Abstract
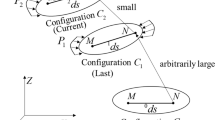
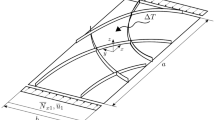
In this article, the elastic-plastic finite element formulations using dynamic explicit time-integration schemes are proposed for numerical analysis of automotive body panel stamping processes. A general formulation of finite element simulation for complex sheet forming processes with arbitrarily shaped tools is briefly introduced. In finite element simulation of automotive body panel stamping processes, the robustness and stability of computation are important requirements since the computation time and convergency become major points of consideration besides the solution accuracy due to the complexity of geometry and boundary conditions. For analyses of more complex cases with larger and more refined meshes, the explicit method is more time effective than the implicit method, and it has no convergency problem and has the robust nature of contact and friction algorithms, although the implicit method is widely used because of excellent accuracy and reliability. The elastic-plastic scheme is more reliable and rigorous, while the rigid-plastic scheme requires short computation time. The performance of the dynamic explicit algorithms is investigated by comparing the simulation results of forming of complex-shaped automotive body parts, such as a fuel tank and a rear hinge, with the experimental results. It has been shown that dynamic explicit schemes provide quite similar results to the experimental results. It is thus shown that the proposed dynamic explicit elastic-plastic finite element method enables an effective computation for complicated automotive body panel stamping processes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
C.H. Lee and S. Kobayashi, New Solutions to Rigid-Plastic Deformation Problems Using a Matrix Method, J. Eng. Ind. (Trans. ASME), Vol 95, 1973, p 865–873.
N.M. Wang and B. Budiansky, Analysis of Sheet Metal Stamping by a Finite Element Method, J. Appl. Mech., Vol 45, March 1978, p 73–82.
H.B. Shim and D.Y. Yang, An Elastic-Plastic Finite Element Analysis on Hydrostatic Bulging of Rectangular Diaphragms by Using Layered Degenerated Shell Elements, Int. J. Mech. Sci., Vol. 32, 1990, p 49–64
N.M. Wang and S.C. Tang, Analysis of Bending Effects in Sheet Forming Operations, Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng., Vol 25, 1988, p 253–267
K. Mattiason, Numerical Simulation of Stretching Processes, SI-MOP-I, Proc. of the First Int. Workshop, K. Lange, Ed., Stuttgart, 1985, p 170–213
D.Y. Yang, D.W. Jung, I.S. Song, D.J. Yoo, and J.H. Lee, Comparative Investigation into Implicit, Explicit and Iterative Implicit/Explicit Schemes for the Simulation of Sheet-Metal Forming Processes, J. Mater. Process. Technol., Vol 50, 1995, p 39–53
D.J. Yoo, I.S. Song, D.Y. Yang, and J.H. Lee, Rigid-Plastic Finite Element Analysis of Sheet Metal Forming Processes Using Continuous Contact Treatment and Membrane Elements Incorporating Bending Effect, Int. J. Mech. Sci., Vol 36 (No. 6), 1994, p 513–546
J.C. Nagtegaal and L.M. Taylor, Comparison of Implicit and Explicit Finite Element Methods for Analysis of the FE-Sim. of 3-D Sheet Metal Forming Processes, Automotive Ind. Conf., J. Reissner, et al., Ed., VDI Verlag, Dusseldorf, 1991
ABAQUS/Explicit: User’s Examples and Theory Manuals, Hibbitt, Karlsson and Sorensen, 1991
E. Hinton, T. Rock, and O.C. Zienkiewicz, A Note on Mass Lumping and Related Processes in the Finite Element Method, Earthquake Eng. Struct. Dynamics, Vol 4 (No. 3), 1976, p 145–149.
K.S. Surana, Lumped Mass Matrices with Non-Zero Inertia for General Shell and Axisymmetric Shell Elements, Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng., Vol 12 (No. 11), 1978, p 1635–1650
D.J. Yoo, “Analysis of Three-Dimensional Sheet Metal Forming Processes Using Continuous Surface and Contact Treatment,” Ph.D. thesis, Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology, 1994
I.S. Song, D.J. Yoo, J.W. Yoon, D.Y. Yang, H. Huh, and J.H. Lee, Finite Element Analysis and Design of Binder Wraps for Automobile Sheet Metal Parts Using Surface Boundary Condition, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., Vol 4 (No. 5), 1996, p 593–598
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jung, D.W., Yang, D.Y. Elastic-plastic finite element analysis of automotive body panel stamping processes using dynamic explicit time integration scheme. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 8, 719–729 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1361/105994999770346503
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1361/105994999770346503