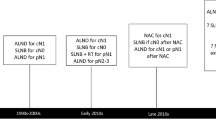
Abstract
Neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NAC) is increasingly being used in the treatment of locally advanced breast cancer as well as for early breast cancer. Axillary lymph node dissection has been the standard method of staging the axilla in the neoadjuvant setting. Since the sentinel lymph node biopsy was introduced in the early 1990s, less invasive approaches to axillary staging in patients undergoing neoadjuvant therapy have been proposed. In this review, we discuss the effects of NAC, the imaging modalities that have been used to evaluate the axillary lymph nodes, and the role and timing of sentinel lymph node biopsy in the neoadjuvant setting. Finally, we propose a treatment algorithm for patients undergoing NAC on the basis of the current data.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kaufmann M, von Minckwitz G, Bear HD, et al. Recommendations from an international expert panel on the use of neoadjuvant (primary) systemic treatment of operable breast cancer: new perspectives, 2006. Ann Oncol. 2007;18:1927–34.
Fisher B, Brown A, Mamounas E, et al. Effect of preoperative chemotherapy on local-regional disease in women with operable breast cancer: findings from National Surgical Adjuvant Breast and Bowel Project B-18. J Clin Oncol. 1997;15:2483–93.
Mamounas EP. Sentinel lymph node biopsy after neoadjuvant systemic therapy. Surg Clin North Am. 2003;83:931–42.
Kuerer HM, Sahin AA, Hunt KK, et al. Incidence and impact of documented eradication of breast cancer axillary lymph node metastases before surgery in patients treated with neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Ann Surg. 1999;230:72–8.
Singletary SE, Connolly JL. Breast cancer staging: working with the sixth edition of the AJCC Cancer Staging Manual. CA Cancer J Clin. 2006;56:37–47.
Carey LA, Metzger R, Dees EC, et al. American Joint Committee on Cancer tumor-node-metastasis stage after neoadjuvant chemotherapy and breast cancer outcome. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2005;97:1137–42.
Kuerer HM, Newman LA, Smith TL, et al. Clinical course of breast cancer patients with complete pathologic primary tumor and axillary lymph node response to doxorubicin-based neoadjuvant chemotherapy. J Clin Oncol. 1999;17:460–9.
Vassallo P, Wernecke K, Roos N, Peters PE. Differentiation of benign from malignant superficial lymphadenopathy: the role of high-resolution US. Radiology. 1992:215–20.
Feu J, Tresserra F, Fabregas R, et al. Metastatic breast carcinoma in axillary lymph nodes: in vitro US detection. Radiology. 1997;205:831–5.
Klauber-Demore N, Kuzmiak C, Rager EL, et al. High-resolution axillary ultrasound is a poor prognostic test for determining pathologic lymph node status in patients undergoing neoadjuvant chemotherapy for locally advanced breast cancer. Am J Surg. 2004;188:386–9.
Oruwari JU, Chung MA, Koelliker S, Steinhoff MM, Cady B. Axillary staging using ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration biopsy in locally advanced breast cancer. Am J Surg. 2002;184:307–9.
Vlastos G, Fornage BD, Mirza NQ, et al. The correlation of axillary ultrasonography with histologic breast cancer downstaging after induction chemotherapy. Am J Surg. 2000;179:446–52.
Kuerer HM, Newman LA, Fornage BD, et al. Role of axillary lymph node dissection after tumor downstaging with induction chemotherapy for locally advanced breast cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. 1998;5:673–80.
Krishnamurthy S, Sneige N, Bedi DG, et al. Role of ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration of indeterminate and suspicious axillary lymph nodes in the initial staging of breast carcinoma. Cancer. 2002;95:982–8.
Alkuwari E, Auger M. Accuracy of fine-needle aspiration cytology of axillary lymph nodes in breast cancer patients: a study of 115 cases with cytologic-histologic correlation. Cancer. 2008;114:89–93.
Bonnema J, van Geel AN, van Ooijen B, et al. Ultrasound-guided aspiration biopsy for detection of nonpalpable axillary node metastases in breast cancer patients: new diagnostic method. World J Surg. 1997;21:270–4.
Koelliker SL, Chung MA, Mainiero MB, Steinhoff MM, Cady B. Axillary lymph nodes: US-guided fine-needle aspiration for initial staging of breast cancer—correlation with primary tumor size. Radiology. 2008;246:81–9.
de Kanter AY, van Eijck CH, van Geel AN, et al. Multicentre study of ultrasonographically guided axillary node biopsy in patients with breast cancer. Br J Surg. 1999;86:1459–62.
Boughey JC, Middleton LP, Harker L, et al. Utility of ultrasound and fine-needle aspiration biopsy of the axilla in the assessment of invasive lobular carcinoma of the breast. Am J Surg. 2007;194:450–5.
Kvistad KA, Rydland J, Smethurst HB, et al. Axillary lymph node metastases in breast cancer: preoperative detection with dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI. Eur Radiol. 2000;10:1464–71.
Luciani A, Dao TH, Lapeyre M, et al. Simultaneous bilateral breast and high-resolution axillary MRI of patients with breast cancer: preliminary results. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2004;182:1059–67.
Memarsadeghi M, Riedl CC, Kaneider A, et al. Axillary lymph node metastases in patients with breast carcinomas: assessment with nonenhanced versus uspio-enhanced MR imaging. Radiology. 2006;241:367–77.
Wahl RL, Cody RL, Hutchins GD, Mudgett EE. Primary and metastatic breast carcinoma: initial clinical evaluation with PET with the radiolabeled glucose analogue 2-[F-18]-fluoro-2-deoxy-D-glucose. Radiology. 1991;179:765–70.
Nieweg OE, Kim EE, Wong WH, et al. Positron emission tomography with fluorine-18-deoxyglucose in the detection and staging of breast cancer. Cancer. 1993;71:3920–5.
Avril N, Dose J, Janicke F, et al. Metabolic characterization of breast tumors with positron emission tomography using F-18 fluorodeoxyglucose. J Clin Oncol. 1996;14:1848–57.
Greco M, Crippa F, Agresti R, et al. Axillary lymph node staging in breast cancer by 2-fluoro-2-deoxy-d-glucose-positron emission tomography: clinical evaluation and alternative management. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2001;93:630–5.
Wahl RL, Siegel BA, Coleman RE, Gatsonis CG. Prospective multicenter study of axillary nodal staging by positron emission tomography in breast cancer: a report of the staging breast cancer with PET Study Group. J Clin Oncol. 2004;22:277–85.
Kim T, Giuliano AE, Lyman GH. Lymphatic mapping and sentinel lymph node biopsy in early-stage breast carcinoma: a metaanalysis. Cancer. 2006;106:4–16.
Chung MH, Ye W, Giuliano AE. Role for sentinel lymph node dissection in the management of large (> or = 5 cm) invasive breast cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. 2001;8:688–92.
Lyman GH, Giuliano AE, Somerfield MR, et al. American Society of Clinical Oncology guideline recommendations for sentinel lymph node biopsy in early-stage breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23:7703–20.
Piato JR, Barros AC, Pincerato KM, Sampaio AP, Pinotti JA. Sentinel lymph node biopsy in breast cancer after neoadjuvant chemotherapy. A pilot study. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2003;29:118–20.
Hunt KK, Yi M, Mittendorf EA, et al. Sentinel lymph node surgery after neoadjuvant chemotherapy is accurate and reduces the need for axillary dissection in breast cancer patients. Ann Surg. 27 Aug 2009 [Epub ahead of print].
Tafra L, Verbanac KM, Lannin DR. Preoperative chemotherapy and sentinel lymphadenectomy for breast cancer. Am J Surg. 2001;182:312–5.
Xing Y, Foy M, Cox DD, et al. Meta-analysis of sentinel lymph node biopsy after preoperative chemotherapy in patients with breast cancer. Br J Surg. 2006;93:539–46.
Mamounas EP, Brown A, Anderson S, et al. Sentinel node biopsy after neoadjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer: results from National Surgical Adjuvant Breast and Bowel Project Protocol B-27. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23:2694–702.
Giuliano AE, Kirgan DM, Guenther JM, Morton DL. Lymphatic mapping and sentinel lymphadenectomy for breast cancer. Ann Surg. 1994;220:391–8.
Roumen RM, Valkenburg JG, Geuskens LM. Lymphoscintigraphy and feasibility of sentinel node biopsy in 83 patients with primary breast cancer. Eur J Surg Oncol. 1997;23:495–502.
Krag D, Weaver D, Ashikaga T, et al. The sentinel node in breast cancer—a multicenter validation study. N Engl J Med. 1998;339:941–6.
Crossin JA, Johnson AC, Stewart PB, Turner WW Jr. Gamma-probe-guided resection of the sentinel lymph node in breast cancer. Am Surg. 1998;64:666–8.
Snider H, Dowlatshahi K, Fan M, et al. Sentinel node biopsy in the staging of breast cancer. Am J Surg. 1998;176:305–10.
O’Hea BJ, Hill AD, El-Shirbiny AM, et al. Sentinel lymph node biopsy in breast cancer: initial experience at Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center. J Am Coll Surg. 1998;186:423–7.
Cox CE, Bass SS, McCann CR, et al. Lymphatic mapping and sentinel lymph node biopsy in patients with breast cancer. Annu Rev Med. 2000;51:525–42.
Noguchi M, Motomura K, Imoto S, et al. A multicenter validation study of sentinel lymph node biopsy by the Japanese Breast Cancer Society. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2000;63:31–40.
Lauridsen MC, Garne JP, Hessov I, et al. Sentinel lymph node biopsy in breast cancer—the Aarhus experience. Acta Oncol. 2000;39:421–2.
Fraile M, Rull M, Julian FJ, et al. Sentinel node biopsy as a practical alternative to axillary lymph node dissection in breast cancer patients: an approach to its validity. Ann Oncol. 2000;11:701–5.
Molland JG, Dias MM, Gillett DJ. Sentinel node biopsy in breast cancer: results of 103 cases. Aust N Z J Surg. 2000;70:98–102.
Canavese G, Gipponi M, Catturich A, et al. Technical issues and pathologic implications of sentinel lymph node biopsy in early-stage breast cancer patients. J Surg Oncol. 2001;77:81–7.
Schrenk P, Wayand W. Sentinel-node biopsy in axillary lymph-node staging for patients with multicentric breast cancer. Lancet. 2001;357(9250):122.
Giuliano AE, Haigh PI, Brennan MB, et al. Prospective observational study of sentinel lymphadenectomy without further axillary dissection in patients with sentinel node-negative breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2000;18:2553–9.
Sabel MS, Schott AF, Kleer CG, et al. Sentinel node biopsy prior to neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Am J Surg. 2003;186:102–5.
Ollila DW, Neuman HB, Sartor C, Carey LA, Klauber-Demore N. Lymphatic mapping and sentinel lymphadenectomy prior to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in patients with large breast cancers. Am J Surg. 2005;190:371–5.
Jones JL, Zabicki K, Christian RL, et al. A comparison of sentinel node biopsy before and after neoadjuvant chemotherapy: timing is important. Am J Surg. 2005;190:517–20.
Bonadonna G, Valagussa P, Brambilla C, et al. Primary chemotherapy in operable breast cancer: eight-year experience at the Milan Cancer Institute. J Clin Oncol. 1998;16:93–100.
Cutler SJ, Axtell LM, Schottenfeld D, Farrow JH. Clinical assessment of lymph nodes in carcinoma of the breast. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1970;131:41–52.
Fisher B, Wolmark N, Bauer M, Redmond C, Gebhardt M. The accuracy of clinical nodal staging and of limited axillary dissection as a determinant of histologic nodal status in carcinoma of the breast. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1981;152:765–72.
Sacre RA. Clinical evaluation of axillar lymph nodes compared to surgical and pathological findings. Eur J Surg Oncol. 1986;12:169–73.
de Freitas R Jr, Costa MV, Schneider SV, Nicolau MA, Marussi E. Accuracy of ultrasound and clinical examination in the diagnosis of axillary lymph node metastases in breast cancer. Eur J Surg Oncol. 1991;17:240–4.
Vaidya JS, Vyas JJ, Thakur MH, Khandelwal KC, Mittra I. Role of ultrasonography to detect axillary node involvement in operable breast cancer. Eur J Surg Oncol. 1996;22:140–3.
Miller AR, Thomason VE, Yeh IT, et al. Analysis of sentinel lymph node mapping with immediate pathologic review in patients receiving preoperative chemotherapy for breast carcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol. 2002;9:243–7.
Haid A, Tausch C, Lang A, et al. Is sentinel lymph node biopsy reliable and indicated after preoperative chemotherapy in patients with breast carcinoma? Cancer. 2001;92:1080–4.
Julian TB, Dusi D, Wolmark N. Sentinel node biopsy after neoadjuvant chemotherapy for breast cancer. Am J Surg. 2002;184:315–7.
Brady EW. Sentinel lymph node mapping following neoadjuvant chemotherapy for breast cancer. Breast J. 2002;8:97–100.
Tanaka Y, Maeda H, Ogawa Y, et al. Sentinel node biopsy in breast cancer patients treated with neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Oncol Rep. 2006;15:927–31.
Balch GC, Mithani SK, Richards KR, Beauchamp RD, Kelley MC. Lymphatic mapping and sentinel lymphadenectomy after preoperative therapy for stage II and III breast cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. 2003;10:616–21.
Yu JC, Hsu GC, Hsieh CB, Yu CP, Chao TY. Role of sentinel lymphadenectomy combined with intraoperative ultrasound in the assessment of locally advanced breast cancer after neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Ann Surg Oncol. 2007;14:174–80.
Tausch C, Konstantiniuk P, Kugler F, et al. Sentinel lymph node biopsy after preoperative chemotherapy for breast cancer: findings from the Austrian Sentinel Node Study Group. Ann Surg Oncol. 2008;15:3378–83.
Newman EA, Sabel MS, Nees AV, et al. Sentinel lymph node biopsy performed after neoadjuvant chemotherapy is accurate in patients with documented node-positive breast cancer at presentation. Ann Surg Oncol. 2007;14:2946–52.
Schwartz GF, Meltzer AJ. Accuracy of axillary sentinel lymph node biopsy following neoadjuvant (induction) chemotherapy for carcinoma of the breast. Breast J. 2003;9:374–9.
Kang SH, Kang JH, Choi EA, Lee ES. Sentinel lymph node biopsy after neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Breast Cancer. 2004;11:233–41.
Classe JM, Bordes V, Campion L, et al. Sentinel lymph node biopsy after neoadjuvant chemotherapy for advanced breast cancer: results of Ganglion Sentinelle et Chimiotherapie Neoadjuvante, a French prospective multicentric study. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27:726–32.
Breslin TM, Cohen L, Sahin A, et al. Sentinel lymph node biopsy is accurate after neoadjuvant chemotherapy for breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2000;18:3480–6.
Stearns V, Ewing CA, Slack R, et al. Sentinel lymphadenectomy after neoadjuvant chemotherapy for breast cancer may reliably represent the axilla except for inflammatory breast cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. 2002;9:235–42.
Gimbergues P, Abrial C, Durando X, et al. Sentinel lymph node biopsy after neoadjuvant chemotherapy is accurate in breast cancer patients with a clinically negative axillary nodal status at presentation. Ann Surg Oncol. 2008;15:1316–21.
Lee S, Kim EY, Kang SH, et al. Sentinel node identification rate, but not accuracy, is significantly decreased after pre-operative chemotherapy in axillary node–positive breast cancer patients. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2007;102:283–8.
Kinoshita T, Takasugi M, Iwamoto E, et al. Sentinel lymph node biopsy examination for breast cancer patients with clinically negative axillary lymph nodes after neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Am J Surg. 2006;191:225–9.
Fernandez A, Cortes M, Benito E, et al. Gamma probe sentinel node localization and biopsy in breast cancer patients treated with a neoadjuvant chemotherapy scheme. Nucl Med Commun. 2001;22:361–6.
Nason KS, Anderson BO, Byrd DR, et al. Increased false negative sentinel node biopsy rates after preoperative chemotherapy for invasive breast carcinoma. Cancer. 2000;89:2187–94.
Cox CE, Cox JM, White LB, et al. Sentinel node biopsy before neoadjuvant chemotherapy for determining axillary status and treatment prognosis in locally advanced breast cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. 2006;13:483–90.
van Rijk MC, Nieweg OE, Rutgers EJ, et al. Sentinel node biopsy before neoadjuvant chemotherapy spares breast cancer patients axillary lymph node dissection. Ann Surg Oncol. 2006;13:475–9.
Schrenk P, Tausch C, Wolfl S, et al. Sentinel node mapping performed before preoperative chemotherapy may avoid axillary dissection in breast cancer patients with negative or micrometastatic sentinel nodes. Am J Surg. 2008;196:176–83.
Menard JP, Extra JM, Jacquemier J, et al. Sentinel lymphadenectomy for the staging of clinical axillary node-negative breast cancer before neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2009;35:916–20.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chung, A., Giuliano, A. Axillary Staging in the Neoadjuvant Setting. Ann Surg Oncol 17, 2401–2410 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-010-1001-8
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-010-1001-8