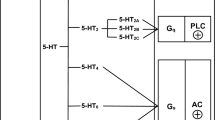
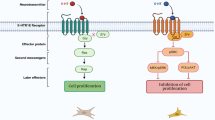
Abstract
Progress in the field of neuronal receptor research has accelerated during the last few years due to developments in pharmacology and molecular biology. This is particularly true in the case of the serotonin 5-HT1A receptor. In 1983 the very selective, high affinity 5-HT1A agonist 8-OH-DPAT was developed which allowed the pharmacology and distribution of the 5-HT1A receptor in the central nervous system of the rat and man to be extensively characterized. By 1987, the gene encoding this receptor protein was cloned and sequenced, allowing not only elucidation of its structure, but also better insight into the nature of its coupling to transmembrane signal transduction systems. Thus in a short period of time considerable knowledge has accumulated on how serotonin exerts its functions in the central nervous system via the 5-HT1A receptor. In the present review we will briefly discuss some of the latest developments regarding the 5-HT1A receptor.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albert, P. R. Zhou, Q. Y., Van Tol, H. H. M. Bunzow, J. R., and Civelli, O. Cloning, mRNA tissue distribution and functional expression of the rat 5-HT1A receptor gene. J. Biol. Chem. 265:5835–5832.
Andrade, R., Malenka, R. C., and Nicoll, R., 1987. A G protein couples serotonin and GABAB receptor to the same channels in the hippocampus. Science. 234:1261–1265.
Andrade, R., and Nicoll, R. 1987. Novel anxiolytics discriminate between postsynaptic serotonin receptors of he rat hippocampus. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg Arch Pharmacol. 336:5–10.
Andrade, R., and Nicoll, R. 1987. Pharmacologically distinct actions of serotonin on single pyramidal neurones of the rat hyppocampus recorded in vitro. J. Physiol (London). 349:99–125.
Benovic, J. R., Bouvier, M., Caron, M. G., and Lefkowitz, R. J. 1988. Regulation of adenylyl cyclase-coupled β-adrenergic receptors. Ann. Rev. Cell Biol. 4:405–428.
Bockaert, J., Dumuis, A., Bouhelal, R., Sebben, M., and Cory, R. N. 1987. Piperazine derivatives including the putative anxiolytic drugs buspirone and ipsapirone, are agonists at 5-HT1A receptors negatively coupled with adenylate cyclase in hippocampal neurons. Naunyn Schmiedeberg Arch. Pharmacol. 335:588–892.
Bradley, P. B., Engel, G., Feniuk, W., Fozard, J. W., Humphrey, P. P. A., Midelmiss, D. N., Mylecherane, E. J., Richardson, B. P. and Saxena, P. R. 1986. Nomenclature of functional receptors for 5-hydroxytryptamine. Neuropharmacol. 24:563–576.
Dourish, C. T., Ahlenius, S., and Huston, P. H. 1987. (eds.) Brain 5-HT1A receptors. Ellis horwood series in biomedicine Ltd., Chichester.
Chopin, P., and Briley, M. 1987 Animal models of anxiety: the effect of compounds that modify 5-HT neurotransmission. TIPS. 8:383–388.
Claustre, Y., Bénavides, J., and Scatton B. 1988. 5-HT1A receptors agonists inhibit carbachol-induced stimulation of phosphoinositide turnover in the rat hippocampus. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 149:149–153.
Colino, A., and Halliwell, J. V. 1987. Differential modulation of three separate K-conductances in hippcampal CA1 neurons by serotonin. Nature 328:73–77.
Cossery, J. M., Gozlan, H., Spampinato, U., Perdicakis, C., Guillaumet, G., Pichat, L., and Hamon, M. 1987. The selective labelling of central 5-HT1A receptor binding site by (3)H-5-Methoxy-3-)di-n-propylamino)chroman. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 140:143–155.
Daval, G., Vergé, D., Basbaum, A. I., Bourgoin, S., and Hamon, M. 1987. Autoradiographic evidence of serotonin 1 binding sites on primary afferent fibres in the dorsal horn of the rat spinal cord. Neuroscience Letters. 83:71–76.
De Vivo M. and Maayani, S. 1986. Characterization of the 5-HT1A receptor mediated inhibition of forskolin-stimulated adenylate cyclase activity in guinca pig and rat hippocampal membranes. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 238:248–253.
Dixon, R. A. F., Kobilka, B. K., Strader, D. J., Benovic, J. L., Dohlman, H. G., Frielle, T., Bolanovski, M. A., Benett, C. D., Rands, E., Diehl, R. E., Mumford R. A., Slater, E. E., Sigal, I. S., Caron, M. G., Lefkowitz, R. J., and Strader, C. D. 1986. Cloning of the gene and cDNA for mammalian β-adrenergic receptor and homology with rhodopsin. Nature 321:75–79.
Dixon, R. A. F., Sigal, I. F., Rands, E., Register, R. B., Candelore, M. R., Blake A. D., and Strader, C. D. 1987. Ligand binding to the β-adrenergic receptor involves its rhodopsin-like core. Nature. 326:73–77.
Dumuis, A., Sebben, M., and Bockaert, J., 1988. Pharmacology of 5-hydroxytyptamine 1A receptors which inhibit cAMP production in hippocampal and cortical neurons in primary culture. Mol. Pharmacol. 33:176–186.
Dumuis, AZ., Sebben, M., Bouhelal, R., Sebben, M., Cory, R., and Bockaert, J. 1988. A nonclassical 5-hydroxytryptamine receptor positively coupled with adenylate cyclase in the central nervous system. Mol. Pharmacol. 34:880–887.
Eide, P. K., Hole, K., and Broch, O. G. 1988. 5-HT depletion with 5,7-DHT, PCA and PCPA in mice: differential effects on the sensitivity to 5-MeODMT, 8-OH-DPAT and 5-HTP as measured by two nociceptive tests. Brain Research. 440:42–52.
El Mestikawy, S., Cognard, C., Gozlan, H., and Hamon, M. 1988. Pharmacological and biochemical characterization of rat hippocampal 5-HT1A receptors solubilized by 3(3-(cholamidopropyl) dimethyl-ammonio)-1-propane sulfonate (CHAPS). J. Neurochem. 51:1031–1040.
El Mestikawy, S., Taussig, D., Gozlan, H., Emerit, M. B., Ponchant, M., and Hamon, M. 1989. Chromatographic analysis of the 5-HT1A receptor solubilized from the rat hippocampus. J. Neurochem. 53:1555–1566.
El Mestikawy, S., Riad, Laporte, A. M., Vergé, D., Daval, G., Gozlan, H., and Hamon, M. 1990. Production of specific anti-rat 5-HT1A receptor antibodies in rabbits injected with a synthetic peptide. Neurosci. Lett. 118:189–192.
Emerit M. B. E. Mestikawy, S., Gozlan, H., Cossery, J. M., Besselievre, R. Marquet, A., and Hamon, M. 1987. Identification of the 5-HT1A receptor binding subunit in the rat brain membranes using the photoaffinity probe, (3H)8-methoxy-2[N-n-propyl, N, 3-(2-nitro-4-azidophenyl) aminopropyl] aminotetralin. J. Neurochem. 49:373–380.
Emerit, M. B., El Mestikawy, S., Gozlan, H., Rouot, B., and Hamon, M. 1990. Physical evidence of the coupling of solubilized 5-HT1A binding sites with G regulatory proteins. Biochem. Pharmacol. 39:7–18.
Fargin, A., Raymond, J. R., Lohse, M. J., Kobilka, B. K., Caron, M. G., and Lefkowitz, R. J. 1988. The genomic clone G21 which resembles a β-adrenergic receptor sequence encodes the human 5-HT1A receptor. Nature 335:358–360.
Fargin, A., Raymond, J. R., Regan, J. W., Cotecchia, S., Lefkowitz, R. J., and Caron, M. 1989. Effector coupling mechanisms of the cloned 5-HT1A receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 2645:14848–14852.
Frielle, T., Collins, S., Daniel K. W., Caron, M. G., Lefkowitz, R. J., and Kobilka, B. K. 1987. Cloning of the cDNA for the human β1-adrenergic receptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci USA. 84:7920–7924.
Frielle, T., Daniel, K., Caron, M. G., and Lefkowitz, R. J. 1988. Structural basis of β-adrenergic receptor subtype specificty studied with chimeric β1/β2 receptors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 85:9494–9498.
Gaddum, H., and Picarelli, Z. P. 1957. Two kinds of tryptamine receptor. Brit. J. Pharmacol. Chemother. 12:323–328.
Glaser, T., and Traber, J. 1985. Binding of the putative anxiolytic TVX Q-7821 to hippocampal 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) recognition sites. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg Arch. Pharmacol. 329:211–215.
Gozlan, H., El Mestikawy, S., Pichat, S., Glowinski, J., and Hamon, M. 1983. Identification of presynaptic autoreceptors serotonin autoreceptors using a new ligand:3H-PAT. Nature 305:140–142.
Gozlan, H., Emerit, M. B., Hall, M. D., Nielsen, M. and Hamon, M. 1987. In situ molecular sizes of the various types of 5-HT binding sites in the rat brain. Biochem. Pharmacol. 35:1891–1897.
Gozlan, H., Emerit, M. B. El Mestikawy, S., Cossery, J. M., Marquet, A., Besselièvre, R., and Hamon, M. 1988 Photoaffinity labeling and solubilization of the central 5-HT1A receptor binding site. J. Recept Res. 7:195–221.
Hall, M. D., El Mestikawy, S., Emerit, M. B., Pichat, L., Hamon, M., and Gozlan, H. 1985. [3H]8-hydroxy-2-(di-n-propylammino)tetralin binding to pre- and postsynaptic 5-hydroxytryptamine sites in various region of the rat brain. J. Neurochem. 44:1685–1696.
Hamon, M., Fataccini, C. M., Adrien, J., Galissot, M. C., Martin, P., and Gozlan, H. 1988. Alterations of central serotonin and dopamine turnover in rats treated with ipsapirone and other 5-HT1A agonists with potential anxiolytic properties. J. Pharmac. Exp. Ther. 246:745–752.
Hamon, M., Emerit, M. B., El Mestikawy, S., Gallissot, M. C., and Gozlan, H. Regional differences in the transduction mechanisms of serotonin receptors in the namalian brain. In: “Cardiovascular pharmacology of 5-HT: prospective therapeutic application”, ed. P.R. Saxena, Kluer, Acad. Publ. B. V. Dordrecht (in press).
Herrick-Davis, K., and Titeler, M. 1988. (3H) Spiroxatrine: a 5-HT1A radioligand with agonist binding properties. J. Neurochem. 50:528–533.
Hoyer, D. 1988. Functional correlates of serotonin 5-HT1 recognition sites, submitted. J. Recept. Res. 8:59–81.
Hoyer, D., Engel, G., and Kalkman, H. O. 1985. Molecular pharmacology of 5-HT1 and 5-HT2 recognition sites in rat and pig brain membranes: radioligand binding studies with [3H] 5-HT, [3H] 8-OH-DPAT, (−) [125I] iodocyanopindolol and [3H]mesulergine. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 118:13–23.
Hoyer, D., Pazos, A., Probst, A., and Palacios, J. M. 1986. Serotonin receptors in human brain I: Characterization and autoradiographic localization of 5-HT1A recognition sites. Apparent absence of 5-HT1B recognition sites. Brain research. 376:85–96.
Julius, D., Mac Dermott, A. B., Axel, R., and Jessel, T. M. 1988. Molecular characterization of a functional cDNA encoding the serotonin 1C receptor. Science 241:558–564.
Kobilka, B. K., Dixon, R. A. F., Frielle, T., Dohlman, H. G., Bolanowski, M. A., Sigal, I. S., Yang-Feng, T., Francke, U., Caron, M. G., and Lefkowitz, R. J. 1987. cDNA for the human β2-adrenergic receptor: a protein with multiple spanning domains encoded by a gene whose chromosomal location is shared with that of the receptor for platelet-derived growth factor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 84:46–50.
Kobilka, B. K., Frielle T., Collins, S., Yang-Feng, T., Kobilka, T. S., Francke, U., Lefkowitz, R.J., and Caron, M. G. 1987. Identification of an intronless gene which encodes a potential member of the family of G protein-coupled receptors. Nature. 329:75–79.
Krupinski, J., Coussen F., Bakalyar, H. A., Tang, W. J., Feinstein, P. G., Orth, K., Slaughter, C., Reed, R. R., and Gilman, A. 1989. Adenylyl cyclase amino acid sequence: possible channel- or transporter-like structure. Science. 244:1558–1564.
Leeb-Lundberg, L. M. F., Cotecchia, S., Lomasney, J., DeBernardis, J. F., Lefkowitz, R. J., and Caron, M. 1985. Phorbol esters promote α1-adrenergic receptors phosphorylation and receptor uncoupling from inositol phospholipid metabolism. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 82:5651–5655.
Leonhart, S., Herrick-Davis, K. and Titeler, M. 1989. Detection of a novel serotonin receptor subtype (5-HT1E) in human brain: interaction with a GTP-binding protein. J Neurochem. 53:465–471.
Leysen, J. (in press). Neuromethods, neuropharmacology II “Drugs as tools in neurotransmitter research,In Boulton, A. A., Baker, G. B. and Jourio, A. V., Clifton (eds) Human press. The use of 5-HT receptor agonists and antagonists for the characterization of their respective sites.
Makman, M. H., Dvorkin, B., and Crain, S. M. 1988. Modulation of adenylate cyclase activity of mouse spinal cord-ganglion explants by opioids, serotonin and pertussis toxin. Brain Res. 445:303–313.
Marcinkiewicz, M., Verge, D., Gozlan, H., Pichat, L., and Hamon, M. 1984. Autoradiographic evidence for the heterogeneity of 5-HT1 sites in the rat brain. brain Res. 291:159–163.
Markstein, R., Hoyer, D., and Engel, G. 1986. 5-HT1A receptors mediate stimulation of adenylate cyclase in the rat hippocampus. Naunym Schmiedeberg Arch. pharmac. 333:335–341.
Middleton, J. P., Raymond, J. R., Whorton, A. R., and Dennis, V. W. 1990. Short-term regulation of Na+/K+ATPase by recombinant 5-HT1A receptor expressed in HeLa cells. J. Clin. Invest. 86:1799–1805, In Press.
Oliveras, J. L., Redjemi, F., Guibaud G. and Besson J. M. 1975. Analgesia induced by electrical stimulation of the inferior centralis nucleus of the raphe in the cat. Pain. I:139–145.
Norman, A. B., Battaglia, G. and Creese, I. 1985. (3H]WB4101 labels the 5-HT1A receptor subtype in rat brain. Mol., Pharmacol. 28:487–494.
Pazos, A. and Palacios, J. M. 1985. Quantitative autoradiographic mapping of serotonin receptors in the rat brain. I Serotonin-1 receptors. Brain Res. 346:205–230.
Pazos, A., Probst, A. and Palacios, J. M. 1986. Serotonin receptors in the human brain. III Autoradiographic maping of serotonin-1 receptors. Neurosci. 21:97–122.
Pedigo, N. W., Yamamura, H. I. and Nelson 1981. Discrimination of multiple (3H]5-hydroxytryptamine binding sites by the neuroleptic spiperone in rat brain. J. Neurochem. 36:220–226.
Peroutka, S. J., and Snyder, S. H. 1979. Multiple serotonin receptors: differential binding of (3H]5-HT, (3H)lysergic acid diethylamide and (3H)spiroperidol. Mol. Pharmacol. 16:687–699.
Pritchett, D. B., Bach, A. W., Wozny, M., Taleb O., Dal Toso, R., Shih, J., and Seeburg, P. 1988. Structure and functional expression of cloned rat 5-HT2 receptor. Embo.J. 7:4135–4140.
Ransom, R. W., Asarch, K. B., and Shih, J. 1986. (3H)1-[2-(4-aminophenyl)ethyl]-4-(3-trifluoromethylphenyl) piperazine: a selective radioligand for 5-HT1A receptors in rat brain. J. Neurochem. 46:68–75.
Ransom, R. W., Asarch, K. B., and Schih,J. 1986. Phototaffinity labeling of the 5-HT1A receptor in rat hippocampus. J. Neurochem. 47:1066–1072.
Raymond, J. R., Fargin, A., Loshe, M., Senogles, S., Regan, J. W., Lefkowitz, R. J., and Caron, M. G. 1989. Identification of the ligand binding subunit of the human 5-HT1A receptor. Mol. Pharmacol. 36:15–21.
Raymond, J. R., Middleton, J. P., and Dennis, V. W. HeLa cells demonstrate cAMP-inhibitable sodium-dependent phosphate uptake. 1990. Am. J. Physiol. 258 F433–F437.
Raymond, J. R., Fargin, A. F. Middleton, J. P., Graff, J. M., Haupt, D. M., Caron, M. G. Lefkowitz, R. J., and Dennis, V. W. The human 5-HT1A receptor expressed in HeLa cells stimulates sodium-dependent phosphate uptake via protein kinase C. 1990. J. Biol. Chem. 264:21943–21950.
Schoeffter, P., and Hoyer, D. 1988. Centrally acting hypotensive agents with affinity to 5-HT1A binding sites inhibit forskolinstimulated adenylate cyclase activity in calf hippocampus. Brit. J. Pharmacol. 85:975–985.
Schulman, H., and Lou, L. 1989. Multifunctional Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein Kinase: domain structure and regulation. TIBS. 14:62–66.
Shenker, A., Maayani, S., Weinstein, H., and Green, J. P. 1985. Two 5-HT receptors linked to adenylate cyclase in guinea pig hippocampus are discriminated by 5-carboxamidotryptamine and spiperone. Eur. J. Pharmac. 109:427–429.
Sprouse, J. S., and Aghajanian, G. K. 1986. (−)Propanolol blocks the inhibition of the sertoninergic, dorsal raphe cell firing by 5-HT1A selective agonists. Eur. J. Pharmac. 128:295–298.
Sprouse, J. S., and Aghajanian, G. K. 1987. Electrophysiological responses of serotoninergic dorsal raphe neurons to the 5-HT1A and 5-HT1B agonists. Synapse. 1:3–9.
Traber, J., and Glaser, T. 1987. 5-HT1A receptor-related anxiolytics. TIPS. 8:432–437.
Vergé, D., Daval, G., Maicinkiewicz, M., Patey, A., El Mestikawy, S., Gozlan, H., and Hamon, M. 1986. Quantitative autoradiography of multiple 5-HT1 receptors subtypes in the brain of control and 5,7-DHT treated rats. J. Neurosci. 6:3474–3482.
Weiss, S., Sebben, M., Kemp, D. E., and Bockaert, J. 1986. Serotonin 5-HT1 receptors mediate inhibition of cyclic AMP production in neurons. Eur. J. Pharmac. 120:227–230.
Weissmann-Nanopoulos, D., Mach, E., Magre, J., Demassey, Y., and Pujol, J. F. 1985. Evidence for the localization of 5-HT1A binding sites on serotonin containing neurons in the raphe dorsalis and the raphe centralis nuclei of the rat brain. Neurochem. Int. 7:1061–1072.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mestikawy, S.E., Fargin, A., Raymond, J.R. et al. The 5-HT1A receptor: an overview of recent advances. Neurochem Res 16, 1–10 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00965820
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00965820