Abstract
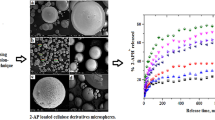
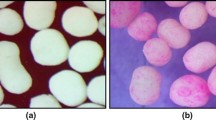
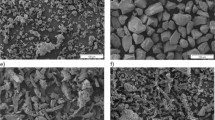
New formulations capable to enhance piroxicam (PRX) water solubility and at the same time to control and adjust its release have been developed. For this purpose, two methods have been used and combined to achieve this goal, namely complexation and microencapsulation by O/W emulsion solvent evaporation. In order to modify the drug release, first, microparticles composed of pure PRX and ethylcellulose (EC) or mixtures of EC and hydroxypropylmethylcellulose (HPMC) were prepared, and then, other micropaticles containing the β-cyclodextrin/piroxicam (β-CD/PRX) complex obtained by the solvent evaporation technique and EC or a mixture of EC and HPMC were produced and tested. These formulations were characterized by FT-IR, XRD, optical microscopy, and SEM methods. Drug dissolution tests were carried out in acidic media at pH = 1.2 and 37°C. Depending on the microparticles composition, their size (d10) ranged between 49 μ.m and 121 μ.m and PRXloaded varied from 10.8 % to 27.7 %. The effect of complexation and HPMC polymer on the drug release was investigated; the results demonstrated that the Higuchi’s release constant significantly increased when using the EC/HPMC mixture as a matrix with pure PRX or only EC as a matrix with the β-CD/PRX complex. The results are remarkably promising since the combination of these processes provided new SD-CR formulations of piroxicam which enabled simultaneous enhancement and control of its release from the carriers.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aejaz, A., & Sadath, A. (2013). Development and characterization of floating microspheres of clarithromycin as gastro retentive dosage form. International Research Journal of Pharmacy, 4(1), 165–168.
Agarwal, S., Wendorff, J. H., & Greiner, A. (2008). Use of elec trospinning technique for biomedical applications. Polymer, 49, 5603–5621. DOI: 10.1016/j.polymer.2008.09.014.
Aquino, R. P., Auriemma, G., d’Amore, M., D’Ursi, A. M., Mencherini, T., & Del Gaudio, P. (2012). Piroxicam loaded alginate beads obtained by prilling/microwave tandem technique: Morphology and drug release. Carbohydrate Polymers, 89, 740–748. DOI: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2012.04.003.
Berkland, C., Kim, K. K., & Pack, D. W. (2003). PLG microsphere size controls drug release rate through several competing factors. Pharmaceutical Research, 20, 1055–1062. DOI: 10.1023/a: 1024466407849.
Bertoluzza, A., Rossi, M., Taddei, P., Redenti, E., Zanol, M., & Ventura, P. (1999). FT-Raman and FT-IR studies of 1:2.5 piroxicam: fi-cyclodextrin inclusion compound. Journal of Molecular Structure, 480–481, 535–539. DOI: 10.1016/s0022-2860(98)00734–0.
Bibby, D. C., Davies, N. M., & Tucker, I. G. (2000). Mechanisms by which cyclodextrins modify drug release from polymeric drug delivery systems. International Journal of Pharmaceutics, 197, 1–11. DOI: 10.1016/s0378–5173(00)00335–5.
Bouchal, F., Skiba, M., Chaffai, N., Hallouard, F., Fatmi, S., & Lahiani-Skiba, M. (2015). Fast dissolving cyclodextrin complex of piroxicam in solid dispersion Part I: Influence of fi-CD and HPfi-CD on the dissolution rate of piroxicam. International Journal of Pharmaceutics, 478, 625–632. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2014.12.019.
Brunton, L. L., Chabner, B. A., & Knollman, B. C. (2011). Goodman and Gilman’s the pharmacological basis of therapeutics (12th ed.). New York, NY, USA: McGraw-Hill Medical.
Canto, G. S., Dalmora, S. L., & Oliveira, A. G. (1999). Piroxicam encapsulated in liposomes: Characterization and in vivo evaluation of topical anti-inflammatory effect. Drug Development and Industrial Pharmacy, 25, 1235–1239. DOI: 10.1081/ddc-100102293.
Challa, R., Ahuja, A., Ali, J., & Khar, R. K. (2005). Cyclodextrins in drug delivery: An updated review. AAPS Pharm-Sci Tech, 6, E329–E357. DOI: 10.1208/pt060243.
Chaudhary, A., Nagaich, U., Gulati, N., Sharma, V. K., & Khosa, R. L. (2012). Enhancement of solubilization and bioavailability of poorly soluble drugs by physical and chemical modifications: A recent review. Journal of Advanced Pharmacy Education & Research, 2, 32–67.
Cilurzo, F., Selmin, F., Minghetti, P., Rimoldi, I., Demartin, F., & Montanari, L. (2005). Fast-dissolving mucoadhesive microparticulate delivery system containing piroxicam. European Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 24, 355–361. DOI: 10.1016/j.ejps.2004.11.010.
Del Valle, E. M. M. (2004). Cyclodextrins and their uses: a review. Process Biochemistry, 39, 1033–1046. DOI: 10.1016/ s0032–9592(03)00258–9.
Diaf, K., El Bahri, Z., Chafi, N., Belarbi, L., & Mesli, A. (2012). Ethylcellulose, polycaprolactone, and eudragit matrices for controlled release of piroxicam from tablets and microspheres. Chemical Papers, 66, 779–786. DOI: 10.2478/s11696–012–0191-x.
Dukic-Ott, A., Remon, J. P., Foreman, P., & Vervaet, C. (2007). Immediate release of poorly soluble drugs from starch- based pellets prepared via extrusion/spheronisation. European Journal of Pharmaceutics and Biopharmaceutics, 67, 715–724. DOI: 10.1016/j.ejpb.2007.04.014.
Escandar, G. M. (1999). Spectrofluororimetric determination of piroxicam in the presence and absence of fi-cyclodextrin. Analyst, 124, 587–591. DOI: 10.1039/a809180c.
Filipovic-Grcic, J., Becirevic-Lacan, M., Skalkom, N., & Jalsenjak, I. (1996). Chitosan microspheres of nifedipine and nifedipine-cyclodextrin inclusion complexes. International Journal of Pharmaceutics, 135, 183–190. DOI: 10.1016/0378-5173(96)04470–5.
Freiberg, S., & Zhu, X. X. (2004). Polymer microspheres for controlled drug release. International Journal of Pharmaceutics, 282, 1–18. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2004.04.013.
Ghosal, K., Chakrabarty, S., & Nanda, A. (2011). Hydrox- ypropyl methylcellulose in drug delivery. Der Pharmacia Sinica, 2(2), 152–168.
Higuchi, T. (1963). Mechanism of sustained-action medication. Theoretical analysis of rate of release of solid drugs dispersed in solid matrices. Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 52, 1145–1149. DOI: 10.1002/jps.2600521210.
Joseph, N. J., Lakshmi, S., & Jayakrishnan, A. (2002). A floating-type oral dosage form for piroxicam based on hollow polycarbonate microspheres: in vitro and in vivo evaluation in rabbits. Journal of Controlled Release, 79, 71–79. DOI: 10.1016/s0168–3659(01)00507–7.
Jug, M., & Becirevic-Lacan, M. (2004). Influence of hydroxypropyl-fi-cyclodextrin complexation on piroxicam release from buccoadhesive tablets. European Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 21, 251–260. DOI: 10.1016/j.ejps.2003.10.029.
Jug, M., Becirevic-Lacan, M., Kwokal, A., & Cetina-Cizmek, B. (2005). Influence of cyclodextrin complexation on piroxicam gel formulations. Acta Pharmaceutica, 55, 223–236.
Jyothi, N. V. N., Prasanna, P. M., Sakarkar, S. N., Prabha, K. S., Ramaiah, P. S., & Srawa, G. Y. (2010). Microencapsulation techniques, factors influencing encapsulation efficiency. Journal of Microencapsulation: Micro and Nano Carriers, 27, 187–197. DOI: 10.3109/02652040903131301.
Kibbe, A. H. (2000). Handbook of pharmaceutical excipients (3rd ed.). Washington, DC, USA: American Pharmacists Association.
Kim, Y. H., Cho, D. W., Kang, S. G., Yoon, M. J., & Kim, D. H. (1994). Excited-state intramolecular proton transfer emission of piroxicam in aqueous fi-cyclodextrin solutions. Journal of Luminescence, 59, 209–217. DOI: 10.1016/0022-2313(94)90043–4.
Korsmeyer, R. W., & Peppas, N. A. (1983). Macromolecular and modeling aspects of swelling-controlled systems. In T. J. Roseman, & S. Z. Mansdorf (Eds.), Controlled release delivery systems (pp. 77–90). New York, NY, USA: Marcel Dekker.
Lai, F., Pini, E., Angioni, G., Manca, M. L., Perricci, J., Sinico, C., & Fadda, A. M. (2011). Nanocrystals as tool to improve piroxicam dissolution rate in novel orally disintegrating tablets. European Journal of Pharmaceutics and Biopharmaceutics, 79, 552–558. DOI: 10.1016/j.ejpb.2011.07.005.
Lee, C. R., & Balfour, J. A. (1994). Piroxicam-fi-cyclodextrin. A review of its pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic properties, and therapeutic potential in rheumatic diseases and pain states. Drugs, 48, 907–929. DOI: 10.2165/00003495199448060–00007.
Loh, Z. H., Samanta, A. K., & Sia Heng, P. W. (2015). Overview of milling techniques for improving the solubility of poorly water soluble drugs. Asian Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 10, 255–274. DOI: 10.1016/j.ajps.2014.12.006.
Lu, X. F., Wang, C., & Wei, Y. (2009). One-dimensional composite nanomaterials: Synthesis by electrospinning and their applications. Small, 5, 2349–2370. DOI: 10.1002/smll.200900 445.
Moffat, A. C., Osselton, M. D., & Widdop, B. (2004). Clarke’s analysis of drugs and poisons (3rd ed). London, UK: Pharmaceutical Press.
Moldenhauer, M. G., & Nairn, J. G. (1990). Formulation parameters affecting the preparation and properties of microencapsulated ion-exchanged resins containing theophylline. Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 79, 659–666. DOI: 10.1002/jps.2600790802.
Mostafa Kamal, M. A. H., Ahmed, M., Ibne Wahed, M. I., Shah Amran, M., Shaheen, S. M., Rashid, M., & Anwar-Ul-Islam, M. (2008). Development of indomethacin sustained release microcapsules using ethyl cellulose and hydroxy propyl methyl cellulose phthalate by O/W emulsification. Dhaka University Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 7, 83–88. DOI: 10.3329/dujps.v7i1.1223.
Mura, P. (2015). Analytical techniques for characterization of cyclodextrin complexes in the solid state: A review. Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis, 113, 226–238. DOI: 10.1016/j.jpba.2015.01.058.
Nagabhushanam, M. V. (2010). Formulation studies on cy-clodextrin complexes of piroxicam. Rasayan Journal of Chemistry, 3, 314–320.
Paaver, U., Lust, A., Mirza, S., Rantanen, J., Veski, P., Heinämäki, J., & Kogermann, K. (2012). Insight into the solubility and dissolution behavior of piroxicam anhydrate and monohydrate forms. International Journal of Pharmaceutics, 431, 111–119. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2012.04.042.
Paaver, U., Heinämäki, J., Kassamakov, I., Hægström, E., Ylitalo, T., Nolvi, A., Kozlova, J., Laidmae, I., Kogermann, K., & Veski, P. (2014). Nanometer depth resolution in 3D topographic analysis of drug-loaded nanofibrous mats without sample preparation. International Journal ofPharmaceutics, 462, 29–37. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2013.12.041.
Paaver, U., Heinämäki, J., Laidmae, I., Lust, A., Kozlova, J., Sillaste, E., Kirsimae, K., Veski, P., & Kogermann, K. (2015). Electrospun nanofibers as a potential controlled- release solid dispersion system for poorly water-soluble drugs. International Journal of Pharmaceutics, 479, 252–260. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2014.12.024.
Patil, J. S., Kadam, D. V., Marapur, S. C., & Kamalapur, M. V. (2010). Inclusion complex system; a novel technique to improve the solubility and bioavailability of poorly soluble drugs: A review. International Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences Review and Research, 2(2), 29–34.
Pelipenko, J., Kristl, J., Janković, B., Baumgartner, S., & Kocbek, P. (2013). The impact of relative humidity during electrospinning on the morphology and mechanical properties of nanofibers. International Journal of Pharmaceutics, 456, 125–134. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2013.07.078.
Phalguna, Y., Venkateshwarlu, B. S., Gudas, G. K., & Debnath, S. (2010). HPMC microspheres of zidovudine for sustained release. International Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences, 2(Suppl 4), 41–43.
Phutane, P., Shidhaye, S., Lotlikar, V., Ghule, A., Sutar, S., & Kadam, V. (2010). In vitro evaluation of novel sustained release microspheres of glipizide prepared by the emulsion solvent diffusion-evaporation method. Journal of Young Pharmacists, 2, 35–41. DOI: 10.4103/0975–1483.62210.
Piao, M. G., Yang, C. W., Li, D. X., Kim, J. O., Jang, K. Y., Yoo, B. K., Kim, J. A., Woo, J. S., Lyoo, W. S., Han, S. S., Lee, Y. B., Kim, D. D., Yong, C. S., & Choi, H. G. (2008). Preparation and in vivo evaluation of piroxicam- loaded gelatin microcapsule by spray drying technique. Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin, 31, 1284–1287. DOI: 10.1248/bpb.31.1284.
Raut, N. S., Somvanshi, S., Jumde, A. B., Khandelwal, H. M., Umekar, M. J., & Kotagale, N. R. (2013). Ethyl cellulose and hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose buoyant microspheres of metoprolol succinate: Influence of pH modifiers. International Journal of Pharmaceutical Investigation, 3, 163–170. DOI: 10.4103/2230–973x.119235.
Redenti, E., Peveri, T., Zanol, M., Ventura, P., Gnappi, G., & Montenero, A. (1996). A study on the differentiation between amorphous piroxicam:β-cyclodextrin complex and a mixture of the two amorphous components. International Journal of Pharmaceutical Science, 129, 289–294. DOI: 10.1016/0378-5173(95)04357-g.
Rozou, S., Voulgari, A., & Antoniadou-Vyza, E. (2004). The effect of pH dependent molecular conformation and dimerization phenomena of piroxicam on the drug:cyclodextrin complex stoichiometry and its chromatographic behaviour: A new specific HPLC method for piroxicam:cyclodextrin formulations. European Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 21, 661–669. DOI: 10.1016/j.ejps.2004.01.007.
Saravanan, M., & Anupama, B. (2011). Development and evaluation of ethylcellulose floating microspheres loaded with ranitidine hydrochloride by novel solvent evaporation-matrix erosion method. Carbohydrate Polymers, 85, 592–596. DOI: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2011.03.020.
Savjani, K. T., Gajjar, A. K., & Savjani, J. K. (2012). Drug solubility: Importance and enhancement techniques. ISRN Pharmaceutics, 2012, 195–727. DOI: 10.5402/2012/195727.
Scarpignato, C. (2013). Piroxicam-β-cyclodextrin: A GI safer piroxicam. Current Medicinal Chemistry, 20, 2415–2437. DOI: 10.2174/09298673113209990115.
Srivastava, A. K., Ridhurkar, D. N., & Wadhwa, S. (2005). Floating microspheres of cimetidine: Formulation, characterization and in vitro evaluation. Acta Pharmaceutica, 55, 277–285.
Taepaiboon, P., Rungsardthong, U., & Supaphol, P. (2006). Drug-loaded electrospun mats of poly(vinyl alcohol) fibres and their release characteristics of four model drugs. Nanotechnology, 17, 2317–2329. DOI: 10.1088/0957–4484/17/9/041.
Tran, P. H. L., Tran, T. T. D., Park, J. B., & Lee, B. J. (2011). Controlled release systems containing solid dispersions: Strategies and mechanisms. Pharmaceutical Research, 28, 2353–2378. DOI: 10.1007/s11095–011–0449-y.
Turro, N. J., Okubo, T., & Chung, C. J. (1982). Analysis of static and dynamic host-guest associations of detergents with cyclodextrins via photoluminescence methods. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 104, 1789–1794. DOI: 10.1021/ja00371a001.
Wade, A., & Weller, P. J. (1994). Handbook of pharmaceutical excipients (2nd ed.). Washington, DC, USA: American Pharmaceutical Association.
Wagenaar, B. W., & Muller, B. W. (1994). Piroxicam release from spray-dried biodegradable microspheres. Biomaterials, 15, 49–54. DOI: 10.1016/0142–9612(94)90196–1.
Wen, H., & Park, K. N. (Eds.) (2010). Oral controlled release formulation design and drug delivery: Theory and practice. Hoboken, NJ, USA: Wiley.
Xua, Q. X., Chin, S. E., Wang, C. H., & Pack, D. W. (2013). Mechanism of drug release from double-walled PDLLA(PLGA) microspheres. Biomaterials, 34, 3902–3911. DOI: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2013.02.015.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khoukhi, O.E., Bahri, Z.E., Diaf, K. et al. Piroxicam/β-cyclodextrin complex included in cellulose derivatives-based matrix microspheres as new solid dispersion-controlled release formulations. Chem. Pap. 70, 828–839 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1515/chempap-2016-0014
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1515/chempap-2016-0014