Abstract
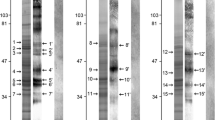
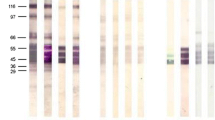
The Western blotting technique was used to determine the antigens ofTrichinella spiralis muscle larvae that were recognized by antibodies in sera from humans and pigs displayingT. spiralis infections. This resulted in the identification of several antigens that were recognized by all sera. Some of these antigens, notably those that were recognized during the early stage of infection, cross-reacted with antibodies to other parasites. This cross-reactivity was caused by the presence of phosphorylcholine on these antigens. A large portion of the antigens that were recognized by antibodies from infected humans and pigs were found to share a singleTrichinella-specific determinant. TheTrichinella-specific antigen population could be isolated from phosphorylcholine-containing antigens by a simple two-step affinity chromatography procedure using monoclonal antibodies to both determinants. The resulting preparation consisted primarily of a single antigen showing an apparent molecular weight of 45 kDa that corresponded to a mamor constituent of excretory-secretory (ES) products of muscle larvae. When tested in an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), this antigen displayed diagnostic specificity that was comparable with the ES fraction and diagnostic sensitivity comparable with the crude muscle-larvae extract.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ancelle T, Dupony-Camet J, Heyer F, Faurant C, Lapierre J (1985) Outbreak of trichinosis due to horse meat in the Paris area. Lancet 21:660
Appleton JA, Bell RG, Homan W, Knapen F van (1991) Consensus onTrichinella spiralis Antigens and Antibodies. Parasitol Res 7:190–192
Arriaga C, Muñiz E, Morilla A, Ortega-Pierres G (1989)Trichinella spiralis: recognition of muscle larva antigens during experimental infection of swine and its potential use in diagnosis. Exp Parasitol 69:363–372
Clinard EH (1978) Serum fractions associated with positive and false positive reactions in the EIA test for trichinellosis in swine. In: Kim CW, Pawlowski ZS (eds) Trichinellosis, 4th International Conference, University Press of New England, Hanover, New Hampshire, pp 509–517
Denckers EY, Wassom DL, Hayes CE (1990a) Characterization ofTrichinella spiralis antigens sharing an immunodominant, carbohydrate-associated determinant distinct from phosphorylcholine. Mol Biochem Parasitol 41:241–250
Denckers EY, Wassom DL, Krco CJ, Hayes CE (1990b) The mouse antibody response toTrichinella spiralis defines a single, immunodominant epitope shared by multiple antigens. J Immunol 144:3152–3159
Despommier DD, Laccetti A (1981)Trichinella spiralis: partial characterization of antigens isolated by immuno-affinity chromatography from the large-particle fraction of muscle larvae. J Parasitol 67:332–339
Dupouy-Camet J, Knapen E van, Ancelle T, Vo Quang D, Lavarde V, Lapierre J (1988) Étude des immunoglobulines spécifiques (totales, IgG, IGM, IgA, IgE) en immunofluorescence indirecte et en ELISA chez quarante malades Trichinés suivis pendant neuf mois. Pathol Biol (Paris) 36:803–807
Gamble HR (1985)Trichinella spiralis: immunization of mice using monoclonal antibody affinity-isolated antigens. Exp Parasitol 59:398–404
Gamble HR, Graham CE (1984) Monoclonal antibody-purified antigen for the immunodiagnosis of trichinosis. Am J Vet Res 45:67–74
Gamble HR, Murrell KD (1986) Conservation of diagnostic antigen epitopes among biologically diverse isolates ofTrichinella spiralis. J Parasitol 72:921–925
Gamble HR, Anderson WR, Graham CE, Murrel KD (1983) Diagnosis of swine trichinosis by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) using an excretory-secretory antigen. Vet Parasitol 13:349–361
Gold AM, Despommier DD, Buck SW (1990) Partial characterization of two antigens secreted by L1 larvae ofTrichinella spiralis. Mol Biochem Parasitol 41:187–196
Knapen F van (1985) The incidence ofTrichinella spiralis in Western Europe in the past decade. Bull Soc Fr Parasitol 2:11–16
Knapen F van (1987) Epidemiological data concerningT. spiralis infections in the Netherlands. Wiad Parazytol 33:566–568
Knapen F van (1988) A propos de cas de trichinose en Europe dus à la consommation de viande chevaline. Ann Med Vet 132:441–446
Knapen F van (1989) Control systems of sylvatic and domestic animals: trichinellosis. Wiad Parazytol 35:475–481
Knapen F van, Franchimont JH, Ruitenberg EJ, Baldelli B, Bradley J, Gibson TE, Gottal C, Henriksen SA, Köhler G, Skovgaard N, Soulé C, Taylor SM (1980) Comparison of the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) with three methods for the detection ofTrichinella spiralis infections in pigs. Vet Parasitol 7:109–121
Knapen F van, Buys J, Ruitenberg EJ (1986)Trichinella spiralis antibodies. In: Bergmeyer HU, Bergmeyer J, Grassel M (eds) Methods of enzymatic analysis, vol 12. Antigens and antibodies 2. VHC Verlagsgesellschaft, Weinheim, pp 393–406
Kolk AHJ, Ho ML, Klatser PR, Eggelte TA, Kuyper S, Jonge S de, Leetiwen J van (1984) Production and characterisation of monoclonal antibodies toMycobacterium tuberculosis, M. bovis (BCG) andM. leprae. Clin Exp Immunol 58:511–521
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during assembly of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680–685
Lal RB, Ottesen EA (1989) Phosphorylcholine epitopes on helminth and protozoal parasites and their presence in the circulation of infected human patients. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg 83:622–655
McLaren DJ, Ortega-Pierres G, Parkhouse RME (1987)Trichinella spiralis: immunocytochemical localisation of surface and intracellular antigens using monoclonal antibody probes. Parasitology 94:101–104
Morrissey JH (1981) Silver stain for proteins in polyacrylamide gels: a modified procedure with enhanced uniform sensitivity. Anal Biochem 117:307–310
O'Farrell PH (1975) High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem 250:4007–4021
Ortega-Pierres G, Muñiz E, Coral-Vázquez R, Parkhouse RME (1989) Protection againstTrichinella spiralis induced by purified stage-specific surface antigens of infective larvae. Parasitol Res 75:563–567
Pawlowski Z, Knapen F van, Kociecka W, Stefaniak J, Franchimont JH (1990) Clinical expression of trichinellosis and immunoglobulins in three different epidemics. Bull Soc Fr Parasitol 8:996
Perry P, Petit A, Poulain J (1974) Phosphorylcholine-bearing components in homogenates of nematodes. Eur J Immunol 4:637–639
Roach TIA, Wakelin D, Else KJ, Bundy DAP (1988) Antigenic cross-reactivity between the human whipwormTrichuris trichiura and the mouse trichuroidsTrichuris muris andTrichinella spiralis. Parasite Immunol 10:279–291
Ruitenberg EJ, Knapen J van (1977) Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) as a diagnostic method forTrichinella spiralis infections in pigs. Vet Parasitol 3:317–326
Ruitenberg EJ, Knapen F van (1983) Report 1987–1982 concerningTrichinella spiralis studies in the Netherlands. Wiad Parazytol 29:624–626
Ruitenberg EJ, Lungström I, Steerenberg PA, Buys J (1976) Reliability of the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) for the serodiagnosis ofTrichinella spiralis infections in conventially raised pigs. J Immunol Methods 10:57–70
Seawright GL, Despommier D, Zimmerman W, Isenstein RS (1983) Enzyme immunoassay for swine trichinelosis using antigens purified by immunoaffinity chromatography. Am J Trop Med Hyg 32:1275–1284
Silberstein DS, Despommier DD (1984) Antigens fromTrichinella spiralis that induce a protective response in the mouse. J Immunol 132:898–904
Taylor SM, Kenny T, Mallon T, Davidson WB (1980) The micro-ELISA for antibodies toTrichinella spiralis: elimination of false positive reactions by antigen fractionation and technical improvements. Z Veterinaermed 27:764–772
Towbin H, Staehelin T, Gordon J (1979) Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 76:4350–4354
Ubeira FM, Leiro J, Santamarina MT, Villa TG, Sanmartín-Durán ML (1987) Immune response toTrichinella epitopes: the antiphosphorylcholine plaque-forming cell response during the biological cycle. Parasitology 94:543–553
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Homan, W.L., Derksen, A.C.G. & van Knapen, F. Identification of diagnostic antigens fromTrichinella spiralis . Parasitol Res 78, 112–119 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00931651
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00931651