Abstract
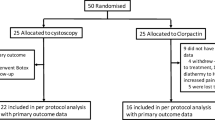
Objective: To determine the safety and tolerability of intravesical resiniferatoxin (RTX) in interstitial cystitis (IC) patients. Materials and Methods: IC patients were instilled with 50 cc of test solution containing either placebo, 0.05 μM or 0.10 μM RTX in the bladder. Plasma concentration of RTX and its degradant resiniferonol 9-, 13-, 14-orthophenylacetate was measured. Immediate post-treatment blood sampling and cystoscopy were performed. Symptoms were evaluated before treatment, at 4- and at 12-week follow-ups, using VAS indicator for pain, voiding diary, and O’Leary’s IC symptom/problem indices. Results: Among 22 patients observed (ten in 0.10 μM RTX, eight in 0.05 μM RTX, and four in placebo groups), the most commonly reported adverse event was pain during instillation (80.0%, 87.5%, and 25.0%). No serious adverse events were reported. Conclusions: Use of intravesical RTX in IC patients is associated with important tolerability issues but safe at 0.10 μM and 0.05 μM.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Batra AK, Hanno PM, de Groat WC. Interstitial cystitis. AUA Update Series. Lesson 2, Volume XIX, 1999
Sant GR (eds) (1997) Interstitial cystitis. Lippincott–Raven Publishers, Philadelphia
Lazzeri M, Beneforti P, Spinelli M, Zanollo A, Barbagli G, Turini D (2000) Intravesical resiniferatoxin for the treatment of hypersensitive disorder: a randomized placebo controlled study. J Urol 164(3 Pt 1):676–679
Blok BF (2002) Central pathways controlling micturition and urinary continence. Urology 59(5 Suppl 1):13–17 (Review)
Chancellor MB, de Groat WC (1999) Intravesical capsaicin and resiniferatoxin therapy: spicing up the ways to treat the overactive bladder. J Urol 162(1):3–11 (Review)
Dodd LG, Tello J (1998) Cytologic examination of urine from patients with interstitial cystitis. Acta Cytol 42(4):923–927
Erickson DR, Belchis DA, Dabbs DJ (1997) Inflammatory cell types and clinical features of interstitial cystitis. J Urol 158(3 Pt 1):790–793
Elbadawi A (1997) Interstitial cystitis: a critique of current concepts with a new proposal for pathologic diagnosis and pathogenesis. Urology 49(5A Suppl):14–40 (Review)
Szallasi A, Conte B, Goso C, Blumberg PM, Manzini S (1993) Vanilloid receptors in the urinary bladder: regional distribution, localization on sensory nerves, and species-related differences. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 347(6):624–629
Ishizuka O, Mattiasson A, Andersson KE (1995) Urodynamic effects of intravesical resiniferatoxin and capsaicin in conscious rats with and without outflow obstruction. J Urol 154(2 Pt 1):611–616
Craft RM, Carlisi VJ, Mattia A, Herman RM, Porreca F (1993) Behavioral characterization of the excitatory and desensitizing effects of intravesical capsaicin and resiniferatoxin in the rat. Pain 55(2):205–215
Szallasi A (2002) Vanilloid (capsaicin) receptors in health and disease. Am J Clin Pathol 118(1):110–121 (Review)
Szallasi A, Blumberg PM (1999) Vanilloid (Capsaicin) receptors and mechanisms. Pharmacol Rev 51(2):159–212 (Review)
Silva C, Avelino A, Souto-Moura C, Cruz F (2001) A light- and electron-microscopic histopathological study of human bladder mucosa after intravesical resiniferatoxin application. BJU Int 88(4):355–360
Maggi CA, Santicioli P, Patacchini R, Geppetti P, Giuliani S, Astolfi GM, Baldi E, Parlani M, Theodorsson E, Fusco B et al (1988) Regional differences in the motor response to capsaicin in the guinea-pig urinary bladder: relative role of pre- and postjunctional factors related to neuropeptide-containing sensory nerves. Neuroscience 27(2):675–688
Amann R (1990) Desensitization of capsaicin-evoked neuropeptide release–influence of Ca2+ and temperature. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 342(6):671–676
Winter J, Dray A, Wood JN, Yeats JC, Bevan S (1990) Cellular mechanism of action of resiniferatoxin: a potent sensory neuron excitotoxin. Brain Res 520(1–2):131–140
Craft RM, Cohen SM, Porreca F (1995) Long-lasting desensitization of bladder afferents following intravesical resiniferatoxin and capsaicin in the rat. Pain 61(2):317–323
Cruz F (1998) Desensitization of bladder sensory fibers by intravesical capsaicin or capsaicin analogs. A new strategy for treatment of urge incontinence in patients with spinal detrusor hyperreflexia or bladder hypersensitivity disorders. Int Urogynecol J Pelvic Floor Dysfunct 9(4):214–220 (Review)
Fowler CJ (2002) Bladder afferents and their role in the overactive bladder. Urology 59(5 Suppl 1):37–42 (Review)
Avelino A, Cruz F, Coimbra A (1999) Intravesical resiniferatoxin desensitizes rat bladder sensory fibres without causing intense noxious excitation. A c-fos study. Eur J Pharmacol 378(1):17–22
Giannantoni A, Di Stasi SM, Stephen RL, Navarra P, Scivoletto G, Mearini E, Porena M (2002) Intravesical capsaicin versus resiniferatoxin in patients with detrusor hyperreflexia: a prospective randomized study. J Urol 167(4):1710–1714
de Seze M, Wiart L, Joseph PA, Dosque JP, Mazaux JM, Barat M (1998) Capsaicin and neurogenic detrusor hyperreflexia: a double-blind placebo-controlled study in 20 patients with spinal cord lesions. Neurourol Urodyn 17(5):513–523
Silva C, Rio ME, Cruz F (2000) Desensitization of bladder sensory fibers by intravesical resiniferatoxin, a capsaicin analog: long-term results for the treatment of detrusor hyperreflexia. Eur Urol 38(4):444–452
Lazzeri M, Spinelli M, Beneforti P, Zanollo A, Turini D (1998) Intravesical resiniferatoxin for the treatment of detrusor hyperreflexia refractory to capsaicin in patients with chronic spinal cord diseases. Scand J Urol Nephrol 32(5):331–334
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, T.Y., Corcos, J., Camel, M. et al. Prospective, randomized, double-blind study of safety and tolerability of intravesical resiniferatoxin (RTX) in interstitial cystitis (IC). Int Urogynecol J 16, 293–297 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00192-005-1307-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00192-005-1307-4