Abstract
Background
Desmoplastic melanoma (DM) has been associated with higher local recurrence rates than other types of cutaneous melanoma. Current controversies regarding locoregional treatment strategies warrant further investigation.
Methods
Retrospective review of a prospectively maintained melanoma database identified 129 patients with DM out of >12,500 melanoma patients referred for treatment from 1980 to 2003. Clinical and histopathologic characteristics, recurrence, and survival were analyzed.
Results
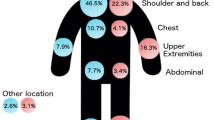
The median follow-up was 4.0 years. Of the 129 patients identified, 82 (63.6%) were male, and the median age was 55.2 years. American Joint Committee on Cancer staging was I, II, and III in 25.6%, 68.0%, and 6.4% of patients, respectively, and the mean tumor thickness was 4.42 mm. Overall survival was 76% at 5 years and 64% at 10 years; median survival was 13.0 years. A total of 51 patients (39.5%) experienced disease recurrence, with a median time to recurrence of 1.3 years. The first recurrence was local in 18 patients (14.0%), nodal in 18 patients (14.0%), and distant in 15 patients (11.6%), with median survivals of 6.7, 7.8, and 1.8 years, respectively. Statistically significant predictors of recurrence were a final positive margin status and stage, and predictors of overall survival were patient age and stage.
Conclusions
Compared with other types of melanoma, DMs do demonstrate a tendency toward local recurrence, thus suggesting that narrower excision margins may not be appropriate in this population. Scrutiny of final surgical margins is critical to the local management of DM. In addition, the potential for regional nodal involvement must be considered at the time of diagnosis and during surveillance for disease recurrence.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Conley J, Lattes R, Orr W. Desmoplastic malignant melanoma (a rare variant of spindle cell melanoma). Cancer 1971;28:914–36
Reed RJ, Leonard DD. Neurotropic melanoma. A variant of desmoplastic melanoma. Am J Surg Pathol 1979;3:301–11
Jain S, Allen PW. Desmoplastic malignant melanoma and its variants. Am J Surg Pathol 1989;13:358–73
Lens MB, Newton-Bishop JA, Boon AP. Desmoplastic malignant melanoma: a systematic review. Br J Dermatol 2005;152:673–8
Smithers BM, McLeod GR, Little JH. Desmoplastic melanoma: patterns of recurrence. World J Surg 1992;16:186–90
Baer SC, Schultz D, Synnestvedt M, Elder DE. Desmoplasia and neurotropism. Prognostic variables in patients with stage I melanoma. Cancer 1995;76:2242–7
Carlson LA, Dickersin GR, Sober AJ, Barnhill RL. Desmoplastic neurotropic melanoma. A clinicopathologic analysis of 28 cases. Cancer 1995;75:478–94
Skelton HG, Smith KJ, Laskin WB, et al. Desmoplastic malignant melanoma. J Am Acad Dermatol 1995;32:717–25
Longacre TA, Egbert BM, Rouse RV. Desmoplastic and spindle cell malignant melanoma: an immunohistochemical study. Am J Surg Pathol 1996;20:1489–500
Quinn MJ, Crotty KA, Thompson JF, Coates AS, O’Brien CJ, McCarthy WH. Desmoplastic and desmoplastic neurotropic melanoma: experience with 280 patients. Cancer 1998;83:1128–35
Jaroszewski DE, Pockaj BA, DiCaudo DJ, Bite U. The clinical behavior of desmoplastic melanoma. Am J Surg 2001;182:590–5
Payne WG, Kearney R, Wells K, et al. Desmoplastic melanoma. Am Surg 2001;67:1004–6
Banerjee SS, Harris M. Morphological and immunophenotypic variations in malignant melanoma. Histopathology 2000;36:387–402
Tsao H, Sober AJ, Barnhill RL. Desmoplastic neurotropic melanoma. Semin Cutan Med Surg 1997;26:131–6
Bruijn JA, Salasche S, Sober AJ, Mihm MC, Barnhill RL. Desmoplastic melanoma: clinicopathologic aspects of six cases. Dermatology 1992;185:3–8
Arbiser ZK, Folpe AL, Weiss SW. Consultative (expert) second opinions in soft tissue pathology. Am J Clin Pathol 2001;116:473–6
Zelger BG, Steiner H, Wambacher B, Zelger B. Malignant melanomas simulating various types of soft tissue tumors. Dermatol Surg 1997;23:1047–54
Eng W, Tschen JA. Comparison of S-100 versus hematoxylin and eosin staining for evaluating dermal invasion and peripheral margins by desmoplastic malignant melanoma. Am J Dermatopathol 2000;22:26–9
Kaneishi NK, Cockerell CJ. Histologic differentiation of desmoplastic melanoma from cicatrices. Am J Dermatopathol 1998;20:128–34
Kamath NV, Ormsby A, Bergfeld WF, House NS. A light microscopic and immunohistochemical evaluation of scars. J Cutan Pathol 2002;29:27–32
Chorny JA, Barr RJ. S100-positive spindle cells in scars: a diagnostic pitfall in the re-excision of desmoplastic melanoma. Am J Dermatopathol 2002;24:309–12
Robson A, Allen P, Hollowood K. S100 expression in cutaneous scars: a potential diagnostic pitfall in the diagnosis of desmoplastic melanoma. Histopathology 2001;38:135–40
Gyorki DE, Busam K, Panageas K, et al. Sentinel lymph node biopsy for patients with cutaneous desmoplastic melanoma. Ann Surg Oncol 2003;10:403–7
Thelmo MC, Sagebiel RW, Treseler PA, et al. Evaluation of sentinel lymph node status in spindle cell melanomas. J Am Acad Dermatol 2001;44:451–5
Su LD, Fullen DR, Lowe L, et al. Desmoplastic and neurotropic melanoma. Analysis of 33 patients with lymphatic mapping and sentinel lymph node biopsy. Cancer 2004;100:598–604
Balch CM, Buzaid AC, Atkins MB, et al. A new AJCC staging system for cutaneous melanoma. Cancer 2000;88:1484–91
Balch CM, Buzaid AC, Soong SJ, et al. Final version of the American Joint Committee on Cancer staging system for cutaneous melanoma. J Clin Oncol 2001;19:3635–48
Balch CM, Soong SJ, Gershenwald JE, et al. Prognostic factors analysis of 17,600 melanoma patients: validation of the American Joint Committee on Cancer melanoma staging system. J Clin Oncol 2001;19:3622–34
Kanik AB, Yaar M, Bhawan J. p75 nerve growth factor receptor staining helps identify desmoplastic and neurotropic melanoma. J Cutan Pathol 1996;23:205–10
Iwamoto S, Odland PB, Piepkorn M, Bothwell M. Evidence that p75 neurotrophin receptor mediates the perineural spread of desmoplastic melanoma. J Am Acad Dermatol 1996;35:725–31
Iwamoto S, Burrows RC, Agoff SN, Piepkorn M, Bothwell M, Schmidt R. The p75 neurotrophin receptor, relative to other Schwann cell and melanoma markers, is abundantly expressed in spindled melanomas. Am J Dermatopathol 2001;24:288–94
Shea CR, Prieto VG. Recent developments in the pathology of melanocytic neoplasia. Dermatol Clin North Am 1999;17:615–30
Hoang MP, Selim MA, Bentley RC, Burchette JL, Shea CR. CD34 expression in desmoplastic melanoma. J Cutan Pathol 2001;28:508–12
Baldi A, Santini D, de Luca A, Paggi MG. cDNA technology in melanoma: an overview. J Cell Physiol 2003;196:219–33
Thomas JM, Newton-Bishop J, A’Hern R, et al. Excision margins in high-risk malignant melanoma. N Engl J Med 2004;350:757–66
Anderson TD, Weber RS, Guerry D, et al. Desmoplastic neurotropic melanoma of the head and neck: the role of radiation therapy. Head Neck 2002;24:1068–71
Dadras SS, Paul T, Bertoncini J, et al. Tumor lymphangiogenesis: a novel prognostic indicator for cutaneous melanoma metastasis and survival. Am J Pathol 2003;162:1951–60.
Nathanson SD. Insights into the mechanisms of lymph node metastasis. Cancer 2003;98:413–23
Schietroma C, Cianfarani F, Lacal PM, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor-C expression correlates with lymph node localization of human melanoma metastases. Cancer 2003;98:789–97
Straume O, Jackson DG, Akslen LA. Independent prognostic impact of lymphatic vessel density and presence of low-grade lymphangiogenesis in cutaneous melanoma. Clin Cancer Res 2003;9:250–6
de Waal RM, van Altena MC, Erhard H, Weidle UH, Nooijen PT, Ruiter DJ. Lack of lymphangiogenesis in human primary cutaneous melanoma. Consequences for the mechanism of lymphatic dissemination. Am J Pathol 1997;150:1951–7
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Evelyn Nicholson, RN, and Nancy J. Pickett, RN, for their dedicated care of melanoma patients at Duke University Medical Center, for their significant contributions to the maintenance of the melanoma database, and for their assistance with this study. Supported, including statistical support and medical photography services, by the Duke Melanoma Research Fund.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Posther, K.E., Selim, M.A., Mosca, P.J. et al. Histopathologic Characteristics, Recurrence Patterns, and Survival of 129 Patients With Desmoplastic Melanoma. Ann Surg Oncol 13, 728–739 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1245/ASO.2006.03.091
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1245/ASO.2006.03.091