Abstract
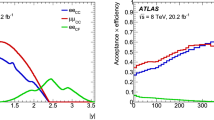
A systematic method for optimizing multivariate discriminants is developed and applied to the important example of a light Higgs boson search at the Tevatron and the LHC. The Significance Improvement Characteristic (SIC), defined as the signal efficiency of a cut or multivariate discriminant divided by the square root of the background efficiency, is shown to be an extremely powerful visualization tool. SIC curves demonstrate numerical instabilities in the multivariate discriminants, show convergence as the number of variables is increased, and display the sensitivity to the optimal cut values. For our application, we concentrate on Higgs boson production in association with a W or Z boson with \( H \to b\bar{b} \) and compare to the irreducible standard model background, \( {{Z} \left/ {W} \right.} + b\bar{b} \). We explore thousands of experimentally motivated, physically motivated, and unmotivated single variable discriminants. Along with the standard kinematic variables, a number of new ones, such as twist, are described which should have applicability to many processes. We find that some single variables, such as the pull angle, are weak discriminants, but when combined with others they provide important marginal improvement. We also find that multiple Higgs boson-candidate mass measures, such as from mild and aggressively trimmed jets, when combined may provide additional discriminating power. Comparing the significance improvement from our variables to those used in recent CDF and DØ searches, we find that a 10-20% improvement in significance against \( {{Z} \left/ {W} \right.} + b\bar{b} \) is possible. Our analysis also suggests that the H + W/Z channel with \( H \to b\bar{b} \) is also viable at the LHC, without requiring a hard cut on the W/Z transverse momentum.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
http://www-cdf.fnal.gov/physics/new/hdg//Results_files/results/whlnubb_jul10/.
http://www-cdf.fnal.gov/physics/new/hdg//Results_files/results/zhllbb_jul10/comb/zhllbb_comb_web/.
http://www-d0.fnal.gov/Run2Physics/WWW/results/prelim/Higgs/H95/.
http://www-d0.fnal.gov/Run2Physics/WWW/results/prelim/Higgs/H92/.
D0 collaboration, V.M. Abazov et al., Search for \( ZH \to {\ell^{+} }{\ell^{-} }b\bar{b} \) production in 4.2 fb −1 of \( p\bar{p} \) collisions at \( \sqrt {s} = 1.96\;TeV \), Phys. Rev. Lett. 105 (2010) 251801 [arXiv:1008.3564] [SPIRES].
ATLAS collaboration, Atlas Technical Design Report “Higgs Searches” (1999) http://www.cern.ch/Atlas/GROUPS/PHYSICS/TDR/physics_tdr/printout/Volume_II/letter/Higgs_searches_letter.ps.gz.
J.M. Butterworth, A.R. Davison, M. Rubin and G.P. Salam, Jet substructure as a new Higgs search channel at the LHC, Phys. Rev. Lett. 100 (2008) 242001 [arXiv:0802.2470] [SPIRES].
ATLAS collaboration, G. Aad et. al., ATLAS Sensitivity to the Standard Model Higgs in the HW and HZ Channels at High Transverse Momenta, ATL-PHYS-PUB-2009-0881.
ATLAS collaboration, G. Aad et. al., ATLAS Sensitivity to the Standard Model Higgs in the HW and HZ Channels at High Transverse Momenta, ATL-COM-PHYS-2009-345.
CDF collaboration, T. Aaltonen et al., A Search for the Standard Model Higgs Boson in the Process \( ZH \to {\ell^{+} }{\ell^{-} }b\bar{b} \) Usnig 5.7fb − 1 of CDF II Data, (July 16, 2010), CDF note 10235.
D. Krohn, J. Thaler and L.-T. Wang, Jet Trimming, JHEP 02 (2010) 084 [arXiv:0912.1342] [SPIRES].
J. Gallicchio and M.D. Schwartz, Seeing in Color: Jet Superstructure, Phys. Rev. Lett. 105 (2010) 022001 [arXiv:1001.5027] [SPIRES].
R.K. Ellis, W.J. Stirling and B.R. Webber, QCD and collider physics, Camb. Monogr. Part. Phys. Nucl. Phys. Cosmol. 8 (1996) 1.
J. Alwall et al., MadGraph/MadEvent v4: The New Web Generation, JHEP 09 (2007) 028 [arXiv:0706.2334] [SPIRES].
T. Sjöstrand, S. Mrenna and P.Z. Skands, A Brief Introduction to PYTHIA 8.1, Comput. Phys. Commun. 178 (2008) 852 [arXiv:0710.3820] [SPIRES].
M. Cacciari and G.P. Salam, Dispelling the N 3 myth for the k t jet-finder, Phys. Lett. B 641 (2006) 57 [hep-ph/0512210] [SPIRES].
A. Djouadi, The Anatomy of electro-weak symmetry breaking. I: The Higgs boson in the standard model, Phys. Rept. 457 (2008) 1 [hep-ph/0503172] [SPIRES].
M. Cacciari, G.P. Salam and G. Soyez, The anti-k t jet clustering algorithm, JHEP 04 (2008) 063 [arXiv:0802.1189] [SPIRES].
A. Hoecker et al., TMVA Toolkit for Multivariate Data Analysis with ROOT, http://tmva.sourceforge.net/.
R. Brun and F. Rademakers, ROOT - An Object Oriented Data Analysis Framework, in Proceedings AIHENP’96 Workshop, Lausanne, Sep. 1996, Nucl. Instrum. Meth. A 389 (1997) 81.
M. Bahr et al., HERWIG++ Physics and Manual, Eur. Phys. J. C 58 (2008) 639 [arXiv:0803.0883] [SPIRES].
CDF and D0 collaboration, T. Chwalek, Measurement of the W-boson helicity fractions in top-quark decays at CDF, arXiv:0705.2966 [SPIRES].
L.G. Almeida et al., Substructure of high-p T Jets at the LHC, Phys. Rev. D 79 (2009) 074017 [arXiv:0807.0234] [SPIRES].
C.F. Berger, T. Kucs and G.F. Sterman, Event shape/energy flow correlations, Phys. Rev. D 68 (2003) 014012 [hep-ph/0303051] [SPIRES].
S.D. Ellis, C.K. Vermilion, J.R. Walsh, A. Hornig and C. Lee, Jet Shapes and Jet Algorithms in SCET, JHEP 11 (2010) 101 [arXiv:1001.0014] [SPIRES].
D0 collaboration, Search for the standard model Higgs boson in the ZH→bbvv channel in 6.4 fb-1 of ppbar collisions at \( \sqrt {s} = 1.96\;TeV \), Preliminary Results for Summer 2010 Conferences, http://www-d0.fnal.gov/Run2Physics/WWW/results/prelim/Higgs/H90/, August 2010, D0Note 6087-CONF.
J.D. Bjorken and S.J. Brodsky, Statistical Model for electron-Positron Annihilation Into Hadrons, Phys. Rev. D 1 (1970) 1416 [SPIRES].
Y. Freund and R.E. Schapire, Experiments with a new boosting algorithm, Proc COLT, 209-217, ACM Press, New York U.S.A. (1996).
B.P. Roe et al., Boosted decision trees, an alternative to artificial neural networks, Nucl. Instrum. Meth. A 543 (2005) 577 [physics/0408124].
B.P. Roe, H.J. Yang and J. Zhu, Boosted decision trees, a powerful event classifier, Prepared for PHYSTATO5: Statistical Problems in Particle Physics, Astrophysics and Cosmology, Oxford, England, United Kingdom, 12–15 Sep 2005.
S. Catani, Y.L. Dokshitzer, M.H. Seymour and B.R. Webber, Longitudinally invariant K t clustering algorithms for hadron hadron collisions, Nucl. Phys. B 406 (1993) 187 [SPIRES].
G.P. Salam and G. Soyez, A practical Seedless Infrared-Safe Cone jet algorithm, JHEP 05 (2007) 086 [arXiv:0704.0292] [SPIRES].
D.E. Soper and M. Spannowsky, Combining subjet algorithms to enhance ZH detection at the LHC, JHEP 08 (2010) 029 [arXiv:1005.0417] [SPIRES].
S.D. Ellis, C.K. Vermilion and J.R. Walsh, Recombination Algorithms and Jet Substructure: Pruning as a Tool for Heavy Particle Searches, Phys. Rev. D 81 (2010) 094023 [arXiv:0912.0033] [SPIRES].
J.M. Butterworth et al., The Tools and Monte Carlo working group Summary Report, arXiv:1003.1643 [SPIRES].
D.E. Kaplan, K. Rehermann, M.D. Schwartz and B. Tweedie, Top Tagging: A Method for Identifying Boosted Hadronically Decaying Top Quarks, Phys. Rev. Lett. 101 (2008) 142001 [arXiv:0806.0848] [SPIRES].
G.P. Salam, Towards Jetography, Eur. Phys. J. C 67 (2010) 637 [arXiv:0906.1833] [SPIRES].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
ArXiv ePrint: 1010.3698
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gallicchio, J., Huth, J., Kagan, M. et al. Multivariate discrimination and the Higgs+W/Z search. J. High Energ. Phys. 2011, 69 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/JHEP04(2011)069
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/JHEP04(2011)069