Abstract
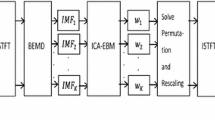
Blind source separation of single-channel mixed recording is a challenging task that has applications in the fields of speech, audio and bio-signal processing. Numerous blind source separation methods are commonly used for blind separation of single input multiple output. However, the priori knowledge of the signal is assumed to be known or the main channels selected from multi-channel output are not self-adaptive and automatic. Presented in this paper is a new method based on dimensionality reduction of ensemble empirical mode decomposition (EEMD), and ICA does not rely on such assumptions. The EEMD represents any time-domain signal as the sum of a finite set of oscillatory components called intrinsic mode functions (IMFs). ICA finds the independent components by maximizing the statistical independence of the dimensionality reduction IMFs. Principal component analysis (PCA) is applied to reduce dimensions of IMFs. The separated performance of EEMD-PCA-ICA algorithm is compared with EEMD-ICA through simulations, and experimental results show EEMD-PCA-ICA algorithm outperforms EEMD-ICA with higher cross-correlation and lower relative root mean squared error (RRMSE).












Similar content being viewed by others
References
F.R. Bach, M.I. Jordan, Blind one-microphone speech separation: a spectral learning approach. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 65–72 (2005)
B.L. Barnhart, W.E. Eichinger, Analysis of sunspot variability using the Hilbert–Huang transform. Sol. Phys. 269(2), 439–449 (2011)
A. Dapena, D. Iglesia, C.J. Escudero, An MSE-based method to avoid permutation/gain indeterminacy in frequency-domain blind source separation. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 29(3), 403–417 (2010)
M.E. Davies, C.J. James, Source separation using single channel ICA. Signal Process. 87, 1819–1832 (2007)
N.Q.K. Duong, E. Vincent, R. Gribonval, Under-determined convolutive blind source separation using spatial covariance models, in Acoustics Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), 2010 IEEE International Conference, 14–19 March 2010 (2010), pp. 9–12
B. Gao, W.L. Woo, S.S. Dlay, Single-channel source separation using EMD-subband variable regularized sparse features. IEEE Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 19(4), 961–976 (2011)
Y. Guo, Y. Li, Single channel electromyography blind recognition system of 3D hand. Comput. Appl. Softw. 27(9), 234–236 (2010)
Y. Guo, D. Zhou, Single channel surface electromyography blind recognition model based on watermarking. J. Vib. Control 18(1), 42–47 (2011)
M.E. Hamid, K. Ogawa, T. Fukabayashi, Improved single-channel noise reduction method of speech by blind source separation. Acoust. Sci. Technol. 28(3), 153–164 (2007)
N.E. Huang, M.L. Wu, S.R. Long, S.S. Shen, W.D. Qu, P. Gloersen, K.L. Fan, The empirical mode decomposition and the Hilbert spectrum for nonlinear and non-stationary time series analysis. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A 454(1971), 903–993 (1998)
X. Huang, H. Zeng, Efficient variant of FastICA algorithm for speech features extraction. Lect. Notes Electr. Eng. 113, 929–935 (2012)
A. Hyvärinen, E. Oja, Independent component analysis: algorithms and application. Neural Netw. 13(4–5), 411–430 (2000)
A. Hyvärinen, J. Karhunen, E. Oja, Independent Component Analysis (Wiley, New York, 2001). ISBN 978-0-471-40540-5
I.T. Jolliffe, Principal Component Analysis. Springer Series in Statistics, 2nd edn. (Springer, New York, 2002). ISBN 978-0-387-95442-4
T. Kristjansson, J. Hershey, P. Olsen, S. Rennie, R. Gopinath, Super-human multi-talker speech recognition: the IBM2006 speech separation challenge system, in Proceedings of the International Conference on Spoken Language Processing (INTERSPEECH), Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania (2006), pp. 97–100
J. Lin, A. Zhang, Fault feature separation using wavelet-ICA filter. NDT E Int. 38(6), 421–427 (2005)
X. Liu, D. Feng, T. Zhang, Multi-user detection of DS-CDMA based on improved-FastICA. ICMTMA 2012, Sanya, 6 January. Appl. Mech. Mater. 128–129, 633–636 (2012)
H.-G. Ma, Q.-B. Jiang, Z.-Q. Liu, G. Liu, Z.-Y. Ma, A novel blind source separation method for single-channel signal. Signal Process. 90(12), 3232–3241 (2010)
H. Mehrabian, L. Lindvere, B. Stefanovic, A.L. Martel, A constrained independent component analysis technique for artery-vein separation of two-photon laser scanning microscopy images of the cerebral microvasculature. Med. Image Anal. 16(1), 239–251 (2012)
B. Mijovic, M.D. Vos, I. Gligorijevic, J. Taelman, S.V. Huffel, Source separation from single-channel recordings by combining empirical-mode decomposition and independent component analysis. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 57(9), 2188–2196 (2010)
W.B.A.B. Mikhael, R.A. Ranganathan, T.B. Yang, Complex adaptive ICA employing the conjugate gradient technique for signal separation in time-varying flat fading channels. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 29(3), 469–480 (2010)
G.R. Naik, D.K. Kumar, M. Palaniswami, Multi run ICA and surface EMG based signal processing system for recognising hand gestures, in IEEE CIT 2008 (2008), pp. 700–705
E. Norden, S. Huang, The empirical mode decomposition and the Hilbert spectrum for nonlinear and non-stationary time-series analysis. Proc. R. Soc., Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 454(197), 903–995 (1998)
I.M.S. Panahi, K. Venkat, Blind identification of multi-channel systems with single input and unknown orders. Signal Process. 89, 1288–1310 (2009)
L. Parra, C. Spence, Convolutive blind separation of non-stationary sources. IEEE Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 8(3), 320–327 (2000)
K. Pearson, On lines and planes of closest fit to systems of points in space. Philos. Mag. 2(6), 559–572 (1901)
S.T. Roweis, One microphone source separation. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 793–799 (2000)
X.J. Shang, Y.T. Tian, Y. Li, Feature extraction and classification of sEMG based on ICA and EMD decomposition of AR model, in Electronics, Communications and Control (ICECC), 2011 International Conference (2011), pp. 1464–1467
Y.J. Shen, S.P. Yang, D.S. Kong, New method of blind source separation in under-determined mixtures based on singular value decomposition and application. J. Mech. Eng. 45(8), 64–70 (2009)
G. Tzagkarakis, M. Papadopouli, P. Tsakalides, Singular spectrum analysis of traffic workload in a large-scale wireless LAN, in Proceedings MSWIM’07, Chania, Crete Island, Greece, 22–26 October (2007) (CDROM)
D.N. Vizireanu, Generalizations of binary morphological shape decomposition. J. Electron. Imaging 16(1), 1–6 (2007)
D.N. Vizireanu, Morphological shape decomposition interframe interpolation method. J. Electron. Imaging 013007, 1–5 (2008)
D.N. Vizireanu, S. Halunga, G. Marghescu, Morphological skeleton decomposition interframe interpolation method. J. Electron. Imaging 19(2), 1–3 (2010)
F.A. Wang, H.A. Li, R.B. Li, Harmonic signals retrieval approach based on blind source separation. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 29(4), 669–685 (2010)
Z. Wu, N.E. Huang, Ensemble empirical mode decomposition: a noise-assisted data analysis method. Adv. Adapt. Data Anal. 1(1), 1–41 (2009)
W.F. Wu, X.H. Chen, X.J. Su, Blind source separation of single-channel mechanical signal based on empirical mode decomposition. J. Mech. Eng. 47(4), 213–216 (2011)
Y. Yuan, C.M. Li, T.Y. Wang, X. Zhao, Fault diagnosis and classification for bearing based on EMD-ICA, in Electronic and Mechanical Engineering and Information Technology (EMEIT), 2011 International Conference (2011), pp. 2715–2718
X.A. Zhang, Z.B. Liu, Y.A. Guo, L.A. Zhao, Selective facial expression recognition using fastICA. MSIT2011, Singapore, 16 September. Adv. Mater. Res. 433–440, 2755–2761 (2012)
Acknowledgements
Funding for this work was supported by 2010 research project of Shanxi Scholarship Council of China [No. 92] [No. 20101069], 2011 research project of Department of Human Resources and Social Security of Shanxi Province [No. 20121030] and 2010 Youth Foundation of Taiyuan University of Science and Technology of China [No. 20103004].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, Y., Huang, S. & Li, Y. Single-Mixture Source Separation Using Dimensionality Reduction of Ensemble Empirical Mode Decomposition and Independent Component Analysis. Circuits Syst Signal Process 31, 2047–2060 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-012-9414-1
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-012-9414-1