Abstract
C-reactive protein (CRP) is an acute-phase serum protein and a member of the pentraxin protein family. Its host defense functions predate the adaptive immune system by millions of years. Our current understanding of CRP interactions with complement and with Fcγ receptors (FcγR) have led to an increased appreciation of the regulatory role of CRP in inflammation and autoimmunity. This review outlines the role of CRP in infection, inflammation, and autoimmune disease. We provide a discription of recent studies, which suggest that CRP acts through FcγR to reduce inflammation and protect from certain autoimmune diseases. A general description of the proposed function of CRP is provided as a framework for future in vestigation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tillett WS, Francis T, Jr.: Serological reactions in pneumonia with a non-protein fraction of pneumococcus. J Exp Med 1930;52:561–571.
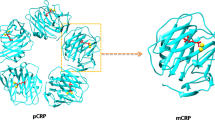
Thompson D, Pepys MB, Wood SP: The physiological structure of human C-reactive protein and its complex with phosphocholine. Structure 1999;7:169–177.
Shrive AK, Cheetham GM, Holden D, Myles DA, Turnell WG, Volanakis JE, et al.: Three dimensional structure of human C-reactive protein. Nature Struct Biol 1996;3:346–354.
Osmand AP, Friedenson B, Gewurz H, Painter RH, Hofmann T, Shelton E: Characteriation of C-reactive protein and the complement subcomponent Clt as homologous proteins displaying cyclic pentameric symmetry (pentraxins). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1977;74:739–743.
5.Agrawal A, Shrive AK, Greenhough TJ, Volanakis JE: Topology and structure of the Clq-binding site on C-reactive protein. J Immunol 2001;166:3998–4004.
Agrawal A, Volanakis JE: Probing the Clq-binding site on human C-reactive protein by site-directed mutagenesis J Immunol 1994;152:5404–5410.
Marnell LL, Mold C, Volzer MA, Burlingame RW, Du Clos TW: C-reactive protein binds to FcγRI in transfected COS cells. J Immunol 1995;155:2185–2193.
Gaboriaud C, Juanhuix J, Gruez A, Lacroix M, Darnault C, Pignol D, et al.: The crystal structure of the globular head of complement protein Clq provides a basis for its versatile recognition properties. J Biol Chem 2003;278:46974–46982.
Hurlimann J, Thorbecke GJ, Hochwald GM: The liver as the site of C-reactive protein formation. J Exp Med 1966;123:365–378.
Weinhold B, Rüther U: Interleukin-6-dependent and independent regulation of the human C-reactive protein gene. Biochem J 1997;327:425–429.
Mackiewicz A, Speroff T, Ganapathi MK, Kushner I: Effects of cytokine combinations on acute phase protein production in two human hepatoma cell lines. J Immunol 1991;146:3032–3037.
Li S-P, Liu T-Y, Goldman ND: cis-Acting elements responsible for interleukin-6 inducible C-reactive protein expression. J Biol Chem 1990;265:4136–4142.
Macintyre S, Samols D, Dailey P: Two carboxylesterases bind C-reactive protein within the endoplasmic reticulum and regulate its secretion during the acute phase response. J Biol Chem 1994;269:24496–24503.
Macintyre SS, Kushner I, Samols D: Secretion of C-reactive protein becomes more efficient during the course of the acute phase response. J Biol Chem 1985;260:4169–4173.
Kushner I, Broder MI, Karp D: Control of the acute phase response. Serum C-reactive protein kinetics after acute myocardial infarction. J Clin Invest 1978;61:235.
Pepys MB, Lanham JG, De Beer FC: C-reactive protein in SLE. Clin Rheum Dis 1982;8:91–103.
Martin MFR, Dieppe PA, whicher J, Bell AM: Defective acute phase responses in scleroderma. Ann Rheum Dis 1988;194.
Becker GJ, Waldburger M, Hughes GR, Pepys MB: Value of serum C-reactive protein measurement in the investigation of fever in systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann Rheum Dis 1980;39:50–52.
Nakahara C, Kanemoto K, Saito N, Oyake Y, Kamoda T, Nagata M, Matsui A: C-reactive protein frequently localizes in the kidney in glomerular diseases. Clin Nephrol 2001;55:365–370.
Baidoshvili A, Nijmeijer R, Lagrand WK, Hack CE, Niessen HW: Localisation of C reactive protein in infarcted tissue sites of multiple organs during sepsis. J Clin Path 2002;55:152–153.
Zuniga R, Markowitz GS, Arkachaisri T, Imperatore EA, D'Agati VD, Salmon JE: Identification of IgG subclasses and C-reactive protein in lupus nephritis: The relationship between the composition of immune deposits and Fc gamma receptor type IIA alleles. Arthritis Rheum 2003;48:460–470.
Kushner I, Rakita L, Kaplan MH: Studies of acutephase protein. II. Localization of Cxreactive protein in heart in induced myocardial infarction in rabbits. J Clin Invest 1963;42:286–292.
Gitlin JD, Gitlin JI, Gitlin D: Localization of C-reactive protein in synovium of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 1977;20:1491–1499.
Du Clos TW, Mold C, Paterson PY, Alroy J, Gewurz H: Localization of C-reactive protein in inflammatory lesions of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. Clin Exp Immunol 1981;43:565–573.
Russell AI, Cunninghame Graham DS, Shepherd C, Roberton CA, Whittaker J, Meeks J, et al.: Polymorphism at the C-reactive protein locus influences gene expression and predisposes to systemic lupus erythematosus. Hum Mol Genet 2004;13:137–147.
Parish WE: Studies on vasculitis. I. Immunoglobulins, 1C, C-reactive protein, and bacterial antigens in cutaneous vasculitis lesions. Clin Allergy 1971;1:97–109.
Kushner I, Kaplan MH: Studies of acute phase protein. I. An immunohistochemical method for the localization of Cx-reactive protein in rabbits: association with necrosis in inflammatory lesions. J Exp Med 1961;114:961–973.
Szalai AJ, McCrory MA, Cooper GS, Wu J, Kimberly RP: Association between baseline levels of C-reactive protein (CRP) and a dinucleotide repeat polymorphism in the intron of the CRP gene. Genes Immun 2002;3:14–19.
Vickers MA, Green FR, Terry C, Mayosi BM, Julier C, Lathrop M, et al.: Genotype at a promoter polymorphism of the interleukin-6 gene is associated with baseline levels of plasma C-reactive protein. Cardiovasc Res 2002;53:1029–1034.
Ferrari SL, Ahn-Luong L, Garnero P, Humphries SE, Greenspan SL: Two promoter polymorphisms regulating interleukin-6 gene expression are associated with circulating levels of C-reactive protein and markers of bone resorption in postmenopausal women. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2003;88:255–259.
Berger P, McConnell JP, Nunn M, Kornman KS, Sorrell J, Stephenson K, Duff GW: C-reactive protein levels are influenced by common IL-1 gene variations. Cytokine 2002;17:171–174.
Stein MP, Edberg JC, Kimberly RP, Mangan EK, Bharadwaj D, Mold C, Du Clos TW: C-reactive protein binding to FcγRIIa on human monocytes and neutrophils is allele specific. J Clin Invest 2000;105:369–376.
Weiser JN, Pan N, McGowan KL, Musher D, Martin A, Richards J: Phosphorylcholine on the lipopolysaccharide of Haemophilus influenzae contributes to persistence in the respiratory tract and sensitivity to serum killing mediated by C-reactive protein. J Exp Med 1998;187:631–640.
Narkates AJ, Volanakis JE: C-reactive protein binding specificities: artificial and natural phospholipid bilayers. Ann NY Acad Sci 1982;389:172–181.
Li YP, Mold C, Du Clos TW: Sublytic complement attack exposes C-reactive protein binding sites on cell membranes. J Immunol 1994;152:2995–3005.
Vigo C: Effect of C-reactive protein on platelet-activating factor-induced platelet aggregation and membrane stabilization. J Biol Chem 1985;260:3418–3422.
Kilpatrick JM, Virella G: Inhibition of platelet activating factor by rabbit C-reactive protein. Clin Immunol Immunopathol 1985;37:276–281.
Filep JG, Herman F, Kelemen E, Foldes-Filep E: C-reactive protein inhibits binding of platelet-activating factor to human platelets. Thrombosis Res 1991;61:411–421.
Du Clos TW: The interaction of C-reactive protein and serum amyloid P component with nuclear antigens. Mol Biol Rep 1997;23:253–260.
Robey FA, Jones KD, Tanaka T, Liu T-Y: Binding of C-reactive protein to chromatin and nucleosome core particles. A possible physiological role of C-reactive protein. J Biol Chem 1984;259:7311–7316.
Du Clos TW: C-reactive protein reacts with the U1 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein. J Immunol 1989; 143:2553–2559.
Pepys MB, Booth SE, Tennent GA, Butler PJG, Williams DG: Binding of pentraxins to different nuclear structures: C-reactive protein binds to small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles, serum amyloid P component binds to chromatin and nucleoli. Clin Exp Immunol 1994;97:152–157.
Du Clos TW, Zlock L, Marnell LL: Definition of a C-reactive protein binding determinant on histones. J Biol Chem 1991;266:2167–2171.
Jewell WS, Marnell LL, Rokeach LA, Du Clos TW: C-reactive protein binding to the Sm-D protein of snRNPs. Identification of a short polypeptide binding region. Mol Immunol 1993;30:701–708.
Riemekasten M, Trebeljahr K, Hausdorf H, Burmester H: A novel epitope on the C-terminus of SmD1 is recognized by the majority of sera from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Clin Invest 1998;102:754–763.
Riemekasten G, Kawald A, Weiss C, Meine A, Marell J, Klein R, et al.: Strong acceleration of murine lupus by injection of the SmD183-119 peptide. Arthritis Rheum 2001;44:2435–2445.
Kim SJ, Gershov D, Ma X, Brot N, Elkon KB: Opsonization of apoptotic cells and its effect on macrophage and T cell immune responses. Ann NY Acad Sci 2003;987:68–78.
Mold C, Nakayama S, Holzer TJ, Gewurz H, Du Clos TW: C-reactive protein is protective against Streptococcus pneumoniae infection in mice. J Exp Med 1981;154:1703–1708.
Mortensen RF, Osmand AP, Lint TF, Gewurz H: Interaction of C-reactive protein with lymphocytes and monocytes: Complement-dependent adherence and phagocytosis. J Immunol 1976;117:774–781.
Nakayama S, Mold C, Gewurz H, Du Clos TW: Opsonic properties of C-reactive protein in vivo. J Immunol 1982; 128:2435–2438.
Mold C, Rodic-Polic B, Du Clos TW: Protection from Streptococcus pneumoniae infection by C-reactive protein and natural antibody requires complement but not Fc gamma receptors. J Immunol 2002;168:6375–6381.
Szalai AJ: The antimicrobial activity of C-reactive protein. Microbes Infect 2002;4:201–205.
Berman S, Gewurz H, Mold C: Binding of C-reactive protein to nucleated cells leads to complement activation without cytolysis. J Immunol 1986;136:1354–1359.
Mold C, Gewurz H, Du Clos TW: Regulation of complement by C-reactive protein. Immunopharm 1999; 42:23–30.
Giannakis E, Jokiranta TS, Male DA, Ranganathan S, Ormsby RJ, Fischetti VA, et al.: A common site within factor H SCR 7 responsible for binding heparin, C-reactive protein and streptococcal M protein. Eur J Immunol 2003;33:962–969.
Wolbink GJ, Brouwer MV, Buysmann S, ten Berge IJM, Hack EC: CRP-mediated activation of complement in vivo. J Immunol 1996;157:473–479.
Lagrand WK, Niessen HWM, Wolbink G-J, Jaspars LH, Visser CA, Verheugt FWA, et al.: C-reactive protein colocalizes with complement in human hearts during acute myocardial infarction. Circulation 1997;95:97–103.
Ganrot PO, Kindmark C-O. C-reactive protein—a phagocytosis-promoting factor. Scand J Lab Clin Invest 1969;24:215–219.
Mortensen RF, Duszkiewicz JA: Mediation of CRP-dependent phagocytosis through mouse macrophage Fc-receptors. J Immunol 1977;119:1611–1616.
Kilpatrick JM, Volanakis JE: Opsonic properties of C-reactive protein. Stimulation by phorbol myristate acetate enables human neutrophils to phagocytize C-reactive protein-coated cells. J Immunol 1985;134:3364–3370.
Nakagomi A, Freedman SB, Geczy CL: Interferongamma and lipopolysaccharide potentiate monocyte tissue factor induction by C-reactive protein: relationship with age, sex, and hormone replacement treatment. Circulation 2000;101:1785–1791.
Pue CA, Mortensen RF, Marsh CB, Pope HA, Wewers MD: Acute phase levels of C-reactive protein enhance IL-1b and IL-1ra production by human blood monocytes but inhibit IL-1b and IL-1ra production by alveolar macrophages. J Immunol 1996;156:1594–1600.
Tilg H, Vannier E, Vachino G, Dinarello CA, Mier JW: Antiinflammatory properties of hepatic acute phase proteins: Preferential induction of Interleukin 1 (IL-1) receptor antagonist over IL-1β synthesis by human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. J Exp Med 1993;178:1629–1636.
Zeller JM, Kubak BM, Gewurz H: Binding sites for C-reactive protein on human monocytes are distinct from IgG Fc receptors. Immunol 1989;67:51–55.
Muller H, Fehr J: Binding of C-reactive protein to human polymorphonuclear leukocytes: evidence for association of binding sites with Fc receptors. J Immunol 1986;136:2202–2207.
Zeller JM, Landay AL, Lint TF, Gewurz H: Enhancement of human peripheral blood monocyte burst activity by aggregated C-reactive protein. J Leuk Biol 1986;40:769.
Cosio G, Douglas SD, Michael AF: The human FcR: effects of pronase on soluble immune complex binding by polymorphonuclear leucocytes, monocytes and pulmonary macrophages. Immunol 1982;46:395–400.
Debets JMH, van de Winkel JGJ, Ceuppens JL, Dieteren IEM, Buurman WA: Cross-linking of both Fc gamma RI and Fc gamma RII induces secretion of tumor necrosis factor by human monocytes, requiring high affinity Fc-Fc gamma R interactions: functional activation of Fc gamma RII by treatment with proteases or neuraminidase. J Immunol 1990;144:1304–1310.
van de Winkel JGJ, van Ommen R, Huizinga TWJ, de Raad MAHVM, Tuijnman WB, Groenen PJTA, et al.: Proteolysis induces increased binding affinity of the monocyte type II FcR for human IgG. J Immunol 1989;143:571–578.
Crowell RE, Du Clos TW, Montoya G, Heaphy E, Mold C: C-reactive protein receptors on the human monocytic cell line U-937. Evidence for additional binding to FcγRI. J Immunol 1991;147:3445–3451.
Bodman-Smith KB, Melendez AJ, Campbell I, Harrison PT, Allen JM, Raynes JG: C-reactive proteinmediated phagocytosis and phospholipase D signalling through the high-affinity receptor for immunoglobulin G (FcgammaRI). Immunol 2002;107:252–260.
Szabo G, Miller-Graziano CL, Wu JY, Takayama T, Kodys K: Differential tumor necrosis factor production by human monocyte subsets. J Leuk Biol 1990; 47:206–216.
Bharadwaj D, Stein MP, Volzer M, Mold C, Du Clos TW: The major receptor for C-reactive protein on leukocytes is FcγRII. J Exp Med 1999;190:585–590.
Bharadwaj D, Mold C, Markham E, Du Clos TW: Serum amyloid P component binds to Fcgamma receptors and opsonizes particles for phagocytosis. J Immunol 2001;166:6735–6741.
Chi M, Tridandapani S, Zhong W, Coggeshall KM, Mortensen RF: C-reactive protein induces signaling through Fc gamma RIIa on HL-60 granulocytes. J Immunol 2002;168:1413–1418.
Schiff DE, Rae J, Martin TR, Davis BH, Curnutte JT: Increased phagocyte FcgammaRI expression and improved Fcgamma-receptor-mediated phagocytosis after in vivo recombinant human interferon-gamma treatment of normal human subjects. Blood 1997;90:3187–3194.
Ballou SP, Lozanski G: Induction of inflammatory cytokine release from human monocytes by C-reactive protein. Cytokine 1992;4:361–368.
Galve-de Rochemonteix B, Wiktorowicz K, Kushner I, Dayer JM: C-reactive protein increases production of IL-l alpha, IL-1 beta, and TNF-alpha, and expression of mRNA by human alveolar macrophages. J Leuk Biol 1993;53:439–445.
Arend WP, Smith MF, Janson RW, Joslin FG: IL-1 receptor antagonist and IL-1 beta production in human monocytes are regulated differently. J Immunol 1991;147:1530–1536.
Mold C, Rodriguez W, Rodic-Polic B, Du Clos TW: C-reactive protein mediates protection from lipopolysaccharide through interactions with Fc gamma R. J Immunol 2002;169:7019–7025.
Stein MP, Mold C, Du Clos TW: C-reactive protein binding to murine leukocytes requires Fcγ receptors. J Immunol 2000;164:1514–1520.
Sylvestre DL, Ravetch JV: A dominant role for mast cell Fc receptors in the Arthus reaction. Immunity 1996;5:387–390.
Mold C, Gresham HD, Du Clos TW: Serum amyloid P component (SAP) and C-reactive protein (CRP) mediate phagocytosis through murine Fcγ receptors. J Immunol 2001;166:1200–1205.
Sutterwala FS, Noel GJ, Salgame P, Mosser DM: Reversal of proinflammatory responses by ligating the macrophage Fcγ receptor type I. J Exp Med 1998;188:217–222.
Ravetch JV, Lanier LL: Immune inhibitory receptors. Science 2000;290:84–89.
Takai T, Ono M, Hikida M, Ohmori H, Ravetch JV: Augmented humoral and anaphylactic responses in Fc gamma RII-deficient mice. Nature 1995;379:346–349.
Clynes R, Maizes JS, Guinamard R, Ono M, Takai T, Ravetch JV: Modulation of immune complex-induced inflammation in vivo by the coordinate expression of activation and inhibitory Fc receptors. J Exp Med 1999;189:179–185.
Szalai AJ, VanCott JL, McGhee JR, Volanakis JE, Benjamin WH, Jr.: Human C-reactive protein is protective against fatal Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium infection in transgenic mice. Infect Immun 2000;68:5652–5656.
Colina J, Shen Y, Snapper CM: Dendritic cells pulsed with intact Streptococcus pneumoniae elicit both protein-and polysaccharide-specific immunoglobulin isotype responses in vivo through distinct mechanisms. J Exp Med 2002;195:1–13.
Szalai AJ, Briles DE, Volanakis JE: Human C-reactive protein is protective against fatal Streptococcus pneumoniae infection in transgenic mice. J Immunol 1995;155:2557–2563.
Lysenko E, Richards JC, Cox AD, Stewart A, Martin A, Kapoor M, Weiser JN: The position of phosphorylcholine on the lipopolysaccharide of Haemophilus influenzae affects binding and sensitivity to C-reactive protein mediated killing. Mol Immunol 2000;35:234–235.
Szalai AJ, Briles DE, Volanakis JE: Role of complement in C-reactive protein-mediated protection of mice from Streptococcus pneumoniae. Infect Immun 1996;64:4850–4853.
Saeland E, Vidarsson G, Leusen JH, Van Garderen E, Nahm MH, Vile-Weekhout H, et al.: Central role of complement in passive protection by human IgG1 and IgG2 anti-pneumococcal antibodies in mice. J Immunol 2003;170:6158–6164.
Xia D, Samols D: Transgenic mice expressing rabbit C-reactive protein are resistant to endotoxemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1997;94:2575–2580.
Chae MR, Park BH, Kim JS, Rho JW, Kim HR: Protective effect of C-reactive protein against the lethality induced by Vibrio vulnificus lipopolysaccharide. Microbiol Immunol 2000;44:335–340.
Noursadeghi M, Bickerstaff MC, Gallimore JR, Herbert J, Cohen J, Pepys MB: Role of serum amyloid P component in bacterial infection: protection of the host or protection of the pathogen. Proc Natl Acad USA 2000;97:14584–14589.
Heuertz RM, Samols D, Webster RO: Transgenic mice expressing plasma rabbit C-reactive protein exhibit diminished vascular permeability and neutrophil infiltration in C5a-induced alveolitis. FASEB J 1994;8:A1064.
Heuertz RM, Dongyuan X, Samols D, Webster RO: Inhibition of C5a des Arg-induced neutrophil alveolitis in transgenic mice expressing C-reactive protein. Am J Physiol 1994;266:L649-L654.
Kew RM, Hyers TM, Webster RO: Human C-reactive protein inhibits neutrophil chemotaxis in vitro: Possible implications for the adult respiratory distress syndrome. J Lab Clin Med 1990;115:339–345.
Gerard C, Bruyns C, Marchant A, Abramowicz D, Vandenabeele P, Delvaux A, et al. Interleukin 10 reduces the release of Tumor Necrosis Factor and prevents lethality in experimental endotoxemia. J Exp Med 1993;177:547–550.
Du Clos TW, Zlock L, Hicks PS, Mold C: Decreased autoantibody levels and enhanced survival of (NZB X NZW) F1 mice treated with C-reactive protein. Clin Immunol Immunopath 1994;70:22–27.
Szalai AJ, Weaver CT, McCrory MA, van Ginkel FW, Reiman RM, Kearney JF, et al.: Delayed lupus onset in (NZBxNZW)F1 mice expressing a human C-reactive protein transgene. Arthritis Rheum 2003;48:1602–1611.
Groux H, O'Garra A, Bigler M, Rouleau M, Antonenko S, de Vries JE, Roncarolo MG: A CD4+T-cell subset inhibits antigen-specific T-cell responses and prevents colitis. Nature 1997;389:737–742.
Ridker PM, Cushman M, Stampfer MJ, Tracy RP, Hennekens CH: Inflammation, aspirin and the risk of cardiovascular disease in apparently healthy men. N Engl J Med 1997;336:973–979.
Ridker P, Buring J, Shih J, Matiaws M, Hennekens C: Prospective study of C-reactive protein and the risk of future cardiovascular events among apparently healthy women. Circulation 1998;98:731–733.
Griselli M, Herbert J, Hutchinson WL, Taylor KM, Sahail M, Drausz T, Pepys MB: C-reactive protein and complement are important mediators of tissue damage in acute myocardial infarction. J Exp Med 1999; 190:1733–1739.
Nagpurkar A, Mookerjea S: A novel phosphorylcholine-binding protein from rat serum and its effect on heparin-lipoprotein complex formation in the presence of calcium. J Biol Chem 1981;256:7440–7446.
Diaz Padilla N, Bleeker WK, Lubbers Y, Rigter GM, Van Mierlo GJ, Daha MR, Hack CE: Rat C-reactive protein activates the autologous complement system. Immunol 2003;109:564–571.
Cermak J, Key N, Bach R, Balla J, Jacob H, Vercellotti G: C-reactive protein induces human peripheral blood monocytes to synthesize tissue factor. Blood 1993;82:513–520.
Zhou P, Thomassen MJ, Pettay J, Deodhar SD, Barna BP: Human monocytes produce monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 (MCP-1) in response to a synthetic peptide derived from C-reactive protein. Clin Immunol Immunopathol 1995;74:84–88.
Pasceri V, Cheng JS, Willerson JT, Yeh ET, Chang J: Modulation of C-reactive protein-mediated monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 induction in human endothelial cells by anti-atherosclerosis drugs. Circulation 2001;103:2531–2534.
Danenberg HD, Szalai AJ, Swaminathan RV, Peng L, Chen Z, Seifert P, et al.: Increased thrombosis after arterial injury in human C-reactive protein-transgenic mice C-reactive protein, lipoprotein(a), homocysteine, and male sex contribute to carotid atherosclerosis in peritoneal dialysis patients. Circulation 2003;108:512–515.
Rodriguez W, Mold C, Katavanovski M, Hutt J, Marnell LL, DuClos TW: C-reactive protein reverses on going proteinuria in autoimmune mice. Arthritis Rheum 2004; in press.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Du Clos, T.W., Mold, C. C-reactive protein. Immunol Res 30, 261–277 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1385/IR:30:3:261
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1385/IR:30:3:261