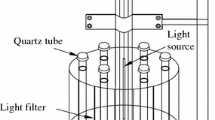
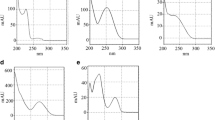
Abstract
Photodegradation kinetics of fleroxacin were investigated in different injections. Five commercial formulations were analyzed before and after irradiation by determining residual volumes of fleroxacin with high-pressure liquid chromatography (HPLC), and different decomposition functions and models were obtained. Concentration levels of fleroxacin in injections caused the differences in photodegradation kinetics instead of ingredients. Influences of different pH values and presence of NaCl on photodegradation of fleroxacin were observed. Low pH value decreased the efficacy of photolysis and enhanced photostability of fleroxacin injections. Tentative structure of a new degradation product afforded was proposed. An acute toxicity assay using the bioluminescent bacterium Q67 was performed for fleroxacin injections after exposure to light. The research proved that fleroxacin was more photolabile in dilute injection, and acute toxicity of dilute injection increased more rapidly than that of concentrated injection during irradiation.






Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Djurdjevic P, Laban A, Jelikic-Stankov M. Validation of an HPLC method for the determination of fleroxacin and its photo-degradation products in pharmaceutical forms. Ann Chim. 2004;94:71–83.
Cullmann W, Geddes AM, Weidekamm E, Urwyler H, Braunsteiner A. Fleroxacin: a review of its chemistry, microbiology, toxicology, pharmacokinetics, clinical efficacy and safety. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 1993;2:203–30.
Tiefenbacher EM, Haen E, Przybilla B, Kurz H. Photodegradation of some quinolones used as antimicrobial therapeutics. J Pharm Sci. 1994;83:463–7.
Albini A, Monti S. Photophysics and photochemistry of fluoroquinolones. Chem Soc Rev. 2003;32:238–50.
Martinez LJ, Li G, Chignell CF. Photogeneration of fluoride by the fluoroquinolone antimicrobials agents lomefloxacin and fleroxacin. Photochem Photobiol. 1997;65:599–602.
Wang J, Li W, Li CG, Hu YZ. Photodegradation of fleroxacin injection: different products with different concentration levels. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2011;12:872–8. doi:10.1208/s12249-011-9658-2.
Shaojun J, Shourong Z, Daqiang Y, Lianhong W, Liangyan C. Aqueous photolysis of tetracycline and toxicity of photolytic products to luminescent bacteria. Chemosphere. 2008;73:377–82. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2008.05.042.
Marina I, Margherita L, Angela N, Luigia P, Alfredo P. Toxic and genotoxic evaluation of six antibiotics on non-target organisms. Sci Total Environ. 2005;346:87–98.
Ma M, Tong Z, Wang Z, Zhu W. Acute toxicity bioassay using the freshwater luminescent bacterium Vibrio-qinghaiensis sp. Nov.-Q67. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol. 1999;62:247–53.
Ma XY, Wang XC, Liu YJ. Study of the variation of ecotoxicity at different stages of domestic wastewater treatment using Vibrio-qinghaiensis sp.-Q67. J Hazard Mater. 2011;190:100–5.
Zhang YY, Zhang WJ, Liao XJ, Zhang JN, Hou YX, Xiao ZY, et al. Degradation of diazinon in apple juice by ultrasonic treatment. Ultrason Sonochem. 2010;17:662–8.
Zhang YH, Liu SS, Song XQ, Geb HL. Prediction for the mixture toxicity of six organophosphorus pesticides to the luminescent bacterium Q67. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2008;71:880–8.
ICH. Q1B photostability testing of new drug substances and products. International Conference on Harmonisation. 1996. http://www.fda.gov/Drugs/GuidanceComplianceRegulatoryInformation/Guidances/ucm065005.htm. Accessed 10 Sept 2012
Garcia CV, Nudelman NS, Steppe M, Schapoval EES. Structural elucidation of rabeprazole sodium photodegradation products. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2008;46:88–93. doi:10.1016/j.jpba.2007.09.002.
International Organization for Standardization. International standard. ISO 11348. Water quality-determination of the inhibitory effect of water samples on the light emission of Vibrio fischeri (Luminescent bacteria test)-part 3: Method using freeze-dried bacteria. First edition. 1998.
Tetsuya A, Yukinori K, Ikumi O, Hiroaki K. Photochemical behavior of sitafloxacin, fluoroquinolone antibiotic, in an aqueous solution. Chem Pharm Bull. 2002;50:229–34.
Ge LK, Chen JW, Zhang SY, Cai YX, Wang Z, Wang CL. Photodegradation of fluoroquinolone antibiotic gatifloxacin in aqueous solutions. Chin Sci Bull. 2010;55:996–1001. doi:10.1007/s11434-010-0139.
Song Z, Chen XH, Zhang D, Ren L, Fang L, Cheng WM, et al. Kinetic study of the degradation of PAC-1 and identification of a degradation product in alkaline condition. Chromatographia. 2009;70:1575–80. doi:10.1365/s10337-009-1348-90009-5893/09/12.
Claudia G, Marcela L. Development of HPLC and UV spectrophotometric methods for the determination of ascorbic acid using hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin and triethanolamine as photostabilizing agents. Anal Chim Acta. 2010;659:159–66.
Zhang Y, Liu XL, Cui Y, Huang HF, Chi N, Tang X. Aspects of degradation kinetics of azithromycin in aqueous solution. Chromatographia. 2009;70:67–73. doi:10.1365/s10337-009-1116-x. 0009-5893/09/07.
Hanne HT. Formulation and stability testing of photolabile drugs. Int J Pharm. 2001;225:1–14.
Ragno G, Cione E, Garofalo A, Genchi G, Ioele G, Risoli A, et al. Design and monitoring of photostability systems for amlodipine dosage forms. Int J Pharm. 2003;265:125–32.
Torniainen K, Tammilehto S, Ulvi V. The effect of pH, buffer type and drug concentration on the photodegradation of ciprofloxacin. Int J Pharm. 1996;132:53–61.
Gomeza M, Murciaa MD, Gomeza JL, Matafonova G, Batoevb V, Christofi N. Testing a KrCl excilamp as new enhanced UV source for 4-chlorophenol degradation: experimental results and kinetic model. Chem Eng Process. 2010;49:113–9. doi:10.1016/j.cep.2009.11.016.
Park HR, Kim TH, Bark KM. Physicochemical properties of quinolone antibiotics in various environments. Eur J Med Chem. 2002;37:443–60.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, W., Wang, J. & Hu, YZ. Photodegradation of Fleroxacin Injection: II. Kinetics and Toxicological Evaluation. AAPS PharmSciTech 14, 578–584 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1208/s12249-013-9942-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1208/s12249-013-9942-4