Abstract
Background
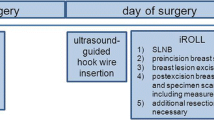
Accurate preoperative localization of nonpalpable breast cancer is essential to achieve complete resection. Radioguided occult lesion localization (ROLL) has been introduced as an alternative for wire-guided localization (WGL). Although efficacy of ROLL has been established in a randomized controlled trial, cost-effectiveness of ROLL compared with WGL is not yet known. The objective of this study was to determine whether ROLL has acceptable cost-effectiveness compared with WGL.
Methods
An economic evaluation was performed along with a randomized controlled trial (ClinicalTrials.gov, No. NCT00539474). Women (>18 years) with histologically proven nonpalpable breast cancer and eligible for breast conserving treatment with sentinel node procedure were randomized to ROLL (n = 162) or WGL (n = 152). Empirical data on direct medical costs were collected, and changes in quality of life were measured over a 6-month period. Bootstrapping was used to assess uncertainty in cost-effectiveness estimates, and sensitivity of the results to the missing data approach was investigated.
Results
In total, 314 patients with 316 invasive breast cancers were enrolled. On average ROLL required the same time as WGL for the surgical procedure (119 vs 118 min), resulted in a 7 % higher reinterventions risk, and 13 % more complications. Quality of life effects were similar (difference 0.00 QALYs 95 % CI (−0.04–0.05). Total costs were also similar for ROLL and WGL (+€26 per patient 95 % CI €−250–311).
Conclusion
ROLL is comparable to WGL with respect to both costs and quality of life effects as measured with the EQ5D and will therefore not lead to more cost-effective medical care.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
NKR cijfers over kanker. 2011. Available: www.cijfersoverkanker.nl.
Fleming FJ, Hill AD, McDermott EW, O’Doherty A, O’Higgins NJ, Quinn CM. Intraoperative margin assessment and re-excision rate in breast conserving surgery. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2004;30:233–7.
Burkholder HC, Witherspoon LE, Burns RP, Horn JS, Biderman MD. Breast surgery techniques: preoperative bracketing wire localization by surgeons. Am Surg. 2007;73:574–8; discussion 578–9.
Lovrics P, Cornacchi S, Vora R, Goldsmith C, Kahnamoui K. Systematic review of radio-guided surgery for nonpalpable breast cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. 2010;17:S181.
Lovrics PJ, Cornacchi SD, Farrokhyar F, Garnett A, Chen V, Franic S, et al. The relationship between surgical factors and margin status after breast-conservation surgery for early stage breast cancer. Am J Surg. 2009;197:740–6.
Postma EL, Witkamp AJ, van den Bosch MA, Verkooijen HM, van Hillegersberg R. Localization of nonpalpable breast lesions. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2011;11:1295–302.
Dodd G, Fry K, Delany W. Pre-operative localization of occult carcinoma of the breast. In: Nealon TF Jr, editors. Management of the Patient with Cancer. Philadelphia: Saunders; 1965. p. 88–113.
Verkooijen HM, Peeters PH, Buskens E, Koot VC, Borel Rinkes IH, Mali WP, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of large-core needle biopsy for nonpalpable breast disease: a meta-analysis. Br J Cancer. 2000;82:1017–21.
Klimberg VS, Kepple J, Shafirstein G, Adkins L, Henry-Tillman R, Youssef E, et al. eRFA: excision followed by RFA-a new technique to improve local control in breast cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. 2006;13:1422–33.
Helvie MA, Ikeda DM, Adler DD. Localization and needle aspiration of breast lesions: complications in 370 cases. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1991;157:711–4.
Azoury F, Sayad P, Rizk A. Thoracoscopic management of a pericardial migration of a breast biopsy localization wire. Ann Thorac Surg. 2009;87:1937–9.
Chadwick DR, Shorthouse AJ. Wire-directed localization biopsy of the breast: an audit of results and analysis of factors influencing therapeutic value in the treatment of breast cancer. Eur J Surg Oncol. 1997;23:128–33.
Seifi A, Axelrod H, Nascimento T, Salam Z, Karimi S, Avestimehr S, et al. Migration of guidewire after surgical breast biopsy: an unusual case report. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2009;32:1087–90.
Postma EL, Verkooijen HM, van Esser S, et al. Efficacy of ‘radioguided occult lesion localisation’ (ROLL) versus ‘wire-guided localisation’ (WGL) in breast conserving surgery for non-palpable breast cancer: a randomised controlled multicentre trial. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2012;136:469–78.
van Esser S, Hobbelink MG, Peeters PH, Buskens E, van der Ploeg IM, Mali WP, et al. The efficacy of ‘radio guided occult lesion localization’ (ROLL) versus ‘wire-guided localization’ (WGL) in breast conserving surgery for non-palpable breast cancer: a randomized clinical trial—ROLL study. BMC Surg. 2008;8:9.
EuroQol—a new facility for the measurement of health-related quality of life. The EuroQol Group. Health Policy. 1990;16:199–208.
Donders AR, van der Heijden GJ, Stijnen T, Moons KG. Review: a gentle introduction to imputation of missing values. J Clin Epidemiol. 2006;59:1087–91.
van der Heijden GJ, Donders AR, Stijnen T, Moons KG. Imputation of missing values is superior to complete case analysis and the missing-indicator method in multivariable diagnostic research: a clinical example. J Clin Epidemiol. 2006:59:1102–9.
Burton A, Billingham LJ, Bryan S. Cost-effectiveness in clinical trials: using multiple imputation to deal with incomplete cost data. Clin Trials. 2007:;4:154–61.
van Hout BA, Al MJ, Gordon GS, Rutten FF. Costs, effects and C/E-ratios alongside a clinical trial. Health Econ. 1994;3:309–19.
Nadeem R, Chagla LS, Harris O, Desmond S, Thind R, Titterrell C, et al. Occult breast lesions: A comparison between radioguided occult lesion localisation (ROLL) vs. wire-guided lumpectomy (WGL). Breast. 2005;14:283–9.
Moreno M, Wiltgen JE, Bodanese B, Schmitt RL, Gutfilen B, da Fonseca LM. Radioguided breast surgery for occult lesion localization—correlation between two methods. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2008;27:29.
Ronka R, Krogerus L, Leppanen E, Von Smitten K, Leidenius M. Radio-guided occult lesion localization in patients undergoing breast-conserving surgery and sentinel node biopsy. Am J Surg. 2004;187:491–6.
Medina-Franco H, Abarca-Perez L, Garcia-Alvarez MN, Ulloa-Gomez JL, Romero-Trejo C, Sepulveda-Mendez J. Radioguided occult lesion localization (ROLL) versus wire-guided lumpectomy for non-palpable breast lesions: a randomized prospective evaluation. J Surg Oncol. 2008;97:108–11.
Zgajnar J, Hocevar M, Frkovic-Grazio S, Hertl K, Schwarzbartl-Pevec A, Schweiger E, et al. Radioguided occult lesion localization (ROLL) of the nonpalpable breast lesions. Neoplasma. 2004;51:385–9.
Lovrics PJ, Goldsmith CH, Hodgson N, McCready D, Gohla G, Boylan C, et al. A multicentered, randomized, controlled trial comparing radioguided seed localization to standard wire localization for nonpalpable, invasive and in situ breast carcinomas. Ann Surg Oncol. 2011;18:3407–14.
Jakub JW, Gray RJ, Degnim AC, Boughey JC, Gardner M, Cox CE. Current status of radioactive seed for localization of non palpable breast lesions. Am J Surg. 2010;199:522–8.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This study is conducted for the ROLL Study Group. The study group members are listed in Appendix.
Appendix
Appendix
Study Group Members
Amphia Hospital: Breda: G. Van der Schelling, A. Rijken, J. Nuytinck, E. Luiten, E. Tetteroo, H. Dijkstra, P. Raaymakers, P. Van Noorden, J. Baas, D. Vos, J. Wijsman; St. Antonius Hospital, Nieuwegein: R. Koelemij, E. Theunissen, S. van Esser, A. van Wieringen, P. Go, J. Lavalaye, T. Bollen, M. Appelman; UMC Utrecht, Utrecht: E.L. Postma, L. Glaap, A.J. Witkamp, I.H.M Borel Rinkes, R. van Hillegersberg, M. Hobbelink, A. Fernandez, G. Stapper, M. van den Bosch, W. Mali, H. Verkooijen, S.M. Willems, P.J. van Diest; Maasstad ziekenhuis, Rotterdam: C. Contant.
See Table 5.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Postma, E.L., Koffijberg, H., Verkooijen, H.M. et al. Cost-Effectiveness of Radioguided Occult Lesion Localization (ROLL) Versus Wire-Guided Localization (WGL) in Breast Conserving Surgery for Nonpalpable Breast Cancer: Results from a Randomized Controlled Multicenter Trial. Ann Surg Oncol 20, 2219–2226 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-013-2888-7
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-013-2888-7