Abstract
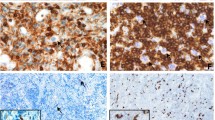
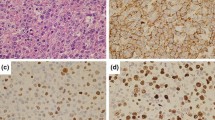
We report a case of composite lymphoma consisting of peripheral T-cell lymphoma and an anaplastic variant of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) and associated with Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) infection and strong p53 expression. A 65-year-old Japanese woman developed fever and generalized lymphadenopathy.A biopsy of the cervical node revealed the morphology of malignant lymphoma with 2 kinds of lymphoma coexisting in 1 lymph node. One lymphoma type consisted of immunoblastic large cells with the T-cell marker phenotype CD3+, CD45RO/UCHL-1+, CD20/L26-, CD79-, CD10-, CD30-, and CD15-; the other type consisted of large cells with abundant cytoplasm and pleomorphic nuclei with the marker phenotype CD79+, CD20/ L26+, CD45RO/UCHL-1-, CD3-, CD10-, CD30+, NPM/ALK-, and CD15-. Therefore, the diagnosis was composite lymphoma of peripheral T-cell lymphoma and an anaplastic variant of DLBCL, stage IVB, because the patient had bone marrow involvement with peripheral T-cell lymphoma. The biopsy led to findings of latent type II EBV-associated lymphoma in both the peripheral T-cell lymphoma and the anaplastic variant of DLBCL as the result of positive signals for EBV small RNAs by in situ hybridization, positive immunostaining results for EBV latent membrane protein 1 antibody, and negative immunostaining results for EBV nuclear antigen 2. Immunostaining of the mass with p53 antibody also yielded positive results for both types of lymphoma cells. This case suggests that the immunocompromised state of this patient with EBV-related peripheral T-cell lymphoma allowed the emergence of an EBV-related anaplastic variant of DLBCL and suggests a close relationship between p53 expression and latent EBV infection.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kim H, Hendrickson MR, Dorfman RF. Composite lymphoma. Cancer. 1977;40:959–976.
Kim H. Composite lymphoma and related disorders. Am J Clin Pathol. 1993;99:445–451.
Gonzalez CL, Meroides LJ, Jaffe ES. Composite lymphoma: a clinicopathologic analysis of nine patients with Hodgkin’s disease and non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Am J Clin Pathol. 1991;96:81–89.
Tobinai K, Ohtsu T, Hayashi M, et al. Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) genome carrying monoclonal B-cell lymphoma in a patient with adult T-cell leukemia-lymphoma. Leuk Res. 1991;15:837–846.
Strickler JG, Amsden TW, Kurtin PJ. Small B-cell lymphoid neoplasms with coexisting T-cell lymphomas. Am J Clin Pathol. 1992; 98:424–429.
Liu YC, Tomashefski JF Jr, Cleveland RP, et al. Composite cutaneous T-cell lymphoma and small B-cell lymphocytic lymphoma: morphologic, and molecular genetic documentation of concurrent lymph node involvement. Mod Pathol. 1994;7:641–646.
Zettl A, Lee SS, Rudiger T, et al. Epstein-Barr virus associated B-cell lymphoproliferative disorders in angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma and peripheral T-cell lymphoma, unspecified. Am J Clin Pathol. 2002;117:368–379.
Delsol G, Ralfkiaer E, Stein H, Wright D, Jaffe ES. Anaplastic large cell lymphoma. In: Jaffe ES, Harris NL, Stein H, Vardiman JW, eds. WHO Classification:Tumors of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues. Lyon, France: IARC Press; 2001:230–235.
Borisch B, Finke J, Hennig I, et al. Distribution and localization of Epstein-Barr virus subtypes A and B in AIDS-related lymphomas and lymphatic tissue of HIV-positive patients. J Pathol. 1992;168: 229–236.
Hamilton-Dutroit SJ, Raphael M, Audouin J, et al. In situ demonstration of Epstein-Barr virus small RNAs (EBER) in acquired immunodeficiency syndrome-related lymphomas: correlation with tumor morphology and primary site. Blood. 1993;82:619–624.
Hanto DW, Frizzera G, Purtilo DT, et al. Clinical spectrum of lymphoproliferative disorders in renal transplant recipients and evidence for the role of Epstein-Barr virus. Cancer Res. 1981;41:4253–4261.
Penn I. Malignant lymphomas in organ transplant recipients. Transplant Proc. 1981;13:736–738.
Kamel OW, van de Riin M, Weiss LM, et al. Brief report: reversible lymphoma associated with Epstein-Barr virus occurring during methotrexate therapy for rheumatoid arthritis and dermatomyositis. N Engl J Med. 1993;328:1317–1321.
Dawson TM, Starkebaum G, Wood BL, Wilkins RF, Gown AM. Epstein-Barr virus, methotrexate, and lymphoma in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and primary Sjögren’s syndrome: case series. J Rheumatol. 2001;28:47–53.
Hirose Y, Masaki Y, Okada J, et al. Epstein-Barr virus associated B-cell type non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma with concurrent p53 protein expression in a rheumatoid arthritis patient treated with methotrexate. Int J Hematol. 2002;75:412–415.
Anagnostopoulos I, Herbst H, Niedobitek G, Stein H. Demonstration of monoclonal EBV genomes in Hodgkin’s disease and Ki-1- positive anaplastic large cell lymphoma by combined Southern blot and in situ hybridization. Blood. 1989;74:810–816.
Herbst H, Dallenbach F, Hummel M, et al. Epstein-Barr virus DNA and latent gene products in Ki-1 (CD30)-positive anaplastic large cell lymphomas. Blood. 1991;78:2666–2673.
Shimakage M, Nakamine H, Tamura S, Takenaka T, Yutsudo M, Hakura H. Detection of Epstein-Barr virus transcript in anaplastic large-cell lymphomas by mRNA in situ hybridization. Hum Pathol. 1997;28:1415–1419.
Hirose Y, Masaki Y, Shimoyama K, et al. Epstein-Barr virus-associated anaplastic large cell variant of diffuse large B-cell-type non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma with concurrent p53 protein expression. Int J Hematol. 2003;77:499–502.
Szekely W, Selivanova G, Magnusson KP, et al. EBNA-5, an Epstein- Barr virus-encoded nuclear antigen, binds to the retinoblastoma and p53 proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993;90:5455–5459.
Chen W, Cooper NR. Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen 2 and latent membrane protein independently transactivate p53 through induction of NF-βB activity. J Virol. 1996;70:4849–4853.
Shibata D, Weiss LM, Nathwani BN, et al. Epstein-Barr virus in benign lymph node biopsies from individuals infected with the human immunodeficiency virus is associated with concurrent or subsequent development of non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Blood. 1991;77: 1527–1533.
Hirose Y, Masaki Y, Shimizu S, et al. Association of Epstein-Barr virus with human immunodeficiency virus-negative T cell lymphomas in Japan, in situ hybridization, polymerase chain reaction and immunohistochemical studies. Leukemia. 1996;10:1673–1675.
Khan G, Norton AJ, Slavin G. Epstein-Barr virus in angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphomas. Histopathology. 1993;22:145–149.
Menke DM, Griesser H, Moder KG, et al. Lymphomas in patients with connective tissue disease: comparison of p53 protein expression and latent EBV infection in patients immunosuppressed and not immunosuppressed with methotrexate. Am J Clin Pathol. 2000; 113:212–218.
Bartek J, Bartkova J, Vojtesek B, et al. Aberrant expression of the p53 oncoprotein is a common feature of a wide spectrum of human malignancies. Oncogene. 1991;6:1699–1703.
Edwards RH, Raab-Traub N. Alterations of p53 gene in Epstein- Barr virus-associated immunodeficiency-related lymphomas. J Virol. 1994;68:1309–1315.
Cesarman E, Inghirami G, Chadburn A, et al. High levels of p53 protein expression do not correlate with p53 gene mutations in anaplastic large cell lymphoma. Am J Pathol. 1993;143:845–856.
Szekely L, Selivanova G, Magnusson KP, et al. EBNA-5, an Epstein- Barr virus-encoded nuclear antigen, binds to the retinoblastoma and p53 proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993;90:5459–5459.
Chen W, Cooper NR. Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen-2 and latent membrane protein independently transactivate p53 through induction of NF-βB activity. J Virol. 1996;70:4849–4853.
Oyama T, Ichimura K, Suzuki R, et al. Senile EBV+ B-cell lymphoproliferative disorders: a clinicopathologic study of 22 patients. Am J Surg Pathol. 2003;27:16–26.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
About this article
Cite this article
Hirose, Y., Fukushima, T., Masaki, Y. et al. Epstein-barr virus-associated composite lymphoma composed of peripheral t-cell lymphoma and an anaplastic variant of a diffuse large b-cell type of non-hodgkin’s lymphoma and strongly expressing P53 protein. Int J Hematol 79, 260–265 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1532/IJH97.03156
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1532/IJH97.03156