Abstract
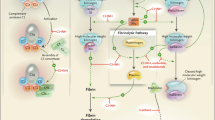
Ecallantide, a recombinant protein that is a selective, highly potent and reversible inhibitor of human plasma kallikrein, is indicated for the treatment of acute attacks of hereditary angioedema (HAE) in patients aged ≥16 years.
In the randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicentre, phase III trial EDEMA3, mean symptom response to treatment at 4 hours (assessed using the Treatment Outcome Score [TOS]; primary endpoint) was significantly greater with a single subcutaneous dose of ecallantide 30 mg than with placebo in patients with acute, moderate to severe attacks of HAE.
In addition, the mean change from baseline in symptom severity at 4 hours (assessed using the Mean Symptom Complex Severity [MSCS] scale) was significantly greater with ecallantide than with placebo.
At 4 hours in the similarly designed EDEMA4 trial, the mean change from baseline in MSCS score (primary endpoint) and mean TOS were both significantly greater in recipients of a single subcutaneous dose of ecallantide 30 mg than in placebo recipients.
Subcutaneous ecallantide 30 mg was generally well tolerated in patients with acute attacks of HAE in the EDEMA3 and EDEMA4 trials. Adverse events were mostly of mild to moderate severity, and no event that was more common in ecallantide than placebo recipients occurred in >10% of patients.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Craig T, Riedl M, Dykewicz MS, et al. When is prophylaxis for hereditary angioedema necessary? Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol 2009 May; 102(5): 366–72
Kaplan A, Joseph K. The bradykinin-forming cascade and its role in hereditary angioedema. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol 2010 Mar; 104(3): 193–204
Dyax Corp. Kalbitor® (ecallantide subcutaneous injection): US prescribing information [online]. Available from URL: http://www.kalbitor.com/pdf/KalbitorFullPrescribingInformation.pdf [Accessed 2010 Mar 30]
Zuraw B, Yasothan U, Kirkpatrick P. Ecallantide. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2010 Mar; 9(3): 189–90
US FDA. Center for Drug Evaluation and Research application number 125277: ecallantide summary review [online]. Available from URL: http://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/nda/2009/125277s000SumR.pdf [Accessed 2010 Mar 31]
US FDA. Center for Drug Evaluation and Research application number 125277: ecallantide pharmacology review part 1 [online]. Available from URL: http://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/nda/2009/125277s000PharmR_P1.pdf [Accessed 2010 Apr 12]
Levy JH, O’Donnell PS. The therapeutic potential of a kallikrein inhibitor for treating hereditary angioedema. Expert Opin Invest Drugs 2006 Sep; 15(9): 1077–90
Dyax Corp. Kalbitor® (ecallantide) for acute attacks of hereditary angioedema (BLA 125277). Pulmonary-Allergy Drugs Advisory Committee briefing document [online]. Available from URL: http://www.fda.gov/ohrms/dockets/AC/09/briefing/2009-4413b1-03-Dyax.pdf [Accessed 2010 May 20]
US FDA. Center for Drug Evaluation and Research application number 125277: ecallantide medical review part 2 [online]. Available from URL: http://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/nda/2009/125277s000MedrR_P2.pdf [Accessed 2010 Apr 12]
Schneider L, Lumry W, Vegh A, et al. Critical role of kallikrein in hereditary angioedema pathogenesis: a clinical trial of ecallantide, a novel kallikrein inhibitor. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2007 Aug; 120(2): 416–22
Levy R, McNeil D, Li H, et al. Results of a phase 3 double-blind, placebo-controlled trial, EDEMA3®: a study of subcutaneous DX-88 (ecallantide) in patients with hereditary angioedema [abstract no. 15]. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol 2008 Jan; 100 (1 Suppl. 1): A6
Levy R, McNeil D, Li H, et al. Results of a 2-stage, phase 3 pivotal trial, EDEMA3®: a study of subcutaneous DX-88 (ecallantide), a plasma kallikrein inhibitor, in patients with hereditary angioedema [abstract no. 398-A]. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2008 Feb; 121 (2 Suppl. 2A): S103
Li HH, Levy RJ, McNeil DL, et al. Interim open-label results of EDEMA3sm: a study of subcutaneous ecallantide in patients with hereditary angioedema [abstract no. 1081]. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2007 Jan; 119 (1 Suppl.): S276
Levy RJ, Lumry WR, McNeil DL, et al. EDEMA4: a phase 3, double-blind study of subcutaneous ecallantide treatment for acute attacks of hereditary angioedema. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol 2010 Jun; 104(6): 523–9
Sheffer A, Levy R, Li H, et al. Subcutaneous DX-88 (ecallantide) for the treatment of acute attacks of hereditary angioedema: results from the integrated analysis of phase 3, double-blind, placebo-controlled studies [abstract no. 29]. Allergy 2009 Jun; 64 Suppl. 90: 13–4
Riedl M, Campion M, Horn PT. Time to response with ecallantide for the treatment of acute attacks of hereditary angioedema: results from the edema development program [abstract no. 57]. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol 2009 Nov; 103 (5 Suppl. 3): A35
Pullman W, Riedl M, Campion M, et al. Ecallantide treatment for acute attacks of HAE by primary attack location [abstract no. 743]. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2010 Feb; 125 (2 Suppl. 1): AB189
Levy R, Lumry W, McNeil D, et al. Subcutaneous DX-88 (ecallantide) for the treatment of acute attacks of hereditary angioedema: results from the pivotal phase 3, double-blind, placebo-controlled EDEMA4 trial [abstract no. 268]. Allergy 2009 Jun; 64 Suppl. 90: 120–1
Levy R, Lumry W, McNeil D, et al. Results of a phase 3, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial, EDEMA4(R): a study of subcutaneous DX-88 (ecallantide) for the treatment of acute attacks of hereditary angioedema [abstract no. P247]. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol 2009 Jan; 102 (1 Suppl. 1): A91
Lumry W, Li H, Schneider L, et al. Results of a repeat-dosing study of intravenous and subcutaneous administration of ecallantide, a recombinant plasma kallikrein inhibitor, in patients with hereditary angioedema [abstract no. 60]. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol 2007 Jan; 98 (1 Suppl. 1): A29
Dyax Corp. Safety and efficacy study of repeated doses of DX-88 (ecallantide) to treat attacks of hereditary angioedema (HAE) [online]. Available from URL: http://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00456508 [Accessed 2010 Apr 13]
US FDA. Center for Drug Evaluation and Research application number 125277: ecallantide approval letter [online]. Available from URL: http://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/nda/2009/125277s000Approv.pdf [Accessed 2010 Apr 13]
Acknowledgements and Disclosures
The manuscript was reviewed by: J.H. Levy, Department of Cardiothoracic Anesthesiology and Critical Care, Emory University Hospital, Atlanta, Georgia, USA; N.R. Sodha, Division of Cardiothoracic Surgery, Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Harvard Medical School, Boston, Massachusetts, USA.
The preparation of this review was not supported by any external funding. During the peer review process, the manufacturer of the agent under review was offered an opportunity to comment on this article. Changes resulting from comments received were made on the basis of scientific and editorial merit.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Garnock-Jones, K.P. Ecallantide. Drugs 70, 1423–1431 (2010). https://doi.org/10.2165/11205850-000000000-00000
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2165/11205850-000000000-00000