Abstract
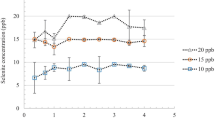
This paper reports the results of an optimisation study for a procedure to determine the total selenium and its inorganic species, Se(IV) and Se(VI) using atomic absorption spectrometry combined with hydride generation and in-situ trapping of the analyte on the inner walls of the graphite tube. With the use of the proposed modification, a detection limit (3σ) of 0.018 ng/ml is achieved. This paper presents exemplary results, according to the proposed procedure, for selenium determination in samples of marine water. The concentrations of selenium in the samples ranged from <0.02 ng/ml to 0.16ng/ml of Se(IV) and from <0.02 ng/ml to 0.10 ng/ml of Se(VI).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
D.L. Tsalev: “Vapor generation of electrothermal atomic absorption spectrometry?-Both!”, Spectrochim. Acta B, Vol. 55, (2000), pp. 917–933.
G. Drasch, L. Meyer, G. Kauert: “Application of the furnace atomic absorption method for the detection of arsenic in biological samples by means of the hydride technique”, Fresen. J. Anal. Chem., Vol. 304, (1980), pp. 141–142.
R.M. Camero and R.E. Sturgeon: “Hydride generation-electrostatic depositiongraphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometric determination of arsenic, selenium and antimony”, Spectrochim. Acta B, Vol. 52, (1999), pp. 753–762.
Z. De-qiang, S. Han-wen, Y. Li-li: “Detarmination of trace inorganic selenium in organoselenium (selenosugar) oral nutrition liquids by graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry with hydride generation”, Fresen. J. Anal. Chem., Vol. 359, (1997), pp. 492–496.
F. Laborda, J. Medrano, J.I. Cortes, J.M. Mir, J.R. Castillo: ”Comparison of palladium and zirconium treated graphite tubes for in-atomizer trapping of hydrogen selenide in hydride generation electrothermal atomization atomic absorption spectrometry”, Spectrochim. Acta B, Vol. 54, (1999), pp. 343–353.
P. Niedzielski, M. Siepak, J. Siepak: “Comparison of modifiers for determination of arsenic, antimony and selenium by absorption atomic spectrometry with atomization in a graphite tube or hydride generation and in-situ preconcentration in a graphite tube”, Microchem. J., Vol. 72, (2002), pp. 137–145.
R. Kalahne, G. Henrion, A. Hulanicki, S. Garbos, M. Walcerz: “Comparison of AAS with hydride concentration in a graphite furnace with other spectrometric techniques”, Spectrochim. Acta B, Vol. 52, (1997), pp. 1509–1516.
H. Matusiewicz and R.E. Sturgeon: “Atomic spectrometric detection of forming elements following in situ trapping within a graphite furnace”, Spectrochim. Acta B, Vol. 51, (1996) pp. 377–397.
H.O. Haug and Y. Liao: “Investigation of the automated determination of As, Sb and Bi by flow-injection hydride generation using in-situ trapping on stable coatings in graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry”, Fresen. J. Anal. Chem., Vol. 356, (1996), pp. 435–444.
M. Elsayed, E. Bjorn, W. Frech: “Optimisation of operating parameters for simultaneous multi-element determination of antimony, arsenic, bismuth and selenium by hydride generation, graphite atomiser sequestration atomic absorption spectrometry”, J. Anal. Atom Spectrom., Vol. 15, (2000), pp. 697–703.
J. Murphy, G. Shlemmer, I.L. Shuttler, P. Jones: “Simultaneous multi-element determination of hydride-forming elements by “in-atomiser trapping” electrotermal atomic absorption spectrometry on an iridium-coated graphite tube”, J. Anal. Atom Spectrom., Vol. 14, (1999), pp. 1593–1600.
J.Y. Cabon and W. Erler: “Determination of selenium species in seawater by flow injection hydride generation in situ trapping followed by electrothermal atomic absorption spectrometry”, Analyst, Vol. 123, (1998), pp. 1565–1569.
D.L. Tsalev, V.I. Slaveykovaa, L. Lampugnanib, A. D’Ulivob, R. Georgievac: “Permanent modification in electrothermal atomic absorption spectrometry-advances, anticipations and reality”, Spectrochim. Acta B, Vol. 55, (2000), pp. 473–490.
J.F. Tyson, N.G. Sundin, Ch.P. Hanna, S.A. McIntosh: “Determination of Se in urine by flow injection hydride generation electrothermal atomic absorption spectrometry with in-atomizer trapping”, Spectrochim. Acta B, Vol. 52, (1997), pp. 1773–1781.
J. Moreda-Piñeiro, C. Moscoso-Pérez, P. López-Mahza, S. Muniategui-Lorenzo, E. Fernández-Fernández and D. Prada-Rodrzguez: “Comparative study of different permanently-treated graphite tubes for the determination of As, Sb, and Se in natural waters by hydride generation-electrothermal atomic absorption spectrometry”, Anal. Chim. Acta, Vol. 431, (2001), pp. 157–165.
S. Garboś, M. Wałcerz, E. Bulska, A. Hulanicki: “Simultaneous determination of Se and As by hydride generation atomic absorption spectrometry with analyte concentration in a graphite furnace coated with zirconium”, Spectrochim. Acta B, Vol. 50, (1995), pp. 1669–1677.
J.L. Fischer: “Electrothermal atomization of palladium stabilized selenium in the presence of phosphate”, Spectrochim. Acta B, Vol. 57, (2002), pp. 525–533.
J.L. Fischer and C.J. Rademeyer: “Kinetics of selenium atomization in electrothermal atomization atomic absorption spectrometry (ETA-AAS).”, Spectrochim. Acta B, Vol. 57, (1998), pp. 549–567.
H.M. Ortner, E. Bulska, U. Rohr, G. Schlemmer, S. Weinbruch, B. Welz: “Modifiers and coatings in GFAAS-facts and fictions”, Proceedings of 4 th European Furnace Symposium, (1999), pp. 11–20.
P. Niedzielski, M. Siepak, J. Siepak, J. Przybyłek: “Determination of different forms of arsenic antimony and selenium in water samples using hydride generation”, Pol. J. Environ. Stud., Vol. 11, (2002), pp. 219–224.
R. Allabashi, J. Rendl, M. Grasserbauer: “Validation of three atomic absorption spectrometric methods for the determination of selenium-a comparative evaluation of performance characteristics”, Fresen. J. Anal. Chem., Vol. 357, (1997), pp. 1024–1028.
R.I. Ellis, N.G. Sundin, J.F. Tyson, S.A. McIntosh, Ch.P. Hanna, G. Carnrick: “Effect of high salt concetration of the determination of arsenic and selenium by flow injection hydride generation electrothermal atomic absorption spectrometry”, Analyst, Vol. 123, (1998), pp. 1697–1701.
T. Kubota, K. Suzuki, T. Okutani: “Determination of total selenium content in sediments and natural water by graphite furnace-atomic absorption spectroscopy after collection as a selenium (IV) complex on activated carbon”, Talanta, Vol. 42, (1995), pp. 949–955.
A. Larraya, M.G. Cobo-Fernandez, M.A. Palacios, C. Camara: “Preconcentration of inorganic selenium species (Se (IV) and Se (VI)) in an alumina filled microcolumn and on-line determination by hydride generation atomic absorption spectrometry”, Fresen. J. Anal. Chem., Vol. 350, (1994), pp. 667–670.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
About this article
Cite this article
Niedzielski, P., Siepak, M. & Dudzińska-Huczuk, B. Hydride generation atomic absorption spectrometry with insitu graphite tube trapping for the determination of Se (IV) and Se (VI) in baltic sea water samples. cent.eur.j.chem. 1, 314–324 (2003). https://doi.org/10.2478/BF02476232
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2478/BF02476232