Abstract
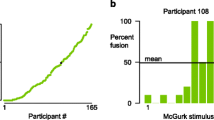
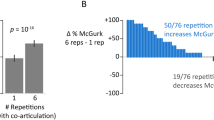
In the McGurk effect, incongruent auditory and visual syllables are perceived as a third, completely different syllable. This striking illusion has become a popular assay of multisensory integration for individuals and clinical populations. However, there is enormous variability in how often the illusion is evoked by different stimuli and how often the illusion is perceived by different individuals. Most studies of the McGurk effect have used only one stimulus, making it impossible to separate stimulus and individual differences. We created a probabilistic model to separately estimate stimulus and individual differences in behavioral data from 165 individuals viewing up to 14 different McGurk stimuli. The noisy encoding of disparity (NED) model characterizes stimuli by their audiovisual disparity and characterizes individuals by how noisily they encode the stimulus disparity and by their disparity threshold for perceiving the illusion. The model accurately described perception of the McGurk effect in our sample, suggesting that differences between individuals are stable across stimulus differences. The most important benefit of the NED model is that it provides a method to compare multisensory integration across individuals and groups without the confound of stimulus differences. An added benefit is the ability to predict frequency of the McGurk effect for stimuli never before seen by an individual.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Angelaki, D. E., Gu, Y., & DeAngelis, G. C. (2009). Multisensory integration: psychophysics, neurophysiology, and computation. Current Opinion in Neurobiology, 19(4), 452–458. doi:10.1016/j.conb.2009.06.008
Beauchamp, M. S., Nath, A. R., & Pasalar, S. (2010). fMRI-Guided transcranial magnetic stimulation reveals that the superior temporal sulcus is a cortical locus of the McGurk effect. Journal of Neuroscience, 30(7), 2414–2417. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4865-09.2010
Bebko, J. M., Schroeder, J. H., & Weiss, J. A. (2014). The McGurk effect in children with autism and Asperger syndrome. Autism Research, 7(1), 50–59. doi:10.1002/aur.1343
Bejjanki, V. R., Clayards, M., Knill, D. C., & Aslin, R. N. (2011). Cue integration in categorical tasks: insights from audio-visual speech perception. PLoS ONE, 6(5), e19812. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0019812
Dinstein, I., Heeger, D. J., Lorenzi, L., Minshew, N. J., Malach, R., & Behrmann, M. (2012). Unreliable evoked responses in autism. Neuron, 75(6), 981–991. doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2012.07.026
Gelman, A., & Hill, J. (2007). Data analysis using regression and multilevel/hierarchical models. Cambridge; New York: Cambridge University Press.
Geschwind, D. H., & Levitt, P. (2007). Autism spectrum disorders: developmental disconnection syndromes. Current Opinion in Neurobiology, 17(1), 103–111. doi:10.1016/j.conb.2007.01.009
Green, K. P., Kuhl, P. K., Meltzoff, A. N., & Stevens, E. B. (1991). Integrating speech information across talkers, gender, and sensory modality: female faces and male voices in the McGurk effect. Perception and Psychophysics, 50(6), 524–536.
Irwin, J. R., Tornatore, L. A., Brancazio, L., & Whalen, D. H. (2011). Can children with autism spectrum disorders "hear" a speaking face? Child Development, 82(5), 1397–1403. doi:10.1111/j.1467-8624.2011.01619.x
Jiang, J., & Bernstein, L. E. (2011). Psychophysics of the McGurk and other audiovisual speech integration effects. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Perception and Performance, 37(4), 1193–1209. doi:10.1037/a0023100
Keil, J., Muller, N., Ihssen, N., & Weisz, N. (2012). On the variability of the McGurk effect: audiovisual integration depends on prestimulus brain states. Cerebral Cortex, 22(1), 221–231. doi:10.1093/cercor/bhr125
Knill, D. C., & Pouget, A. (2004). The Bayesian brain: the role of uncertainty in neural coding and computation. Trends in Neurosciences, 27(12), 712–719. doi:10.1016/j.tins.2004.10.007
Kording, K. P., Beierholm, U., Ma, W. J., Quartz, S., Tenenbaum, J. B., & Shams, L. (2007). Causal inference in multisensory perception. PLoS ONE, 2(9), e943. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0000943
Ma, W. J., Zhou, X., Ross, L. A., Foxe, J. J., & Parra, L. C. (2009). Lip-reading aids word recognition most in moderate noise: a Bayesian explanation using high-dimensional feature space. PLoS ONE, 4(3), e4638. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0004638
MacDonald, J., & McGurk, H. (1978). Visual influences on speech perception processes. Perception and Psychophysics, 24(3), 253–257.
Magnotti, J. F., Ma, W. J., & Beauchamp, M. S. (2013). Causal inference of asynchronous audiovisual speech. Frontiers in Psychology, 4, 798.
Mainen, Z. F., & Sejnowski, T. J. (1995). Reliability of spike timing in neocortical neurons. Science, 268(5216), 1503–1506.
Massaro, D. W. (1998). Perceiving talking faces : from speech perception to a behavioral principle. Cambridge, Mass.: MIT Press.
McGurk, H., & MacDonald, J. (1976). Hearing lips and seeing voices. Nature, 264(5588), 746–748.
Mongillo, E. A., Irwin, J. R., Whalen, D. H., Klaiman, C., Carter, A. S., & Schultz, R. T. (2008). Audiovisual processing in children with and without autism spectrum disorders. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 38(7), 1349–1358. doi:10.1007/s10803-007-0521-y
Munhall, K. G., Gribble, P., Sacco, L., & Ward, M. (1996). Temporal constraints on the McGurk effect. Perception & Psychophysics, 58(3), 351–362.
Nahorna, O., Berthommier, F., & Schwartz, J. L. (2012). Binding and unbinding the auditory and visual streams in the McGurk effect. Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 132(2), 1061–1077. doi:10.1121/1.4728187
Nath, A. R., & Beauchamp, M. S. (2012). A neural basis for interindividual differences in the McGurk effect, a multisensory speech illusion. NeuroImage, 59(1), 781–787. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2011.07.024
Omata, K., & Mogi, K. (2008). Fusion and combination in audio-visual integration. Proceedings of the Royal Society A: Mathematical Physical and Engineering Science, 464(2090), 319–340.
R Core Team. (2012). R: A language and environment for statistical computing. Vienna, Austria: R Foundation for Statistical Computing.
Saalasti, S., Katsyri, J., Tiippana, K., Laine-Hernandez, M., von Wendt, L., & Sams, M. (2012). Audiovisual speech perception and eye gaze behavior of adults with asperger syndrome. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 42(8), 1606–1615. doi:10.1007/s10803-011-1400-0
Schwartz, J. L. (2010). A reanalysis of McGurk data suggests that audiovisual fusion in speech perception is subject-dependent. Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 127(3), 1584–1594. doi:10.1121/1.3293001
Seilheimer, R. L., Rosenberg, A., & Angelaki, D. E. (2014). Models and processes of multisensory cue combination. Current Opinion in Neurobiology, 25, 38–46.
Sekiyama, K. (1997). Cultural and linguistic factors in audiovisual speech processing: the McGurk effect in Chinese subjects. Perception and Psychophysics, 59(1), 73–80.
Shams, L., & Beierholm, U. R. (2010). Causal inference in perception. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 14(9), 425–432. doi:10.1016/j.tics.2010.07.001
Stevenson, R. A., Siemann, J. K., Schneider, B. C., Eberly, H. E., Woynaroski, T. G., Camarata, S. M., & Wallace, M. T. (2014a). Multisensory temporal integration in autism spectrum disorders. Journal of Neuroscience, 34(3), 691–697. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3615-13.2014
Stevenson, R. A., Siemann, J. K., Woynaroski, T. G., Schneider, B. C., Eberly, H. E., Camarata, S. M., & Wallace, M. T. (2014b). Brief report: Arrested development of audiovisual speech perception in autism spectrum disorders. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 44(6), 1470–1477. doi:10.1007/s10803-013-1992-7
Stevenson, R. A., Zemtsov, R. K., & Wallace, M. T. (2012). Individual differences in the multisensory temporal binding window predict susceptibility to audiovisual illusions. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Perception and Performance, 38(6), 1517–1529. doi:10.1037/a0027339
Taylor, N., Isaac, C., & Milne, E. (2010). A comparison of the development of audiovisual integration in children with autism spectrum disorders and typically developing children. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 40(11), 1403–1411. doi:10.1007/s10803-010-1000-4
Tremblay, C., Champoux, F., Voss, P., Bacon, B. A., Lepore, F., & Theoret, H. (2007). Speech and non-speech audio-visual illusions: a developmental study. PLoS ONE, 2(1), e742. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0000742
Woynaroski, T. G., Kwakye, L. D., Foss-Feig, J. H., Stevenson, R. A., Stone, W. L., & Wallace, M. T. (2013). Multisensory Speech Perception in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorders. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders. doi:10.1007/s10803-013-1836-5
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by NIH R01NS065395 to MSB. We thank Wei Ji Ma and xaq pitkow for helpful comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Magnotti, J.F., Beauchamp, M.S. The noisy encoding of disparity model of the McGurk effect. Psychon Bull Rev 22, 701–709 (2015). https://doi.org/10.3758/s13423-014-0722-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3758/s13423-014-0722-2