Abstract
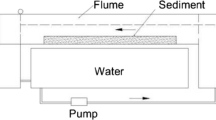
The burrowing marine shrimp Callianassa australiensis (Dana) was collected from an uncontaminated area in Western Port, Victoria, Australia in 1977. The shrimp were exposed to cadmium-contaminated water and sediment for 8 wk. The concentrations ranged from 0.5 to 63 μg Cd 1-1 for water and 0.5 to 63 μg Cd g-1 for sediment. The shrimp accumulated cadmium from water at a rate commensurate with increases in the concentration of cadmium in water and the duration of the experiment. Although the cadmium concentration in the sediments was 103 times higher than that in water, it hat no effect on cadmium uptake by the shrimp. The concentration factors decreased with increasing concentration of cadmium in water but increased as the duration of exposure increased. The shrimp dry weight decreased with increasing concentration of cadmium in water and duration of exposure. As was the case with cadmium uptake by the shrimp, these two factors acted interactively on the shrimp dry weight, but the third factor, concentration of cadmium in sediment, had no effect.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature cited
Ahsanullah, M., D. S. Negilski and M. C. Mobley: Toxicity of zinc, cadmium and copper to the shrimp Callianassa australiensis. I. Effects of individual metals. Mar. Biol. 64, 299–304 (1981a)
Ahsanullah, M., D. S. Negilski and M. C. Mobley: Toxicity of zinc, cadmium and copper to the shrimp Callianassa australiensis. III. Accumulation of metals. Mar. Biol. 64, 311–316 (1981b)
Benayoun, G., S. W. Fowler and B. Oregioni: Flux of cadmium through euphausiids. Mar. Biol. 27, 205–212 (1974)
Bryan, G. W.: Bioaccumulation of marine pollutants. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. (Ser. B) 286, 483–505 (1979)
Bryan, G. W. and E. Ward: Potassium metabolism and the accumulation of 137Cs by the decapod Crustacea. J. mar. biol. Ass. U.K. 42, 199–214 (1962)
Cochran, W. G. and G. M. Cox: Experimental designs (2nd ed.), New York: John Wiley & Sons 1957
E.P.A.: The waters of Westernport Bay and catchment. In: Government Gazette, pp 369–380. Melbourne, Australia: F. D. Atkinson, Government Printer 1979. (State Environmental Protection Policy No. W-28)
Fowler, S. W. and G. Benayoun: Experimental studies on cadmium flux through marine biota. In: Comparative studies of food and environmental contamination, pp 159–178. Vienna: International Atomic Energy Agency 1974
Fowler, S. W. and G. Benayoun: Accumulation and distribution of selenium in mussel and shrimp tissues. Bull. envir. Contam. Toxicol. 16, 339–346 (1976)
Harris, J. E., G. J. Fabris, P. J. Statham and F. Tawfik: Biogeochemistry of selected heavy metals in Western Port, Victoria, and use of invertebrates as indicators with emphasis on Mytilus edulis planulatus. Aust. J. mar. Freshwat. Res. 30, 159–178 (1979)
Helz, G. R., R. J. Huggett and J. M. Hill: Behaviour of Mn, Fe, Cu, Zn, Cd and Pb discharged from a wastewater treatment plant into an estuarine environment. Wat. Res. 9, 631–636 (1975)
Jenne, E. A.: Controls on Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu and Zn concentrations in soils and water: the significant role of hydrous Mn and Fe oxides. In: Trace inorganics in water, pp 337–379. Ed. by R. F. Gould. Washington, D.C.: American Chemical Society 1968
Luoma, S. N.: Mercury cycling in a small Hawaiian estuary. Water Resour. Res. Cent. Tech. Memor. Rep. Univ. Hawaii 42, 1–38 (1974). (Cited from Luoma and Jenne, 1975)
Luoma, S. N.: The dynamics of biologically available mercury in a small estuary. Estuar. cstl mar. Sci. 5, 643–652 (1977)
Luoma, S. N. and G. W. Bryan: Factors controlling the availability of sediment-bound lead to the estuarine bivalve Scrobicularia plana. J. mar. biol. Ass. U.K. 58, 793–802 (1978)
Luoma, S. N. and G. W. Bryan: A statistical study of environmental factors controlling concentrations of heavy metals in the burrowing bivalve Scrobicularia plana and the polychaete Nereis diversicolor. Estuar. cstl Shelf Sci. 15, 95–108 (1982)
Luoma S. N. and E. A. Jenne: Factors affecting the availability of sediment-bound cadmium to the estuarine, deposit feeding clam, Macoma balthica. Proc. 4th natn. Symp. Radioecol. (Oregon State University, May 12–14, 1975) 283–290 (1975). (Ed. by C. E. Cushing Jr. et al., Pennsylvania: Dowden, Hutchisson & Ross Inc.)
Negilski, D. S.: Incidence of heavy metal contamination in Port Phillip Bay and Westernport. A critique of selected documents and recommendations for future research and monitoring investigations. Victoria, Australia: Ministry for Conservation 1976 (Environmental Studies Program, Report T605/ESS 132)
Negilski, D. S., M. Ahsanullah and M. C. Mobley: Toxicity of zinc, cadmium and copper to the shrimp Callianassa australiensis. II. Effects of paired and triad combinations of metals. Mar. Biol. 64, 305–309 (1981)
Nimmo, D. R., D. V. Lightner and L. H. Bahner: Effects of cadmium on the shrimp, Penaeus duorarum, Palaemonetes pugio and Palaemonetes vulgaris. In: Physiological responses of marine biota to pollutants, pp 131–183. Ed. by F. J. Vernberg, A. Calabrese, F. P. Thurberg and W. B. Vernberg. New York, San Francisco, London: Academic Press, Inc. 1977
Small, L. F., S. W. Fowler and S. Keckes. Flux of zinc through a macroplanktonic crustacean. Radioactivity in the sea, Vienna: International Atomic Energy Agency 1973
Spotte, S. H.: Fish and invertebrate culture. Water management in closed systems. 145 pp. New York: Wiley-Interscience 1970
Ueda, T., R. Nakamura and Y. Suzuki: Comparisons of 115Cd accumulation from sediment and seawater by polychaete worms. Bull. Jap. Soc. scient. Fish. 42, 299–306 (1976)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by G. F. Humphrey, Sydney
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ahsanullah, M., Mobley, M.C. & Negilski, D.S. Accumulation of cadmium from contaminated water and sediment by the shrimp Callianassa australiensis . Mar. Biol. 82, 191–197 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00394102
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00394102