
Collection
Modelling and assessing energy and climate strategies for Switzerland
- Submission status
- Closed
Climate change has become a focal point of the societal and political debate in many countries. Economists have contributed to this debate by assessing the climate problem as well as different proposals for climate policy. A central part of this work is to analyse the economic consequences of different emission scenarios.
In this context, we are happy to introduce the special issue on modelling climate policy in Switzerland. Under the umbrella of the Swiss Energy Modelling Platform (SEMP), five modelling teams have contributed to assessing the economic and technological consequences of reaching Swiss emission targets up to 2050. Working with harmonised business-as-usual assumptions, most models find that the climate targets can be reached at modest aggregate costs. Also, most models find that a cost-effective approach towards reducing greenhouse gas emissions relies on replacing fossil fuels with electricity and thus do not recommend a decrease in electricity use, as envisioned in the Swiss Energy Strategy 2050.
In addition to these contributions to the current policy debate, the multi-model comparison facilitated by SEMP helps to identify common trends and differences across models that stem from different modelling frameworks and parametrizations and thus to gain more robust insights to what extent the choice of a modelling framework shapes the results of the analysis.
Editors
-
Adriana Marcucci
ETH Zürich, Switzerland
-
Florian Landis
ZHAW School of Management and Law, Switzerland
-
Frank Krysiak
University of Basel, Switzerland
Articles (5 in this collection)
-

-
Welfare effects of technology-based climate policies in liberalized electricity markets: seeing beyond total system cost
Authors
- Sophie Maire
- Philippe Thalmann
- Frank Vöhringer
- Content type: Original article
- Open Access
- Published: 13 September 2019
- Article: 13

-
Lowering CO2 emissions in the Swiss transport sector
Authors
- Philippe Thalmann
- Marc Vielle
- Content type: Original Article
- Open Access
- Published: 13 September 2019
- Article: 10

-
Cost distribution and equity of climate policy in Switzerland
Authors
- Florian Landis
- Content type: Original article
- Open Access
- Published: 13 September 2019
- Article: 11
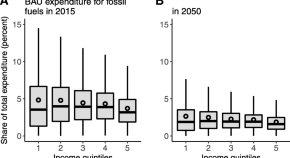
-
Multi-model comparison of Swiss decarbonization scenarios
Authors (first, second and last of 5)
- Florian Landis
- Adriana Marcucci
- Lucas Bretschger
- Content type: Original Article
- Open Access
- Published: 13 September 2019
- Article: 12



