Abstract
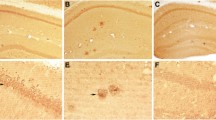
Transgenic mouse models with knock-in (KI) expression of human mutant amyloid precursor protein (APP) and/or human presenilin 1 (PS1) may be helpful to elucidate the cellular consequences of APP and PS1 misprocessing in the aging brain. Age-related alterations in total numbers of neurons and in numbers of synaptophysin-immunoreactive presynaptic boutons (SIPB), as well as the amyloid plaque load were analyzed in the hippocampal dentate gyrus (DG), CA3, and CA1-2 of 2- and 10-month-old APPSL/PS1 homozygous KI, APPSL (expressing human mutant APP751 carrying the Swedish [K670N/M671L] and London [V717I] mutations under Thy-1 promoter), and PS1 homozygous KI mice (expressing human PS1 mutations [M233T and L235P]). APPSL/PS1 homozygous KI mice, but neither APPSL mice nor PS1 homozygous KI mice, showed substantial agerelated loss of neurons (−47.2%) and SIPB (−22.6%), specifically in CA1-2. PS1 homozygous KI mice showed an age-related increase in hippocampal granule cell numbers (+37.9%). Loss of neurons and SIPB greatly exceeded the amount of local extracellular Aβ aggregation and astrocytes, whereas region-specific accumulation of intraneuronal Aβ preceded neuron and synapse loss. An age-related increase in the ratio of SIPB to neuron numbers in CA1-2 of APPSL/PS1 homozygous KI mice was suggestive of compensatory synaptic plasticity. These findings indicate a region-selectivity in intra- and extraneuronal Aβ accumulation in connection with neuron and synapse loss in the hippocampus of APPSL/PS1 homozygous KI mice.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Scheff S.W., Price D.A., Schmitt F.A., Scheff M.A., Mufson E.J., Synaptic loss in the inferior temporal gyrus in mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease, J. Alzheimers Dis., 2011, 24, 547–557
Selkoe D.J., Alzheimer’s disease is a synaptic failure, Science, 2002, 298, 789–791
Walsh D.M., Selkoe D.J., Deciphering the molecular basis of memory failure in Alzheimer’s disease, Neuron, 2004, 44, 181–193
Yu W., Lu B., Synapses and dendritic spines as pathogenic targets in Alzheimer’s disease, Neural Plast., 2012, 2012, 1–8
Tam J.H., Pasternak S.H., Amyloid and Alzheimer’s disease: inside and out, Can. J. Neurol. Sci., 2012, 39, 286–298
Luque F.A., Jaffe S.L., The molecular and cellular pathogenesis of dementia of the Alzheimer’s type an overview, Int. Rev. Neurobiol., 2009, 84, 151–165
Fjell A.M., Walhovd K.B., Neuroimaging results impose new views on Alzheimer’s disease-the role of amyloid revised, Mol. Neurobiol., 2012, 1–20
Hardy J., Selkoe D.J., The amyloid hypothesis of Alzheimer’s disease: progress and problems on the road to therapeutics, Science, 2002, 297, 353–356
Mucke L., Masliah E., Yu G.Q., Mallory M., Rockenstein E.M., Tatsuno G., et al., High-level neuronal expression of abeta 1–42 in wild-type human amyloid protein precursor transgenic mice: synaptotoxicity without plaque formation, J. Neurosci., 2000, 20, 4050–4058
Klein W.L., Krafft G.A., Finch C.E., Targeting small Abeta oligomers: the solution to an Alzheimer’s disease conundrum?, Trends Neurosci., 2001, 24, 219–224
Schmitz C., Rutten B.P., Pielen A., Schafer S., Wirths O., Tremp G., et al., Hippocampal neuron loss exceeds amyloid plaque load in a transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease, Am. J. Pathol., 2004, 164, 1495–1502
Boncristiano S., Calhoun M.E., Howard V., Bondolfi L., Kaeser S.A., Wiederhold K.H., et al., Neocortical synaptic bouton number is maintained despite robust amyloid deposition in APP23 transgenic mice, Neurobiol. Aging, 2005, 26, 607–613
Dickey C.A., Loring J.F., Montgomery J., Gordon M.N., Eastman P.S., Morgan D., Selectively reduced expression of synaptic plasticityrelated genes in amyloid precursor protein + presenilin-1 transgenic mice, J. Neurosci., 2003, 23, 5219–5226
Hsia A.Y., Masliah E., McConlogue L., Yu G.Q., Tatsuno G., Hu K., et al., Plaque-independent disruption of neural circuits in Alzheimer’s disease mouse models, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 1999, 96, 3228–3233
Rutten B.P., Van der Kolk N.M., Schafer S., van Zandvoort M.A., Bayer T.A., Steinbusch H.W., et al., Age-related loss of synaptophysin immunoreactive presynaptic boutons within the hippocampus of APP751SL, PS1M146L, and APP751SL/PS1M146L transgenic mice, Am. J. Pathol., 2005, 167, 161–173
West M.J., Bach G., Soderman A., Jensen J.L., Synaptic contact number and size in stratum radiatum CA1 of APP/PS1DeltaE9 transgenic mice, Neurobiol. Aging, 2009, 30, 1756–1776
Nizzari M., Thellung S., Corsaro A., Villa V., Pagano A., Porcile C., et al., Neurodegeneration in Alzheimer disease: role of amyloid precursor protein and presenilin 1 intracellular signaling, J. Toxicol., 2012, 2012, 1–13
Revett T.J., Baker G.B., Jhamandas J., Kar S., Glutamate system, amyloid β peptides and tau protein: functional interrelationships and relevance to Alzheimer disease pathology, J. Psychiatry Neurosci., 2013, 38, 6–23
Casas C., Sergeant N., Itier J.M., Blanchard V., Wirths O., van der Kolk N., et al., Massive CA1/2 neuronal loss with intraneuronal and N-terminal truncated Abeta42 accumulation in a novel Alzheimer transgenic model, Am. J. Pathol., 2004, 165, 1289–1300
Wirths O., Breyhan H., Schafer S., Roth C., Bayer T.A., Deficits in working memory and motor performance in the APP/PS1ki mouse model for Alzheimer’s disease, Neurobiol. Aging, 2008, 29, 891–901
Wirths O., Weis J., Szczygielski J., Multhaup G., Bayer T.A., Axonopathy in an APP/PS1 transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease, Acta Neuropathol., 2006, 111, 312–319
Takahashi H., Brasnjevic I., Rutten B.P., Van Der Kolk N., Perl D.P., Bouras C., et al., Hippocampal interneuron loss in an APP/PS1 double mutant mouse and in Alzheimer’s disease, Brain Struct. Funct., 2010, 214, 145–160
Borchardt T., Camakaris J., Cappai R., Masters C.L., Beyreuther K., Multhaup G., Copper inhibits beta-amyloid production and stimulates the non-amyloidogenic pathway of amyloid-precursorprotein secretion, Biochem. J., 1999, 344, 461–467
Schmitz C., Hof P.R., Design-based stereology in neuroscience, Neuroscience, 2005, 130, 813–831
Franklin K., Paxinos G., The mouse brain in stereotaxic coordinates, Academic Press, San Diego, 1997
Van de Berg W.D., Blokland A., Cuello A.C., Schmitz C., Vreuls W., Steinbusch H.W., et al., Perinatal asphyxia results in changes in presynaptic bouton number in striatum and cerebral cortex-a stereological and behavioral analysis, J. Chem. Neuroanat., 2000, 20, 71–82
Heinonen O., Soininen H., Sorvari H., Kosunen O. Paljarvi L., Koivisto E., et al., Loss of synaptophysin-like immunoreactivity in the hippocampal formation is an early phenomenon in Alzheimer’s disease, Neuroscience, 1995, 64, 375–385
Terry R.D., Masliah E., Salmon D.P., Butters N., DeTeresa R., Hill R., et al., Physical basis of cognitive alterations in Alzheimer’s disease: synapse loss is the major correlate of cognitive impairment, Ann. Neurol, 1991, 30, 572–580
Ingelsson M., Fukumoto H., Newell K.L., Growdon J.H., Hedley-Whyte E.T., Frosch M.P., et al., Early Aβ accumulation and progressive synaptic loss, gliosis, and tangle formation in AD brain, Neurology, 2004, 62, 925–931
Clare R., King V.G., Wirenfeldt M., Vinters H.V., 2010, Synapse loss in dementias, J. Neurosci. Res., 88, 2083–2090
Cotel M.C., Bayer T.A., Wirths O., Age-dependent loss of dentate gyrus granule cells in APP/PS1KI mice, Brain Res., 2008, 1222, 207–213
Breyhan H., Wirths O., Duan K., Marcello A., Rettig J., Bayer T.A., APP/PS1KI bigenic mice develop early synaptic deficits and hippocampus atrophy, Acta Neuropathol., 2009, 117, 677–685
Tomiyama T., Matsuyama S., Iso H., Umeda T., Takuma H., Ohnishi K., et al., A mouse model of amyloid β oligomers: their contribution to synaptic alteration, abnormal tau phosphorylation, glial activation, and neuronal loss in vivo, J. Neurosci., 2010, 30, 4845–4856
Sanchez-Varo R., Trujillo-Estrada L., Sanchez-Mejias E., Torres M., Baglietto-Vargas D., Moreno-Gonzalez I., et al., Abnormal accumulation of autophagic vesicles correlates with axonal and synaptic pathology in young Alzheimer’s mice hippocampus, Acta Neuropathol., 2012, 1–18
Irizarry M.C., Soriano F., McNamara M., Page K.J., Schenk D., Games D., et al., Abeta deposition is associated with neuropil changes, but not with overt neuronal loss in the human amyloid precursor protein V717F (PDAPP) transgenic mouse, J. Neurosci., 1997, 17, 7053–7059
Calhoun M.E., Wiederhold K.H., Abramowski D., Phinney A.L., Probst A., Sturchler-Pierrat C., et al., Neuron loss in APP transgenic mice, Nature, 1998, 395, 755–756
Takeuchi A., Irizarry M.C., Duff K., Saido T.C., Hsiao Ashe K., Hasegawa M., et al., Age-related amyloid beta deposition in transgenic mice overexpressing both Alzheimer mutant presenilin 1 and amyloid beta precursor protein Swedish mutant is not associated with global neuronal loss, Am. J. Pathol., 2000, 157, 331–339
Dickson D.W., Building a more perfect beast: APP transgenic mice with neuronal loss, Am. J. Pathol., 2004, 164, 1143–1146
Howlett D.R., Bowler K., Soden P.E., Riddell D., Davis J.B., Richardson J.C., et al., Abeta deposition and related pathology in an APP x PS1 transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease, Histol. Histopathol., 2008, 23, 67–76
Van Broeck B., Vanhoutte G., Pirici D., Van Dam D., Wils H., Cuijt I., et al., Intraneuronal amyloid beta and reduced brain volume in a novel APP T714I mouse model for Alzheimer’s disease, Neurobiol. Aging, 2008, 29, 241–252
Elder G.A., Gama Sosa M.A., De Gasperi R., Dickstein D.L., Hof P.R., Presenilin transgenic mice as models of Alzheimer’s disease, Brain Struct. Funct., 2010, 214, 127–143
Mukaetova-Ladinska E.B., Garcia-Siera F., Hurt J., Gertz H.J., Xuereb J.H., Hills R., et al., Staging of cytoskeletal and beta-amyloid changes in human isocortex reveals biphasic synaptic protein response during progression of Alzheimer’s disease, Am. J. Pathol., 2000, 157, 623–636
Counts S.E., Nadeem M., Lad S.P., Wuu J., Mufson E.J., Differential expression of synaptic proteins in the frontal and temporal cortex of elderly subjects with mild cognitive impairment, J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol., 2006, 65, 592–601
Bell K.F., Bennett D.A., Cuello A.C., Paradoxical upregulation of glutamatergic presynaptic boutons during mild cognitive impairment, J. Neurosci., 2007, 27, 10810–10817
Akram A., Christoffel D., Rocher A.B., Bouras C., Kovari E., Perl D.P., et al., Stereologic estimates of total spinophilin-immunoreactive spine number in area 9 and the CA1 field: relationship with the progression of Alzheimer’s disease, Neurobiol. Aging, 2008, 29, 1296–1307
Bronfman F.C., Moechars D., Van Leuven F., Acetylcholinesterasepositive fiber deafferentation and cell shrinkage in the septohippocampal pathway of aged amyloid precursor protein london mutant transgenic mice, Neurobiol. Dis., 2000, 7, 152–168
Briones T.L., Suh E., Jozsa L., Rogozinska M., Woods J., Wadowska M., Changes in number of synapses and mitochondria in presynaptic terminals in the dentate gyrus following cerebral ischemia and rehabilitation training, Brain Res., 2005, 1033, 51–57
DeKosky S.T., Scheff S.W., Styren S.D., Structural correlates of cognition in dementia: quantification and assessment of synapse change, Neurodegeneration, 1996, 5, 417–421
Seeger G., Gärtner U., Ueberham U., Rohn S., Arendt T., FAD-mutation of APP is associated with a loss of its synaptotrophic activity, Neurobiol. Dis., 2009, 35, 258–263
Dong H., Martin M.V., Chambers S., Csernansky J.G., Spatial relationship between synapse loss and β-amyloid deposition in Tg2576 mice, J. Comp. Neurol., 2006, 500, 311–321
Hu L., Wong T.P., Cote S.L., Bell K.F., Cuello A.C., The impact of Abetaplaques on cortical cholinergic and non-cholinergic presynaptic boutons in alzheimer’s disease-like transgenic mice, Neuroscience, 2003, 121, 421–432
Savage M.J., Lin Y.G., Ciallella J.R., Flood D.G., Scott R.W., Activation of c-Jun N-terminal kinase and p38 in an Alzheimer’s disease model is associated with amyloid deposition, J. Neurosci., 2002, 22, 3376–3385
Gruart A., Lopez-Ramos J.C., Munoz M.D., Delgado-Garcia J.M., Aged wild-type and APP, PS1, and APP + PS1 mice present similar deficits in associative learning and synaptic plasticity independent of amyloid load, Neurobiol. Dis., 2008, 30, 439–450
Koo E.H., Kopan R., Potential role of presenilin-regulated signaling pathways in sporadic neurodegeneration, Nat. Med., 2004, Suppl. 10, S26–33
Morfini G., Pigino G., Beffert U., Busciglio J., Brady S.T., Fast axonal transport misregulation and Alzheimer’s disease, Neuromolecular Med., 2002, 2, 89–99
Gadadhar A., Marr R., Lazarov O., Presenilin-1 regulates neural progenitor cell differentiation in the adult brain, J. Neurosci., 2011, 31, 2615–2623
Lemmens M.A.M., Sierksma A.S.R., Rutten B.P.F., Dennissen F., Steinbusch H.W.M., Lucassen P.J., et al., Age-related changes of neuron numbers in the frontal cortex of a transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease, Brain Struct. Funct., 2011, 216, 227–237
van Tijn P., Kamphuis W., Marlatt M.W., Hol E.M., Lucassen P.J., Presenilin mouse and zebrafish models for dementia: focus on neurogenesis, Prog. Neurobiol., 2011, 93, 149–164
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
equal contributions
About this article
Cite this article
Brasnjevic, I., Lardenoije, R., Schmitz, C. et al. Region-specific neuron and synapse loss in the hippocampus of APPSL/PS1 knock-in mice. Translat.Neurosci. 4, 8–19 (2013). https://doi.org/10.2478/s13380-013-0111-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2478/s13380-013-0111-8