Abstract
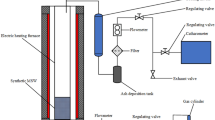
Bamboo was a popular material substituting for wood, especially for one-off commodity in China. In order to recover energy and materials from waste bamboo, the basic characteristics of bamboo pyrolysis were studied by a thermogravimetric analyzer. It implied that the reaction began at 190∼210 °C, and the percentage of solid product deceased from about 25% to 17% when temperature ranged from 400 °C to 700 °C. A lab-scale fluidized-bed furnace was setup to research the detailed properties of gaseous, liquid and solid products respectively. When temperature increased from 400 °C to 700 °C, the mass percent of solid product decreased from 27% to 17% approximately, while that of syngas rose up from 19% to 35%. When temperature was about 500°C, the percentage of tar reached the top, about 31%. The mass balance of these experiments was about 93%∼95%. It indicated that three reactions involved in the process: pyrolysis of exterior bamboo, pyrolysis of interior bamboo and secondary pyrolysis of heavy tar.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ayşe, E.P., Başak, B.U., Esin, A., Ersan, P., 2005. Bio-oil from olive oil industry wastes: Pyrolysis of olive residue under different conditions. Fuel Processing Technology, 86:25–32. [dio:10.1016/j.fupro.2005.04.003]
Chen, G., Andries, J., Luo, Z., Spliethoff, H., 2003a. Biomass pyrolysis/gasification for product gas production the overall investigation of parametric effects. Energy Conversion and Management, 44(11):1875–1884. [doi:10.1016/S0196-8904(02)00118-7]
Chen, G.Y., Fang, M.X., Andries, J., Luo, Z.Y., Spliethoff, H., Cen, K.F., 2003b. Kinetics study on biomass pyrolysis for fuel gas production. Journal of Zhejiang University SCIENCE, 4(4):441–447.
Du, Y., Qi, W.Y., Miao, X., Li, G.Y., Hu, C.W., 2004. Chemical analysis of pubescens and its pyrolysis. Journal of Chemical Industry and Engineering, 55(12):2099–2102 (in Chinese).
Li, A.M., Yan, J.H., Li, S.Q., Gu, Y.L., Li, X.D., Ren, Y., Chi, Y., 2000. Pyrolysis of municipal solid waste in rotary klin: studies on characteristics of pyrolytic tar. Journal of Combustion Science and Technology, 6(3):195–199 (in Chinese).
Li, S.G., Xu, S.P., Liu, S.Q., Yang, C., Lu, Q.H., 2004. Fast pyrolysis of biomass in free-fall reactor for hydrogen-rich gas. Fuel Processing Technology, 85(8–10):1201–1211. [doi:10.1016/j.fuproc.2003.10.043]
Li, Z.J., Lin, P., He, J.Y., Yang, Z.W., Lin, Y.M., 2006. Silicon’s organic pool and biological cycle in moso bamboo community of Wuyishan Biosphere Reserve. Journal of Zhejiang University SCIENCE B, 7(11): 849–857. [doi:10.1631/jzus.2006.B0849]
Ni, M., Leung, D.Y.C., Leung, M.K.H., Sumathy, L.K., 2006a. An overview of hydrogen production from biomass. Fuel Processing Technology, 87(5):461–472. [doi:10.1016/j.fupro.2005.11.003]
Ni, M.J., Xiao, G., Chi, Y., Yan, J.H., Miao, Q., Zhu, W.L., Cen, K.F., 2006b. Study on pyrolysis and gasification of wood in MSW. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 18:407–415.
Tan, H., Wang, S.R., Luo, Z.Y., Yu, C.J., 2005. Experimental study of lignin flash pyrolysis. Journal of Zhejiang University (Engineering Science), 39(5):710–714 (in Chinese).
Wang, W.J., Hui, C.M., Liu, C., Wang, C.M., Chen, Y.H., Fu, H., 1999. A study on the chemical components of 14 timber bamboo species in Yunnan Province. Journal of Bamboo Research, 18(2):74–78 (in Chinese).
Wang, S.R., Liu, Q., Luo, Z.Y., Wen, L.H., Cen, K.F., 2006. Mechanism study of cellulose pyrolysis using thermogravimetric analysis coupled with infrared spectroscopy. Journal of Zhejiang University (Engineering Science), 40(7):1154–1157 (in Chinese).
Xiao, G., Chi, Y., Ni, M.J., Miao, Q., Zhu, W.L., Zheng, J., Tu, H.B., Cen, K.F., 2007. Fluidized-bed pyrolysis and gasification of waste paper. Journal of Engineering Thermophysics, 28(1):161–163 (in Chinese).
Yan, J.H., Peng, Z., Lu, S.Y., Li, X.D., Cen, K.F., 2006. Removal of PCDDs/Fs from municipal solid waste incineration by entrained-flow adsorption technology. Journal of Zhejiang University SCIENCE A, 7(11):1896–1903. [doi:10.1631/jzus.2006.A1896]
Zhang, Y.F., Deng, N., Zhang, S.T., Li, X.G., Zhou, X., Zhou, Y., 2005. Pyrolysis on screen residue of municipal household waste. Journal of Tianjin University, 38(6):556–560 (in Chinese).
Zhou, J.Z., Xu, G.H., 2004. Measurement of the constituent of bamboo powder and its precision analysis. Research and Exploration in Laboratory, 23(1):25–27 (in Chinese).
Zhou, J., Yang, Y.R., Ren, X.H., Stapf, S., 2006. Investigation of reinforcement of the modified carbon black from waste tires by nuclear magnetic resonance. Journal of Zhejiang University SCIENCE A, 7(8):1440–1446. [doi:10.1631/jzus.2006.A1440]
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Project supported by the National Basic Research Program (973) of China (Nos. G199902210534, 2005CB221202 and 2007CB210208), the Hi-Tech Research and Development Program (863) of China (No. 2006AA020101), and the Open Foundation of State Key Laboratory of Clean Energy Utilization of China (No. ZJUCEU2006004)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xiao, G., Ni, Mj., Huang, H. et al. Fluidized-bed pyrolysis of waste bamboo. J. Zhejiang Univ. - Sci. A 8, 1495–1499 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.2007.A1495
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.2007.A1495