Abstract
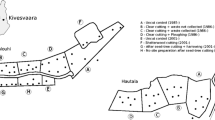
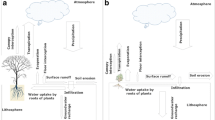
Stream and land salinisation brought about by rising groundwater levels due to the clearing of native forest for agricultural development is a major environmental and resource problem in Western Australia and several other semi-arid regions of the world. One potential approach to reclamation with simultaneous economic benefits is agroforestry. To determine the effects of agroforestry on groundwater level and salinity, two experiments were carried out in Western Australia. In Experiment I a pinius-pasture agroforestry covering 58% of the cleared area with final stem densities of 75–225 stems ha−1 was successful in lowering a saline groundwater table. Over the period 1979–1989, groundwater levels decliend by 1.0 m relative to groundwater levels beneath a nearby pasture site. In Experiment II the eucalyptus-pasture agroforestry covering 57% of farmland at a final density of 150–625 stems ha−1 was found to successfully lower the yearly minimum groundwater level by 2.0 m relative to a pasture site over seven years. The salinity of the groundwater beneath agroforestry decreased by 9% and 6% for Experiments I and II respectively, which was contrary to some early expectations. The design of agroforestry for controlling saline groundwater tables needs further evaluation with respect to species, stem densities and proportion of cleared area planted.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson GW and Moore RM (1987) Productivity in the first seven years of a Pinus radiata annual pasture agroforest in Western Australia. Aust. J. Exp. Agric. 27: 231–238
Anderson GW, Moore RM and Jenkins PJ (1988) The integration of pasture, livestock and widely-spaced pine in south-west Western Australia. Agroforestry Systems 6: 195–211
Batini FE, Anderson GW and Moore RM (1983) The practice of agroforestry in Australia. In: Hannaway DB, ed, Foothills for Food and Forest, Symposium Series No. 2, Oregon State University College of Agricultural Science, Oregon, pp 223–246
Conacher A (1982) Dryland agriculture and secondary salinity. In: Hanley W and Cooper M, eds, Man and the Australian Environment, McGraw-Hill, Sydney, pp 113–125
Dudal R and Purnell MF (1986) Land resources: salt affected soils. Reclam Reveg Res 5: 1–9
Engel R (1987) Agroforestry management of saltland using salt tolerant eucalypts. Trees and Nat Resour 28: 12–13
Luke GJ, Burke KL and O'Brien TM (1988) Evaporation data for Western Australia. W. A. Dept. of Agric., Div. Resour. Manag., Tech. Pap. No. 65, 29 pp
Malajczuk G, Morrison D, Havel J, Anderson G and Moore R (1984) An economic study of agroforestry in the Manjimup region, Western Australia. Tech. Paper No. 10, Forest Dept. W. A., 35 pp
Morris JD and Thomson LAJ (1983) The role of trees in dryland salinity control. Proc R Soc Vic 95: 123–131
Mulqueen J and Kirkham D (1972) Leaching a surface layer of sodium chloride into the drains in a sand tank model. Soil Sci Soc Amer Proc 36: 3–9
Peck AJ (1973) Analysis of multi-dimensional leaching. Soil Sci Soc Amer Proc 37: p 320
Peck AJ, Thomas JF and Williamson DR (1983) Salinity issues: effects of man on salinity in Australia. Water 2000 Consultants Rep. No. 8, Aust. Gov. Publ. Serv., 78 pp
Peck AJ and Williamson DR (1987) Effects of forest clearing on groundwater. J Hydrol 94: 47–65
Pittock AB (1988) Actual and anticipated changes in Australia's climate. In: Pearman GI ed, Greenhouse — Planning for Climate Change, CSIRO, Melb. Aust., pp 35–51
Schofield NJ (1990) Determining reforestation area and distribution for salinity control. J Hydrol Sci 35: 1–19
Schofield NJ, Loh IC, Scott PR, Bartle JR, Ritson P, Bell RW, Borg H, Anson B and Moore R (1989) Vegetation strategies to reduce stream salinities of water resource catchments in south-west Western Australia. Water Authority W. A., Rep. No. WS 33, 98 pp
Schofield NJ and Ruprecht JK (1989) Regional analysis of stream salinisation in south west Western Australia. J Hydrol 112: 18–38
Schofield NJ, Ruprecht JK and Loh IC (1988) The impact of agricultural development on the salinity of surface water resources of south-west Western Australia. Water Authority of W. A., Rep. No. WS 27, 69 pp
Sharma ML, Barron RJW and Fernie MS (1987) Areal distribution of infiltration parameters and some soil physical properties in lateritic catchments. J Hydrol 94: 109–127
Western Australian Water Resources Council (1986) Water Resource Perspectives Western Australia: Report No. 2. Water Resources and Water Use, Summary of Data for the 1985 National Survey. Publ. No. WRC 7/86, 164 pp
Williamson DR (1986) The hydrology of salt affected soils in Australia. Reclam Reveg Res 5: 181–196
Williamson DR, Stokes RA and Ruprecht JK (1987) Response of input and output of water and chloride to clearing for agriculture. J Hydrol 94: 1–28
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bari, M.A., Schofield, N.J. Effects of agroforestry-pasture associations on groundwater level and salinity. Agroforest Syst 16, 13–31 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00053194
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00053194