Abstract
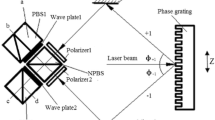
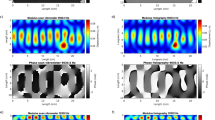
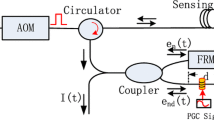
We proposed novel phase-shifting interferometry using a fiber-optic vibration sensor. The Doppler shift in the coiled fiber caused by vibrations can be used to detect the vibrations by using a fiber-optic interferometer. The principle can be applied to induce phase shifts. While applying vibrations to the coiled fiber at various vibration frequencies, we recorded the variations in the interference fringes. The interference fringe moved to longer wavelengths when a vibration frequency was increased from 38.00 to 38.40 kHz. Phase variations of 3.59 rad/kHz were obtained. The ability to accurately control the phase by using the vibrations in the coiled fiber was demonstrated by the elimination of the depth degeneracy using the complex signal generated by the phase-shifted interference fringes. Using vibrations to control phase shifting can be an acceptable alternative to conventional methods and can be applied to resolve the depth ambiguity in Fourier domain optical coherence tomography.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
C. T. Farrell and M. A. Player, Meas. Sci. Technol. 5, 648 (1994).
H. J. Tiziani, Opt. Quantum Electron. 21, 253 (1989).
Y. Surrel, Appl. Opt. 32, 3598 (1993).
R. N. Shagam and J. C. Wyant, Appl. Opt. 17, 3034 (1978).
G. Hausler and M. W. Lindner, J. Biomed. Opt. 3, 21 (1998).
A. F. Fercher, W. Drexler, C. K. Hitzenberger and T. Lasser, Rep. Prog. Phys. 66, 239 (2003).
R. W. Wang, Appl. Phys. Lett. 90, 054103 (2007).
Y. Yasuno, S. Makita, T. Endo, G. Aoki, M. Itoh and T. Yatagai, Appl. Opt. 45, 1861 (2006).
R. A. Leitgeb, R. Michaely, T. Lasser and S. C. Sekhar, Opt. Lett. 32, 3453 (2007).
E. J. Min, J. G. Shin, J. H. Lee, Y. Yasuno and B. H. Lee, Opt. Lett. 37, 3105 (2012).
K. Kageyama, H. Murayama, I. Ohsawa, M. Kanai, K. Nagata et al., Smart Mater. Struct. 14, S52 (2005).
K. Kageyama, H. Murayama, K. Uzawa, I. Ohsawa, M. Kanai et al., J. Lightwave Technol. 24, 1768 (2006).
H. J. Ma, Y. Shin and E. S. Choi, New Phys.: Sae Mulli 60, 817 (2010).
S. S. Lee, J. H. Kim and E. S. Choi, New Phys.: Sae Mulli 65, 1028 (2015).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, S.S., Kim, J.H. & Choi, E.S. Phase shifting interferometry based on a vibration sensor - feasibility study on elimination of the depth degeneracy. Journal of the Korean Physical Society 70, 687–692 (2017). https://doi.org/10.3938/jkps.70.687
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3938/jkps.70.687