Abstract
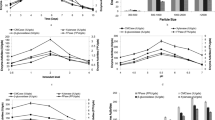
Pleurotus sajor-caju (Fr.) Singer was cultivated on selected agro wastes viz. cotton stalks, groundnut haulms, soybean straw, pigeon pea stalks and leaves and wheat straw, alone or in combinations. Cotton stalks, pigeon pea stalks and wheat straw alone or in combination were found to be more suitable than groundnut haulms and soybean straw for the cultivation. Organic supplements such as groundnut oilseed cake, gram powder and rice bran not only affected growth parameters but also increased yields. Thus bioconversion of lignocellulosic biomass by P. sajor-caju offers a promising way to convert low quality biomass into an improved human food.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anastazia, G., Michael, C., Olger, J., 1982. Substrates for growing oyster mushrooms. Ceska Mycol., 36(4):232–235.
Bahukhandi, D., Munjal, R.L., 1989. Cultivation of Pleurotus sp. on different agricultural residues. Indian Phytopath., 42(4):492–495.
Bano, Z., Srivastava, H.C., 1962. Studies in the cultivation of Pleurotus sp. on paddy straw. Food Sci., 12:363–368.
Bano, Z., Rajarathnam, S., 1982. Studies on cultivation of Pleurotus sajor-caju. Mushroom J., 115:243–245.
Bhandari, T.P.S., Singh, R.N., Verma, B.L., 1991. Cultivation of oyster mushroom on different substrates. Indian Phytopath., 44(4):555–557.
Bhatti, M., Mir, F.A., Siddiq, M., 1987. Effect of different bedding material on relative yield of oyster mushroom in successive flushes. Pak. J. Agric. Res., 8:256–259.
Bisht, S., Harsh, N.S., 1983. Cultivation of Pleurotus ostreatus on used tea leaves. British. Mycol. Soc. Bull., 17(1):51–52.
Bonatti, M., Karnopp, P., Soares, H.M., Furlan, S.A., 2004. Evaluation of Pleurotus ostreatus and Pleurotus sajor-caju nutritional characteristics when cultivated in different lignocellulosic wastes. Food Chem., 88(3):425–428. [doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2004.01.050]
Chang, S.T., Miles, P.G., 1993. Edible Mushrooms and Their Cultivation. CBS Publ., Delhi, India, p.8–40.
Das, N., Mukherjee, M., 2007. Cultivation of Pleurotus ostreatus on weed plants. Biores. Technol., 98(14):2723–2726. [doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2006.09.061]
Diwakar, B., Munjal, R.L., Bahukhandi, D., 1989. Cultivation of Pleurotus sp. on different agricultural residues. Indian Phytopath., 42(4):492–499.
Garcha, H.S., Dhanda, S., Khanna, P., 1984. Evaluation of various organic residues for the cultivation of Pleurotus (Dhingri) species. Mush. Newslett. Trop., 5(1):13–16.
Gurjar, K.L., Doshi, A., 1995. Effect of substrates and supplements on fruit bodies production of Pleurotus cornucopiae. Mush. Inform., 108:12–22.
Guzman, G., Martinez, D., 1986. Pleurotus growing on coffee-pulp in a semi-industrial plant—a new promising mushroom cultivation technology in the subtropics of Mexico. Mush. Lett., 6(3):6–7.
Jadhav, A.B., Bagal, P.K., Jadhav, S.W., 1996. Effect of different substrates on yield of oyster mushroom. J. Maharashtra Agric. Univ., 21(4):424–426.
Jadhav, A.B., Bagal, P.K., Jadhav, S.W., 1998. Biochemical changes in different agro residue to oyster mushroom cultivation. J. Maharashtra Agric. Univ., 23(1):22–24.
Jain, S.K., Gujral, G.S., Bisaria, H., Vasudevan, P., 1988. Cultivation of Pleurotus sajor-caju on aquatic weeds. Aquatic. Bot., 30(4):242–251.
Jandaik, C.L., 1989. Response of Pleurotus sajor-caju to supplementation prior to and after pasteurisation of straw. Indian Phytopath., 42(2):284–285.
Jandaik, C.L., Kapoor, J.N., 1974. Studies on cultivation of Pleurotus sajor-caju (Fr.) Singer. Mush. Sci., 9(1):667–672.
Jandaik, C.L., Goyal, S.P., 1995. Farm and Farming of Oyster Mushroom (Pleurotus Species). In: Singh, R.P., Chaube, H.S. (Eds.), Mushroom Production Technology. G.B. Pant University of Agriculture and Technology, Pantnagar, India, p. 72–78.
Kadlag, G.K., 1997. Comparative Performance of Different Pleurotus spp. on Green Gram and Gram Straws. M.Sc. (Agric.) Dissertation, Mahatma Phule Krishi Vidyapeeth, Rahuri (in India).
Kandaswamy, T.K., Ramaswamy, K., 1978. Effect of organic substrates with different C:N ratio on the yield of Pleurotus sajor-caju. Indian Mush. Sci., 1:423–427.
Kaul, T.N., Janardhan, K.K., 1970. Experimental cultivation of Plerurotus ostreatus white form in Jammu. Indian Phytopath., 3:578–581.
Khanna, P., Garcha, H.S., 1982. Utilization of paddy straw for cultivation of Pleurotus species. Mush. Newslett. Trop., 2(1):5–9.
Lavie, D., 1988. Production of oyster mushroom on cotton straw. Mush. J., 82:453–463.
Leong, P.C., 1980. Utilization of cotton waste substrate with temperature for cultivation of oyster mushroom in Singapore. J. Primary Industry, 8:21–27.
Madan, M., Sharma, S., Bisaria, R., 1994. Cultivation of edible mushrooms. Inven. Intell., 29:117–120.
Mani, P.K., Philip, B., 1995. Potential application of African wood (Savinia molesta) for the cultivation of oyster mushroom, Pleurotus sajor-caju (Fr.) Singer. Indian J. Expt. Biol., 33:806–808.
Mueller, J.C., Gawley, J.R., 1983. Cultivation of phoenix mushroom on pulp mill sludge. Mush. Newslett. Trop., 4(1):3–7.
Muhamad, I., Khan, S.M., 1993. Yield performance of different species/strains of oyster mushroom (Pleurotus sp.) on cotton waste. Pakistan J. Phytopath., 5:53–57.
Mukherjee, R., Nandi, B., 2001. Changes in dry matter digestibility and composition of bioconverted mustard biomass by two Pleuorotus sp. under mushroom growing conditions. J. Sci. Ind. Res., 60:405–409.
Murugesan, A.G., Vijayalakshami, G.S., Sukumaran, N., Mariappan, C., 1995. Utilization of water hyacinth for oyster mushroom cultivation. Biores. Technol., 51(1):97–98. [doi:10.1016/0960-8524(95)00063-K]
Pal, J., Thapa, C.D., 1979. Cultivation of Dhingri (Pleurotus sajor-caju) made easy. Indian J. Mush., 5(1):17–20.
Pal, J., Paul, Y.S., 1985. Cultivation of Pleurotus sajor-caju on lyma wastes. Indian J. Mycol. Pl. Pathol., 15(1):76–78.
Patil, B.D., Jadhav, S.W., Kakade, S.S., 1989. Studies on cultivation of Pleurotus sajor-caju on different substrates. J. Maharashtra Agric. Univ., 14(1):156–158.
Patrabansh, S., Madan, M., 1995. The microbial conversion of different agricultural residues and its biological efficiency. Acta Biotechnol., 15(1):131–135. [doi:10.1002/abio.370150119]
Poo-Chow, L., 1980. Utilization of cotton waste substrate wit temperature treatment for the cultivation of oyster mushroom, Pleurotus in Singapore. J. Prim. Indust., 8(1):1–27.
Ramesh, C.R., Ansari, M.M., 1987. Substrate evaluation for cultivation of oyster mushroom Pleurotus sajor-caju in Andamans. J. Andaman Sci. Assoc., 3(2):110–112.
Rana, R.S., Subag, L.S., 1990. Effect of Legume Pod Waste Addition on Biological Efficiency of Pleurotus sajor-caju. Proc. Ann. Conf. on Mushroom. Soc. Mycol. Pl. Path. Hissar, p.19–20.
Royse, D.J., 2002. Influence of spawn rate and commercial delayed release nutrient levels on Pleurotus cornucopiae (oyster mushroom) yield, size and time to production. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 58(4):527–531. [doi:10.1007/s00253-001-0915-2]
Sharma, A.D., 1983. Effect of cropping environment on some quality parameter of oyster mushroom Pleurotus sajor-caju. Mush. Sci., 4:1–5.
Sharma, S., Madan, M., 1992. Optimal utilization of sericulture waste. Resour. Conserv. Recycl., 7(4):295–304. [doi:10.1016/0921-3449(92)90024-V]
Silanikove, N., Danai, O., Leavanan, O., 1988. Cotton straw silage as a substrate for Pleurotus sp. cultivation. Biol. Wastes, 25(3):219–226. [doi:10.1016/0269-7483(88)90081-X]
Suharban, M., Nair, M.C., 1991. Cultivation of oyster mushroom on wooden logs of common trees. Adv. Mush. Sci., 1:39–43.
Thampi, S.C., Wani, P.V., Bachchhav, M.B., Sawant, D.M., 1996. Studies on Different Pleurotus Species: Spawn Production and Morphological Features. Natu Symp. on Integrated Disease Manag. Indian Soc. Pl. Pathol. Rahuri, India, p.53–54.
Vats, S.K., Sood, R.P., Gulati, A., Sharma, O.P., 1994. Lantana camara A lignocellulosic substrate for cultivation of Pleurotus sajor-caju. Biores. Technol., 48(1):49–52. [doi:10.1016/0960-8524(94)90135-X]
Veena, S.V., Savalgi, V.P., 1991. Studies on Cultivation of Oyster Mushroom on Different Farm Substrates in Konkan. Proc. Nat. Mush. Symp. Thiruanantapuram, Kerala, p.109–112.
Yamashita, I., Mori, T., Tino, K., Yanai, S., 1983. Utilization of cobs tears husk, peanut shell, lawn grass and porous stone for cultivation of oyster mushroom (Pleurotus ostreatus Jacqex. Fr.) Quat. J. Fd. Sci. Technol., 30:693–697.
Zadražil, F., 1980. Conversion of different plant waste into feed by Basidomycetes. Eur. J. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 9(3):243–248. [doi:10.1007/BF00504491]
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mane, V.P., Patil, S.S., Syed, A.A. et al. Bioconversion of low quality lignocellulosic agricultural waste into edible protein by Pleurotus sajor-caju (Fr.) singer. J. Zhejiang Univ. - Sci. B 8, 745–751 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.2007.B0745
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.2007.B0745