Abstract
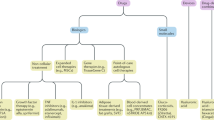
Osteoarthritis is common, incurable and difficult to treat. Because osteoarthritis is symptomatic only in a limited number of weight-bearing joints and lacks obvious extra-articular manifestations, it is well suited to local therapy administered by intra-articular injection. Several biologically based, local therapies of this type are either in clinical use or in development. Intra-articular injections of hyaluronic acid are widely used, but are highly controversial because their mode of action is unclear and clinical trials have provided contradictory results. The conclusions of meta-analyses are also discordant. An alternative therapy, based on the intra-articular injection of autologous conditioned serum, is used in Europe. This product, known as Orthokine®, is generated by incubating venous blood with etched glass beads. In this way, peripheral blood leukocytes produce elevated amounts of the interleukin-1 receptor antagonist and other anti-inflammatory mediators that are recovered in the serum. Considerable symptomatic relief has been reported in clinical trials of this product. Alternatively, instead of injecting a heterogeneous, incompletely characterized mixture of native molecules into the joint, it is possible to inject recombinant growth factors and cytokine antagonists. None of these are in routine clinical use, but promising preliminary human trials have been performed with insulin-like growth factor-1 and the interleukin-1 receptor antagonist. It is possible that sustained intra-articular production of such factors could be achieved by gene transfer. Although gene therapy for osteoarthritis is not yet a clinical reality, the first human trial should begin next year.




Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
The use of trade names is for product identification purposes only and does not imply endorsement.
References
Jordan KM, Arden NK, Doherty M, et al. EULAR Recommendations 2003: an evidence based approach to the management of knee osteoarthritis: report of a Task Force of the Standing Committee for International Clinical Studies Including Therapeutic Trials (ESCISIT). Ann Rheum Dis 2003; 62(12): 1145–55
Chadwick DJ, Goode J, editors. Osteoarthritic joint pain. Chichester (UK): Wiley, 2004
Sandell LJ, Aigner T. Articular cartilage and changes in arthritis. An introduction: cell biology of osteoarthritis. Arthritis Res 2001; 3(2): 107–13
Fukui N, Purple CR, Sandell LJ. Cell biology of osteoarthritis: the chondrocyte’s response to injury. Curr Rheumatol Rep 2001; 3(6): 496–505
Iannone F, Lapadula G. The pathophysiology of osteoarthritis. Aging Clin Exp Res 2003; 15(5): 364–72
van den Berg WB. Lessons from animal models of osteoarthritis. Curr Opin Rheumatol 2001; 13(5): 452–6
Alexander CJ. Idiopathic osteoarthritis: time to change paradigms? Skeletal Radiol 2004; 33(6): 321–4
Scott Simonet W. Genetics of primary generalized osteoarthritis. Mol Genet Metab 2002; 77(1-2): 31–4
Ulrich-Vinther M, Maloney MD, Schwarz EM, et al. Articular cartilage biology. J Am Acad Orthop Surg 2003; 11(6): 421–30
van den Berg WB. The role of cytokines and growth factors in cartilage destruction in osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis. Z Rheumatol 1999; 58(3): 136–41
Berenbaum F. Signaling transduction: target in osteoarthritis. Curr Opin Rheumatol 2004; 16(5): 616–22
Kuhn K, D’Lima DD, Hashimoto S, et al. Cell death in cartilage. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 2004; 12(1): 1–16
Aigner T, Kim HA, Roach HI. Apoptosis in osteoarthritis. Rheum Dis Clin North Am 2004; 30(3): 639–53, xi
Hardingham T, Tew S, Murdoch A. Tissue engineering: chondrocytes and cartilage. Arthritis Res 2002; 4Suppl. 3: S63–8
Balazs EA, Watson D, Duff IF, et al. Hyaluronic acid in synovial fluid: I. Molecular parameters of hyaluronic acid in normal and arthritis human fluids. Arthritis Rheum 1967; 10(4): 357–76
Balazs EA. Viscoelastic properties of hyaluronic acid and biological lubrication. Univ Mich Med Cent J 1968: 255-9
Butler J, Rydell NW, Balazs EA. Hyaluronic acid in synovial fluid: VI. Effect of intra-articular injection of hyaluronic acid on the clinical symptoms of arthritis in track horses. Acta Vet Scand 1970; 11(2): 139–55
Peyron JG, Balazs EA. Preliminary clinical assessment of Na-hyaluronate injection into human arthritic joints. Pathol Biol (Paris) 1974; 22(8): 731–6
Moreland LW. Intra-articular hyaluronan (hyaluronic acid) and hylans for the treatment of osteoarthritis: mechanisms of action. Arthritis Res Ther 2003; 5(2): 54–67
Lo GH, LaValley M, McAlindon T, et al. Intra-articular hyaluronic acid in treatment of knee osteoarthritis: a meta-analysis. JAMA 2003; 290(23): 3115–21
Wang CT, Lin J, Chang CJ, et al. Therapeutic effects of hyaluronic acid on osteoarthritis of the knee: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2004; 86-A(3): 538–45
Arrich J, Piribauer F, Mad P, et al. Intra-articular hyaluronic acid for the treatment of osteoarthritis of the knee: systematic review and meta-analysis. CMAJ 2005; 172(8): 1039–43
Bellamy N, Campbell J, Robinson V, et al. Viscosupplementation for the treatment of osteoarthritis of the knee. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2005; (2): CD005321
Smith MM, Ghosh P. The synthesis of hyaluronic acid by human synovial fibroblasts is influenced by the nature of the hyaluronate in the extracellular environment. Rheumatol Int 1987; 7(3): 113–22
Arend WP, Leung DY. IgG induction of IL-1 receptor antagonist production by human monocytes. Immunol Rev 1994; 139: 71–8
Meijer H, Reinecke J, Becker C, et al. The production of anti-inflammatory cytokines in whole blood by physico-chemical induction. Inflamm Res 2003; 52(10): 404–7
Wright-Carpenter T, Klein P, Schaferhoff P, et al. Treatment of muscle injuries by local administration of autologous conditioned serum: a pilot study on sportsmen with muscle strains. Int J Sports Med 2004; 25(8): 588–93
Wright-Carpenter T, Opolon P, Appell HJ, et al. Treatment of muscle injuries by local administration of autologous conditioned serum: animal experiments using a muscle contusion model. Int J Sports Med 2004; 25(8): 582–7
van Beuningen HM, Glansbeek HL, van der Kraan PM, et al. Osteoarthritis-like changes in the murine knee joint resulting from intra-articular transforming growth factor-beta injections. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 2000; 8(1): 25–33
Martel-Pelletier J, Di Battista JA, Lajeunesse D, et al. IGF/IGFBP axis in cartilage and bone in osteoarthritis pathogenesis. Inflamm Res 1998; 47(3): 90–100
Studer RK, Levicoff E, Georgescu H, et al. Nitric oxide inhibits chondrocyte response to IGF-I: inhibition of IGF-IRbeta tyrosine phosphorylation. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 2000; 279(4): C961–9
Furst DE. Anakinra: review of recombinant human interleukin-I receptor antagonist in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Ther 2004; 26(12): 1960–75
Pelletier JP, Caron JP, Evans C, et al. In vivo suppression of early experimental osteoarthritis by interleukin-1 receptor antagonist using gene therapy. Arthritis Rheum 1997; 40(6): 1012–9
Chevalier X, Giraudeau B, Conrozier T, et al. Safety study of intra-articular injection of interleukin 1 receptor antagonist in patients with painful knee osteoarthritis: a multicenter study. J Rheumatol 2005; 32(7): 1317–23
Bandara G, Robbins PD, Georgescu HI, et al. Gene transfer to synoviocytes: prospects for gene treatment of arthritis. DNA Cell Biol 1992; 11(3): 227–31
Bandara G, Mueller GM, Galea-Lauri J, et al. Intraarticular expression of biologically active interleukin 1-receptor-antagonist protein by ex vivo gene transfer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1993; 90(22): 10764–8
Evans CH, Ghivizzani SC, Robbins PD. Arthritis gene therapy: what next? Arthritis Rheum. In press
Evans CH, Robbins PD, Ghivizzani SC, et al. Gene transfer to human joints: progress toward a gene therapy of arthritis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2005; 102(24): 8698–703
Evans CH, Gouze JN, Gouze E, et al. Osteoarthritis gene therapy. Gene Ther 2004; 11(4): 379–89
Evans CH. Gene therapies for osteoarthritis. Curr Rheumatol Rep 2004; 6(1): 31–40
Evans CH, Ghivizzani SC, Herndon JH, et al. Gene therapy for the treatment of musculoskeletal diseases. J Am Acad Orthop Surg 2005; 13: 230–42
Zhang X, Mao Z, Yu C. Suppression of early experimental osteoarthritis by gene transfer of interleukin-1 receptor antagonist and interleukin-10. J Orthop Res 2004; 22(4): 742–50
Frisbie DD, Ghivizzani SC, Robbins PD, et al. Treatment of experimental equine osteoarthritis by in vivo delivery of the equine interleukin-1 receptor antagonist gene. Gene Ther 2002; 9(1): 12–20
Fernandes J, Tardif G, Martel-Pelletier J, et al. In vivo transfer of interleukin-1 receptor antagonist gene in osteoarthritic rabbit knee joints: prevention of osteoarthritis progression. Am J Pathol 1999; 154(4): 1159–69
Luyten FP. Mesenchymal stem cells in osteoarthritis. Curr Opin Rheumatol 2004; 16(5): 599–603
Chondrogen™clinical trial information. Baltimore (MD): Osiris Therapeutics, Inc. [online]. Available from URL: http://www.osiristx.com/index_files/ClinTrialChondrogen.htm [Accessed 2005 Nov 4]
Garnero P, Delmas PD. Biomarkers in osteoarthritis. Curr Opin Rheumatol 2003; 15(5): 641–6
Acknowledgments
The author is on the Scientific Advisory Board of TissueGene Inc. and Orthogen, A.G.
Funding was received from TissueGene, Inc., Orthogen, A.G. and Osiris Therapeutics, Inc.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Evans, C.H. Novel Biological Approaches to the Intra-Articular Treatment of Osteoarthritis. BioDrugs 19, 355–362 (2005). https://doi.org/10.2165/00063030-200519060-00003
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2165/00063030-200519060-00003