Abstract
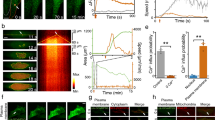
The calcium ion (Ca2+) concentrations in a cell are responsible for the control of vital cellular functions and have been widely studied as a means to investigate and control cell activities. Here, we demonstrate Ca2+ wave generation in HeLa cells by femtosecond laser irradiation and show unexpected properties of the Ca2+ release and propagation. When the laser was focused in the cell cytoplasm, Ca2+ release was independent of both external Ca2+ influx and the phosphoinositide-phospholipase C (PLC) signaling pathway. The nucleus was not a susceptible target for laser-induced Ca2+ release, whereas irradiation of the plasma membrane produced evidence of transient poration, through which the extracellular solution could enter the cell. By chelating extracellular Ca2+, we found that laser-induced influx of ethylene glycol tetra-acetic acid (EGTA) can compete with calcium-induced calcium release and significantly delay or suppress the onset of the Ca2+ wave in the target cell. Intercellular Ca2+ propagation was adenosine triphosphate-dependent and could be observed even when the target cell cytosolic Ca2+ rise was suppressed by influx of EGTA. The irradiation effect on overall cell viability was also tested and found to be low (85% at 6h after irradiation by 60 mW average power). Laser-induced Ca2+ waves can be reliably generated by controlling the exposure and focal position and do not require the presence of caged Ca2+. The technique has the potential to replace other methods of Ca2+ stimulation, which either require additional caged molecules in the cell or do not have an interaction that is as well localized.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berridge, M. J., Lipp, P., and Bootman, M. D. (1998) Calcium—a life and death signal. Nature 395, 645–648.
Berridge, M. J., Lipp, P., and Bootman, M. D. (2000) The versatility and universality of calcium signaling. Nat. Rev. Mol. 1, 11–21.
Cheng, H., Lederer, W. J., and Cannell, M. B. (1993) Calcium sparks: elementary events underlying excitation-contraction coupling in heart muscle. Science 262, 740–744.
Bootman, M. D., Berridge, M. J., and Lipp, P. (1997) Cooking with calcium; the recipes for composing global signals from elementary events. Cell 91, 367–373.
Paemeleire, K., Martin, P. E. M., Coleman, S. L., et al. (2000) Intercellular calcium waves in HeLa cells expressing GFP-labeled Connexin 43, 32, or 26. Mol. Biol. Cell 11, 1815–1827.
Fauquier, T., Guérineau, N. C., McKinney, R. A., Bauer, K., and Mollard, P. (2001) Folliculostellate cell network: a route for long-distance communication in the anterior pituitary. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 98, 8891–8896.
Jacob, R., Merritt, J. E., Hallam, J. E., and Rink, T. J. (1998) Repetitive spikes in cytoplasmic calcium evoked by histamine in human endothelial cells. Nature 335, 40–45.
Parpura, V., and Haydon, P. G. (2000) Physiological astrocytic calcium levels stimulate glutamate release to modulate adjacent neurons. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 97, 8629–8634.
Brown, E. B., Shear, J. B., Adams, S. R., Tsien, R. Y., and Webb, W. W. (1999) Photolysis of caged calcium in femooliter volumes using two-photon excitation. Biophys. J 76, 489–499.
Lipp, P., and Niggli, E. (1998) Fundamental calcium release events revealed by two-photon excitation photolysis of caged calcium in guinea-pig cardiac myocytes. J. Physiol. 508, 801–809.
Smith, N. I., Fujita, K., Kaneko, T. et al. (2001) Generation of calcium waves in living cells by pulsed-laser-induced photodisruption. Appl. Phys. Lett. 79, 1208–1210.
König, K., Riemann, I., Fischer, P., and Halbhuber, K. J. (1999) Intracellular nanosurgery with near infrared femtosecond laser pulses. Cell. Mol. Biol. 45, 195–201.
Yanik, M. F., Cinar, H., Cinar, H. N., Chisholm, A. D., Jin, Y., and Ben-Yakar, A. (2004) Functional regeneration after laser axotomy. Nature 432, 882.
Yeh, C. J., Hsi, B. L., and Faulk, W. P. (1981) Propidium iodide as a nuclear marker in immunofluorescence. II. Use with cellular identification and viability studies. J. Immunol. Methods. 43, 269–275.
Boutonnat, J., Barbier, M., Muirhead, K., Mousseau, M., Ronot, X., and Seigneurin, D. (1999) Optimized fluorescent probe combinations for evaluation of proliferation and necrosis in anthracycline-treated leukaemic cell lines. Cell Prolif. 32, 203–213.
Goeppert-Meyer, M. (1931) Ueber Elementarakte mit zwei Quantenspruengen. Ann. Phys. 9, 273–295.
Vogel, A., and Venugopalan, V. (2003) Mechanisms of pulsed laser ablation of biological tissues. Chem. Rev. 103, 577–644.
Schönle, A., and Hell, S. W. (1998) Heating by absorption in the focus of an objective lens. Opt. Lett. 23, 325–327.
Denk, W., Piston, D. W., and Webb, W. W. (1995). In Two-Photon Molecular Excitation in Laser Scanning Microscopy (Pawley, J. B. ed). Plenum, New York, pp. 445–458.
Chrico, G., Cannone, F., Baldini, G., and Diaspro, A. (2003) Two-photon thermal bleaching of single fluorescent molecules. Biophys. J. 84, 588–598.
Xu, C., Williams, R. M., Zipfel, W., and Webb, W. W. (1996) Multiphoton excitation cross-sections of molecular fluorophores. Bioimaging 4, 198–207.
Smith, N. I., Fujita, K., Nakamura, O., and Kawata, S. (2001) Three-dimensional subsurface microprocessing of collagen by ultrashort laser pulses. Appl. Phys. Lett. 78, 999–1001.
Tirlapur, U. K., König, K., Peuckert, C., Krieg, R., and Halbhuber, K. J. (2001) Femtosecond near-infrared laser pulses elicit generation of reactive oxygen species in mammalian cells leading to apoptosis-like death. Exp. Cell Res. 263, 88–97.
Jornot, L., Maechler, P., Wollheim, C. B., and Junod, A. F. (1999) Reactive oxygen metabolites increase mitochondrial calcium in endothelial cells implication of the Ca2+/Na+ exchanger. J. Cell. Sci. 112, 1013–1022.
Berridge, M. J. (1993) Inositol trisphosphate and calcium signaling, Nature 361, 315–325.
Barrero, M. J., Montero, M., and Alvarez, J. (1997) Dynamics of [Ca2+] in the endoplasmic reticulum and cytoplasm of intact HeLa cells. A comparative study. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 27694–27699.
Missiaen, L., De Smedt, H., Parys, J. B., et al. (1996) Kinetics of the non-specific calcium leak from non-mitochondrial calcium stores in permeabilized A7r5 cells. Biochem. J. 317, 849–853.
Lipp, P., Thomas, D., Berridge, M. J., and Bootman, M. D. (1997) Nuclear calcium signalling by individual cytoplasmic calcium puffs. EMBO J. 16, 7166–7173.
Tirlapur, U. K., and Konig, K. (2002) Targeted transfection by femtosecond laser. Nature 418, 290–291.
Okuda, A., Furuya, K., and Kiyohara, T. (2003) ATP-induced calcium oscillations and change of P2Y subtypes with culture conditions in HeLa cells. Cell Biochem. Funct. 21, 61–68.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Iwanaga, S., Kaneko, T., Fujita, K. et al. Location-dependent photogeneration of calcium waves in HeLa cells. Cell Biochem Biophys 45, 167–176 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1385/CBB:45:2:167
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1385/CBB:45:2:167