., Theisen K., Sellmayer A. 2004. Immmediate effects of n-3 fatty acid infusion on the induction of sustained ventricular tachycardia. Lancet 363:1412–1413
Singh R.B., Niaz M.A., Sharma J.P., Kumar R., Soshin M. 1997. Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of fish oil and mustard oil in patients with suspected acute myocardial infarction; the India experiment of infarct survival. Cardiovasc. Drugs Ther. 3:485–491
Siscovick D.S., Raghunathan I.E., King I., Weinmann S., Wicklund K.G., Albright J., Bovbjerg V., Arbogast P., Smith H., Kushi L.H., Cobb L.A., Copass M.K., Psaty B.M., Lenaite R., Retzlaff B., Childs M., Knopp R.H. 1995. Dietary intake and cell membrane levels of long-chain n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids and the risk of primary cardiac arrest. JAMA 274:1363–1367
Talavera K., Staes M., Janssens A., Droogmans G., Nilius B. 2004. Mechanism of arachidonic acid modulation of the T-type Ca2+ channel {alpha} 1G. J. Gen. Physiol 124:225–238
Tiknonov, D.B., Zhorov, B.S. 2005. Sodium channel activators: Model of binding inside the pore and a possible mechanism of action. FEBS Lett. 579: 4207–4212
Wang O.K., Russell C., Wang S.Y. 2003. State-dependent block of wild-type and inactivation-deficient Na+ channels by flecainide. J. Gen. Physiol. 122:365–374
Xiao Y.-F., Kang J.X., Morgan J.P., Leaf A. 1995. Blocking effects of polyunsaturated fatty acids on Na+ channels of neonatal rat ventricular myocytes. Proc.Natl Acad. Sci. USA 92:1000–11004
Xiao Y.-F., Gomez A.M., Morgan J.P., Lederer W.J., Leaf A. 1997. Suppression of voltage-gated L-type Ca2+ currents by polyunsaturated fatty acids in adult and neonatal rat cardiac myocytes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 94:4182–4187
Xiao Y.-F., Morgan J.P., Leaf A. 2002. Effects of polyunsaturated fatty acids on cardiac voltage-activated K+ currents in adult ferret cardiomyocytes. Sheng Li Xue Bao 54:271–281
Xiao Y.-F, Wright S.N., Wang O.K., Morgan J.P., Leaf A. 1998. Fatty acids suppress voltage-gated Na+ currents in HEK293t cells transfected with the a-subunit of the human cardiac Na+ channel. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95:2680–2685
Xiao Y.-F, Wright S.N., Wang O.K., Morgan J.P., Leaf A. 2000. Coexpression with beta(1)-subunit modifies the kinetics and fatty acid block of hH1 (alpha) Na+ channels. Am. J. Physiol. 279:H35–H46
Xiao Y.-F, Ke Q., Wang S.Y., Yang Y., Wang O.K., Morgan J.P., Leaf A. 2001. Point mutations in alpha-subunit of human cardiac Na+ channels alter Na+ current kinetics. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 281:45-52
Xiao Y.-F., Ke Q., Wang S.Y., Auktor K., Yang Y., Wang O.K., Morgan J.P., Leaf A. 2001. Single point mutations affect fatty acid block of human myocardial sodium channel alpha subunit Na+ channels. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 98:3606–3611
Xiao, Y.-F., Ma, L., Wang, S.Y., Josephson, M.E., Wang, G.K., Morgan, J.P., Leaf, A. 2005. Potent block of inactivation-deficient Na+ channels by n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids. Am. J. Physiol. In press.
Xiao Y.-F, Ke Q., Wang S.Y., Yang Y., Chen Y., Wang O.K., Morgan J.P., Cox B., Leaf A. 2004. Electrophysiologic properties of lidocaine, cocaine, and n-3 fatty-acids block of cardiac Na+ channels. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 485:31–41
Xiao, Y.-F., Sigg, D.C. 2005. Hyperpolarization-activated cyclic-nucleotide-gated channel and cardiac biological pacemaker. Mol. Cardiol. of China 5: 513–522
Xiao Y.-F., Ke Q., Chen Y., Morgan J.P., Leaf A. 2004. Inhibitory effect of n-3 fish oil fatty acids on cardiac Na+/Ca2+ exchange currents in HEK293t cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 321:116–123
Acknowledgements
Our studies have been supported in part by grants DK38165 from NIDDK and by HL62284 from NHLBI of the National Institutes of Health (AL) and American Heart Association (Y-FX). We wish to thank our colleagues who have contributed to the project for several years.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xiao, YF., Sigg, D. & Leaf, A. The Antiarrhythmic Effect of n-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids: Modulation of Cardiac Ion Channels as a Potential Mechanism. J Membrane Biol 206, 141–154 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00232-005-0786-z
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00232-005-0786-z