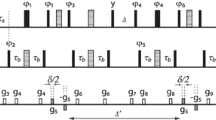
Abstract
Relatively efficient spin diffusion among unprotonated carbons with large chemical-shift anisotropies can be achieved by a13C nuclear magnetic resonance multiple-pulse sequence with a lowduty cycle of ∼5% on the13C channel, which minimizes sample heating and reduces cumulative effects of pulse imperfections. The spin diffusion occurs among transverse-magnetization isochromats, while the total transverse magnetization is a conserved quantity under the average Hamiltonian. The “flip-flop” term of the dipolar-coupling average Hamiltonian is the same as in the full dipolar coupling, i.e., its scaling factor is unity. For a sample of 40%13COO-labeled poly(vinyl acetate), with13C in ester groups accounting for 7% of all heavy atoms, magnetization equilibrates within 20 ms over a volume of (0.9 nm)3, corresponding to a molecular mass of 500 Da, while the T2 relaxation time of the total transverse magnetization is ∼40 ms. The spin diffusion coefficient is estimated asD = 3 ± 1.5 nm2/s.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Henrichs P.M., Under M.: J. Magn. Reson.58, 458 (1984)
Edzes H.T., Bernards J.P.C.: J. Am. Chem. Soc.106, 1515 (1984)
Robyr P., Meier B.H., Ernst R.R.: Chem. Phys. Lett.162, 417 (1989)
Robyr P., Tomaselli M., Straka J., Grob-Pisano C., Suter U.W., Meier B.H., Ernst R.R.: Mol. Phys.84, 995 (1995)
Tracht U., Wilhelm M., Heuer A., Feng H., Schmidt-Rohr K., Spiess H.W.: Phys. Rev. Lett.81, 2727 (1998)
Heuer A., Wilhelm M., Zimmermann H., Spiess H.W.: Phys. Rev. Lett.75, 2851 (1995)
Madi Z.L., Brutscher B., Schulte-Herbruggen T., Bruschweiler R., Ernst R.R.: Chem. Phys. Lett.268, 300 (1997)
Schulte-Herbruggen T., Madi Z.L., Sorensen O.W., Ernst R.R.: Mol. Phys.72, 847 (1991)
Waugh J.S., Huber L.M., Haeberlen U.: Phys. Rev. Lett.20, 180 (1968)
Haeberlen U., Waugh J.S.: Phys. Rev.175, 453 (1968)
Haeberlen U.: High Resolution NMR of Solids: Selective Averaging. Advances in Magnetic Resonance Supplement 1. New York: Academic Press 1976.
Pastawski H.M., Usaj G., Levstein P.R.: Chem. Phys. Lett.261, 329 (1996)
Schmidt-Rohr K., Spiess H.W.: Multidimensional Solid-State NMR and Polymers. London: Academic Press 1994.
Van Kampen N.G.: Stochastic Processes in Physics and Chemistry. Amsterdam: North-Holland 1981.
Kentgens A.P.M., de Boer E., Veeman W.S.: J. Chem. Phys.87, 6859 (1987)
Clauss J., Schmidt-Rohr K., Spiess H.W.: Acta Polymer.44, 1 (1993)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, W.G., Zimmermann, H. & Schmidt-Rohr, K. Efficient spin diffusion of transverse13C magnetization. Appl. Magn. Reson. 17, 197–209 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03162161
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03162161