Abstract
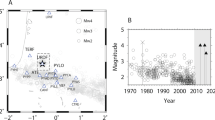
The Tehri Dam is located in a seismotectonically active region in the Indian Himalayan belt. This 260.5 m high dam has a live water storage of 2615 × 106 m3 and is capable of generating crustal deformation corresponding to water fluctuation. Filling of the reservoir started in October 2005. Seismic data around the dam between 2000 and 2010 shows that seismicity is corresponding to drawdown levels of the reservoir rather than to higher water levels. GPS data at twelve local benchmarks were collected from 2006 to 2008 during filling and drawdown reservoir levels. The velocity vectors show ground motion to be between ∼0.69–1.50 mm in the different filling-drawdown cycles with reference to the permanent station at Ghuttu. The motion appears to be inwards into the reservoir when the reservoir is filled and outwards when the reservoir is drained. This ground motion corresponds to elastic deformation and rebound due to effect of the oscillating water levels.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Banerjee, P., and R. Bürgmann (2002), Convergence across the northwest Himalaya from GPS measurements, Geophys. Res. Lett. 29,13, 30-1–30-4, DOI: 10.1029/2002GL015184.
Carder, D.S. (1945), Sesimic investigations in the Boulder Dam area, 1940–1944, and the influence of reservoir loading on local earthquake activity, Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 35,4, 175–192.
Gough, D.I. (1969), Incremental stress under a two-dimensional artificial lake, Can. J. Earth Sci. 6,5, 1067–1075, DOI: 10.1139/e69-109.
Gough, D.I., and W.I. Gough (1970a), Stress and deflection in the lithosphere near Lake Kariba — I, Geophys. J. Roy. Astron. Soc. 21,1, 65–78, DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-246X.1970.tb01767.x.
Gough, D.I., and W.I. Gough (1970b), Load-induced earthquakes at Lake Kariba — II, Geophys. J. Roy. Astron. Soc. 21,1, 79–101, DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-246X.1970.tb01768.x.
Gupta, H.K. (1992), Reservoir-Induced Earthquakes, Elsevier, Amsterdam.
Kayal, J.R. (2001), Microearthquake activity in some parts of the Himalaya and the tectonic model, Tectonophysics 339,3–4, 331–351, DOI: 10.1016/S0040-1951(01)00129-9.
Khattri, K.N., R. Chander, V.K. Gaur, I. Sarkar, and S. Kumar (1989), New seismological results on the tectonics of the Garhwal Himalaya, Proc. Indian Acad. Sci. — Earth Planet. Sci. 98,1, 91–109, DOI: 10.1007/BF02880378.
King, R.W., and Y. Bock (2002), Documentation for the GAMIT analysis software, release 10.32, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, USA.
Moreira, J.R., and A.D. Poole (1993), Hydropower and its constraints. In: T.B. Johansson, H. Kelly, A.K.N. Reddy, R.H. Williams (eds.), and L. Burnham (ex. ed.), Renewable Energy: Sources for Fuels and Electricity, Island Press, Washington D.C., 73–119.
Nawani, P.C., T.S. Pangtey, R. Sanwal, and J.S. Rawat (1990), On the continuation of construction stage geological investigations of Tehri Dam project on river Bhagirathi, Tehri (Garhwal) District, Uttar Pradesh, FS: 1988–1989, Geol. Surv. India, Progress Rep. No. 27, Accession No. NRO-S6484.
Powers, P.M., R.J. Lillie, and R.S. Yeats (1998), Structure and shortening of the Kangra and Dehra Dun reentrants, Sub-Himalaya, India, Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 110,8, 1010–1027, DOI: 10.1130/0016-7606(1998)110〈1010: SASOTK〉2.3.CO;2.
Simpson, D.W. (1976), Seismicity changes associated with reservoir loading, Eng. Geol. 10,2–4, 123–150, DOI: 10.1016/0013-7952(76)90016-8.
Simpson, D.W., W.S. Leith, and C.H. Scholz (1988), Two types of reservoirinduced seismicity, Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 78,6, 2025–2040.
Talwani, P. (1997), Seismotectonics of the Koyna-Warna area, India, Pure Appl. Geophys. 150,3–4, 511–550, DOI: 10.1007/s000240050091.
Valdiya, K.S. (1980), Geology of Kumaun Lesser Himalaya, Wadia Institute of Himalya Geology, Dehradun
Yadav, D.K., N. Kumar, and A. Paul (2009), Recent seismicity and stress pattern in NW Himalaya, J. Himalayan Geol. 30,2, 139–145.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Choudhury, S., Gautam, P.K. & Paul, A. Seismicity and reservoir induced crustal motion study around the Tehri Dam, India. Acta Geophys. 61, 923–934 (2013). https://doi.org/10.2478/s11600-013-0125-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2478/s11600-013-0125-1