Abstract
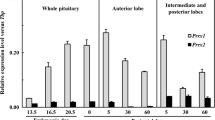
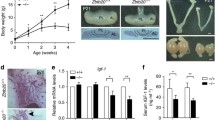
Pax6, an evolutionarily conserved transcription factor, is expressed in the murine and zebrafish embryonic pituitary, but its role in pituitary development and endocrine function has not been described. To study the role of Pax6 in vivo, we examined Pax6 mutant mouse (SeyNeu) pituitaries. Mice homozygous for the SeyNeu mutation die at birth; therefore, we examined peptide hormone expression by the differentiated pituitary cell types as well as developmental marker expression in the intermediate and anterior lobes of the embryonic pituitary. GH- and PRL-immunopositive cells appear severely decreased in an outbred ICR background at embryonic d 17.5, although mRNA expression of these peptide hormones is present, as is expression of other pituitary markers. This suggests that pituitary cell types are able to differentiate in mutant embryos. To identify the cellular or physiologic mechanism responsible for less GH-and PRL-immunoreactivity in Pax6 mutant mice, we tested serum levels of GH and PRL. Pax6 homozygous mutant mice have GH serum levels one fifth that of controls at embryonic d 17.5, and one-third that of controls at postnatal d 0. PRL serum levels, which are very low during embryonic and neonatal stages, were below assay detection limits in both the wild-type and mutant groups. Taken together, these data suggest that Pax6 is not essential for pituitary differentiation, but rather functions to establish appropriate neonatal homeostatic levels of GH and PRL, possibly through regulation of translational or secretory mechanisms.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Roberts, R. C. (1967) Genet Res. 9, 121–122.
Hill, R. E., Favor, J., Hogan, B. L. M, Ton, C. C. T., Saunders, G. F., Hanson, I. M., Prosser J., Jordan, T., Hastie, N. D., and Van Heyningen, V. (1991) Nature 354, 522–525.
Glaser, T., Jepeal, L., Edwards, J. G., Young, S. R., Favor, J., and Maas, R. I. (1994),. Nature Genet. 7, 463–471.
Hogan, B. L. M., Horsburgh, G., Cohen, J., Hetherington, C. M., Fisher, G., and Lyon, M. F. (1986). J. Embryol. Exp. Morph. 97, 95–110.
Matsuo, T., Osumi-Yamashita, N., Noji, S., Ohuchi, H., Koyama, E., Myokai, F., Matsuo, N., Taniguchi, S., Doi, H., Iseki, S., Ninomiya, Y., Fujiwara, M., Watanabe, T., and Eto, K. (1993), Nature Genet. 3, 299–304.
Schmahl, W., Knowedlseder, M., Favor, J., and Davidson, D. (1993). Acta Neuropath. 86, 126–135.
St-Onge, L., Sosa-Pineda, B., Chowdhury, K., Mansourik, A., and Gruss, P. (1997) Nature 387, 406–409.
Frohman, L. A. (1987) In Endocrinology and Metabolism, Felig, P., Baxter, J. D., Broadus, A. E. and Frohman, L. A., eds., McGraw-Hill Book Company, New York, pp. 252–273.
Walther, C., and Gruss, P. (1991) Development 113, 1435–1449.
Puschel, A. W., Gruss, P. and Westerfield, M. (1992) Development 114, 643–651.
Turque N., Plaza, S., Radvanyi F., Carriere, C., and Saule, S. (1994), Mol. Endocrinol. 8, 929–938.
Schwind, J. (1928). Am. J. Anat. 41, 295–315.
Ikeda, H., and Yoshimoto, T. (1991) Cell Tissue Res. 263, 41–47.
Voss, J. W., and Rosenfeld, M. G. (1992) Cell 70, 527–530.
Sornson, M. W., Wu, W., Dasen, J. S., Flynn, S. E., Norman, D. J., O'Connell, S. M., et al (1996), Nature 384, 327–333.
Bodner, M., Castrillo, J. L., Theill, L. E, deerink, T., Ellisman, M., and Karin, M. (1988), Cell 50, 26–275.
Ingrahm, H. A., Chen, R., Mangalam, H. J., Elsholtz, H., Flynn, S. E., Lin, C. R., Simmons D. M., Swanson, L. W., and Rosenfeld, M. G. (1988), Cell 55, 519–529.
Borrelli, E. (1994), Trends Genet. 10, 222–224.
Quinn J. C., West, J. D., and Kaufman, M. H. (1997). Anat. Embryol. 196, 311–321.
Zhadanov, A. B., Bertuzzi, S., Taira, M., Dawid, I. B., and Westphal, H. (1995), Dev. Dyn. 202, 354–364.
Thomas, P. Q., Johnson, B. V., Rathjen, J., and Rathjen, P. D. (1995). J. Biol. Chem. 270, 3869–3875.
Hermesz, E., Mackem, S., and Mahon, K. A. (1996) Development 122, 41–52.
Mackenzie, A., Leeming, G. L., Jowett, A. K., Feguson, M. W. J., and Sharpe, P. T. (1991) Development 111, 269–285.
Yamanouchi, H., Kitauchi, S., and Shiino, M. (1997), Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 134, 101–107.
Quinn, J. C., West, J. D., and Hill, R. E. (1996), Genes Dev. 10, 435–446.
Roberts, V. J., Barth, S., Meunier, H., and Vale, W. (1996), J. Comp. Neurol. 364, 473–493.
MacConell, L. A., Barth, S., and Roberts, V. J. (1996) Endocrinology 137, 2150–2158.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bentley, C.A., Zidehsarai, M.P., Grindley, J.C. et al. Pax6 is implicated in murine pituitary endocrine function. Endocr 10, 171–177 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1385/ENDO:10:2:171
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1385/ENDO:10:2:171