Abstract
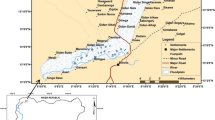
To link regional land use/cover changes with environmental effects, land cover changes are required to reflect vegetation successions, whereas the land cover classification systems commonly used nowadays cannot serve this purpose. In this paper, a new land cover classification system is established in which land covers are classified by the vegetation successions, taking Zamtang County, Barkam County and Jinchuan County in the upper Dadu River watershed as a study area. Using multi-temporal remote sensing images, the land cover data of 1967, 1986 and 2000 are obtained by means of integration of unsupervised classification and visual interpretation methods. The database facilitates the study of land use/cover changes, environmental effects and ecological construction. Land cover changes reflect the main ecological processes in the upper Dadu River watershed. The landscape composed mainly of grasslands, wildwoods and alpine scrubs in 1967 was changed to that of grasslands, secondary forests, alpine scrubs, fragmentary wildwoods, artificial forests, secondary scrubs in 2000, meanwhile, the landscape got more fragmentized. The total area of the forests decreased by 9.43%.
Study results have shown the process of restoration of logged areas in forest centers. From 1967 to 2000, only 6.86 percents of logged areas were converted to shrubs, meadows or croplands, and the rest were converted into artificial forests or secondary forests. So the ecological shelter functions will be restored, stage by stage. Firewood collection, charcoal production and overgrazing are the three major triggers for the extensive degradation of alpine oak forests, Sabina tibetica forests and meadows. The arid valley grasslands expanded too. The degradation of vegetation in the southern slopes impairs ecological shelter functions and affects livelihood of local residents, so it is essential to find effective measures for ecological restoration and reconstruction. Field investigations have found that the current measures have not concerned with how to keep the livelihood of local farmers and herders. The most important measure for ecological protection and restoration is to help the farmers and herders to raise the living standard, which means that they will never need to rely only on the colonizing of croplands, the logging of forests and the grazing of livestock to make a livingKeywords: land use/cover classification, upper Dadu River watershed, vegetation successions, GIS, RS.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson, R.J., Hardy, E. E., Roach, T. J. et al., A land use and land cover classification system for use with remote sensor data, Washington: United States Government Printing Office, 1976.
Leemans, R., Goldewijk, K.K., Oldfield, F., Developing a fast- track global database of land-cover history, LUCC Newsletter, Issue No. 5: 6–7, LUCC International Project Office, Lou-vain-la-Neuve, 2000.
Grigirio, D.A., Jansen, J. M., Land cover classification system (LCCS): classification concepts and user manual, Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, Rome, 2000.
Liu, J.Y., The Macro Investigation and Dynamic Research of the Resources and Environment (in Chinese), Beijing: Science and Technology Press, 1996.
Geist, J. H., Lambin, E. F., What drives tropical deforestation? A meta-analysis of proximate and underlying causes of deforestation based on subnational case study evidence, LUCC report series, 2002, No. 4, LUCC International Project Office, Louvain-la-Neuve, 2001.
Fang, J. Y., Chen, A. P., Peng, C. H. et al., Changes in forest bio-mass carbon storage in China between 1949 and 1998, Science, 2001, 292: 2320–2322.
Solomon, D., Lehmann, J., Mamo, T. et al., Phosphorus forms and dynamics as influenced by land use changes in the subhumid Ethiopian highlands, Geoderma, 2002, 105(1): 21–48.
Islam, K. R., Weil, R. R., Land use effects on soil quality in a tropical forest ecosystem of Bangladesh, Agriculture, Ecosystems and Environment, 2000, 79(1): 9–16.
Fujisaka, S., Escobar, G., Veneklaas, E. J., Weedy fields and forests: interactions between land use and the composition of plant communities in the Peruvian Amazon, Agriculture, Ecosystems and Environment, 2000, 78(2): 175–186.
Guo, X. D., Chen, L. D., Fu, B. J., Effects of land use/land cover changes on regional ecological environment, Advance in Environment Science (in Chinese), 1999, 7(6): 66–75.
Chen, S. Q., Liu, J. Y., Zhuang, D. F. et al., Quantifying land use and land cover change in Xilin River Basin Using Multitemporal Landsat TM/ETM sensor data, Acta Geographica Sinica (in Chinese), 2003, 58(1): 45–52.
Wang, J. L., Ma, J., He, S. F., Land cover changes and the environmental effects, Characteristics of Land Cover Changes in the Nujiang Watershed of Northwest Yunnan Province (ed. Physical Geography Department of Geographical Society of China) (in Chinese), Beijing: Planet Map Press, 2002, 130–140.
Xu, Y., Sidle, C.R., Land use change and its regulation of Yangou watershed in Loess Hilly-gully region, Acta Geographica Sinica (in Chinese), 2001, 56(6): 657–666.
Fu, B. J., Chen, L. D., Ma, K. M., The effect of land use change on the regional environment in the Yangjuangou catchment in the Loess Plateau of China, Acta Geographica Sinica (in Chinese), 1999, 54(3): 241–246.
Fei, S. M., Yang, Y. P., On the position and effect of Sichuan forestry in the construction of the ecological protective screen for the Upper Reaches of the Changjiang River, Journal of Sichuan Forestry Science and Technology (in Chinese), 2002, 23(1): 27–35.
Pan, K. W., Wu, N., Pan, K. Z. et al., A discussion on the issues of the reconstruction of ecological shelter zone on the upper reaches of the Yangtze River, Acta Ecologica Sinica (in Chinese), 2004, 24(3): 617–629.
Editorial Board of Forests in Sichuan, Forests in Sichuan (in Chinese), Beijing: Chinese Forestry Press, 1992, 1335–1352.
Zhou, Y. W., Forest Industry in Aba (in Chinese), Chengdu: Si-chuan Art Press, 1999, 140–203.
Wang, J. X., Quality retrogradation of environment and recovery of forest vegetation of the frail zones of forest ecological environment in the upper reaches of Yangtse River, Journal of Chendu University of Technology (in Chinese), 2000, 27(suppl.): 170–174.
Bai, W. Q., Zhang, Y. L., Bao, W. K., Landscape patterns and dynamics in the upper reaches of the Dadu River, Journal of Natural Resources (in Chinese), 2003, 18(1): 75–80.
Bai, W. Q., Yan, J. Z., Zhang, Y. L., Land use/land cover change and driving forces in the region of upper reaches of the Dadu River, Progress in Geography (in Chinese), 2004, 23(1): 71–78.
Deng, H. P., Li, X. B., Chen, J. F. et al., Simulation of hydrological response to land cover changes in the Suomo Basin, Acta Geographica Sinica (in Chinese), 2003, 58(1): 53–62.
Cooperation Group for Vegetation of SichuanVegetation in Si-chuan (in Chinese), Chengdu: Sichuan People’s Press, 1980, 263–267.
Bao, W. K., Zhang, Y. L., Wang, Q., Rehabilitation and degradation for subalpine coniferous forest on the upper reaches of Dadu River of eastern Tibetan Plateau, Journal of Mountain Science (in Chinese), 2002, 20(2): 194–198.
Edition Committee of CAS of “Vegetation Map of China”, Vegetation Map of China (in Chinese), Beijing: Science Press, 2000.
Su, Y. M., Wang, J. X., Shi, L. X. et al., Vegetation biomass and biological productivity dynamics of cutting-blanks in their early succession stage in western Sichuan, Journal of Sichuan Forestry Science and Technology (in Chinese), 1999, 20(4): 14–21.
He, H., Qiao, Y. K., Liu, Q. et al., Dynamics of biomass and stem volume of Picea asperrata stands in artificial restoration process of subalpine coniferous forest, Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology (in Chinese), 2004, 15(5): 748–752.
Hu, H., Liu, S. Q., Chen, Q. H. et al., Changes of soil properties during artificial recovery of subalpine coniferous forests in western Sichuan, Chinese Journal of Applied and Environmental Biology (in Chinese), 2001, 7(4): 308–314.
Wu, Y., Liu, Q., Qiao, Y. K. et al., Species diversity changes in subalpine coniferous forests of different restoration stages and their effects on soil properties, Acta Phytoecologica Sinica (in Chinese), 2001, 25(6): 648–655.
Liu, S. R., Sun, P. S., Wang, J. X., Hydrological functions of forest vegetation in upper reaches of the Yangtze River, Journal of Natural Resources (in Chinese), 2001, 16(5): 451–456.
Bao, W. K., Zhang, Y. L., Wang, Q. et al., Plant diversity along time sequence (1-30 years) of artificial forest rehabilitation on subalpine cut land in the eastern Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, Acta Phytoecologica Sinica (in Chinese), 2002, 26(3): 330–338.
Chen, W. N., Wu, N., Luo, P. et al., Species diversity and arbor population distribution pattern of Sabina Przewalskill community in the forestgrassland ecotone in the watershed of upper Minjiang River, Chinese Journal of Applied and Environmental Biology (in Chinese), 2003, 9(3): 221–225.
Wu, N., Liu, Z. G., Probing into the causes of geographical pattern of subalpine vegetation on the eastern Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau, Chinese Journal of Applied and Environmental Biology (in Chinese), 1998, 4(3): 290–297.
Bao, W. K., Chen, Q. H., Chen, K. M., Environment control techniques for vegetation restoration in dry valley of upper reaches of Minjiang River, Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology (in Chinese), 1999, 10(5): 542–544.
Zhang, R. Z., The Dry Valleys of the Hengduan Mountains Region (in Chinese), Beijing: Science Press, 1992, 7–14.
He, Q. H., He, Y. H., Bao, W. K., Dynamics of soil water contents on south-facing of dry valley in the upper reaches of the Minjiang River, Chinese Journal of Applied and Environmental Biology (in Chinese), 2004, 10(1): 68–74.
Guo, X. M., The main issues and countermeasures of ecological construction of the dry valleys in Sichuan, Social Science Study (in Chinese), 2001(5): 33–36.
Bao, W. K., Wu, N., Human-induced disturbance on alpine and subalpine meadow and its afereffects in Deqin County of north-western Yunan Province, Grassland of China (in Chinese), 2003, 25(2): 1–8.
Editorial Committee of Chorography of Rangtang County, Aba Tibetan Autonomic Prefecture, Sichuan, Rangtang Chorography (in Chinese), Beijing: The Ethical Publishing House, 1997, 305–306.
Editorial Committee of Chorography of Jinchuan County, Aba Tibetan Autonomous Prefecture, Sichuan, Jinchuan Chorography (in Chinese), Beijing: The Ethical Publishing House, 1994, 450–451.
Editorial Committee of Chorography of Barkam County, Sichuan, Barkam chorography (in Chinese), Chengdu: Sichuan People’s Press, 1997, 120.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yan, J., Zhang, Y., Bai, W. et al. Land cover changes based on plant successions: Deforestation, rehabilitation and degeneration of forest in the upper Dadu River watershed. Sci. China Ser. D-Earth Sci. 48, 2214–2230 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1360/04yd0128
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1360/04yd0128