Abstract
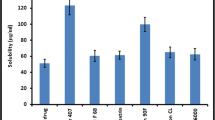
Ritonavir is an antiretroviral drug characterized by low solubility and high permeability which corresponds to BCS class II drug. The purpose of the study was to develop solid dispersion by different methods and investigate them for in vitro and in vivo performance for enhancing dissolution and bioavailability, respectively. Since the drug possesses food-related absorption, the effect of biorelevant media (FaSSIF and FeSSIF state) on dissolution behavior was also studied. The solid dispersion was prepared using Gelucire as carrier in 1:4 ratio by different methods and were characterized for differential scanning calorimetry (DSC), X-ray diffractometry, scanning electron microscopy, and FT-IR. Oral bioavailability of 10 mg of ritonavir in solid dispersion prepared by solvent evaporation (SE1) and melt method (MM1) was compared with pure drug after oral administration of solid dispersion and pure drug to Albino Wistar rats of either sex. The results suggested formation of eutectic solid dispersion. In vitro dissolution studies was performed in 0.1 N HCl and biorelevant media showed enhanced dissolution rate as compared to pure drug in both FeSSIF media and 0.1 N HCl. The apparent rate of absorption of ritonavir from SE1 (C max 20221.37 ng/ml, t max 0.5 h) was higher than that of MM1 (C max 2,462.2, t max 1 h) and pure drug (C max 1,354.8 ng/ml, t max 0.5 h). On the basis of the result obtained, it was concluded that solid dispersion is a good approach to enhance solubility and bioavailability of poorly water-soluble ritonavir.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lipinski CA, Lombardo F, Dominyl BW, Feeney PJ. Experimental and computational approaches to estimate solubility and permeability in drug discovery and development settings. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 1997;23:3–25. doi:10.1016/S0169-409X(96)00423-1.
Dannenfelser R, He H, Joshi Y, Bateman S, Serajuddin ATM. Development of clinical dosage forms for a poorly water soluble drug I: Application of polyethylene glycol-polysorbate 80 solid dispersion carrier system. J Pharm Sci. 2004;93:1165–75. doi:10.1002/jps.20044.
Mooter GVD, Augustijns P, Blaton N, Kinget R. Physico-chemical characterization of solid dispersions of temazepam with polyethylene glycol 6000 and PVP K30. Int J Pharm. 1998;164:67–80. doi:10.1016/S0378-5173(97)00401-8.
Habib MJ. Pharmaceutical solid dispersion technology. Washington: CRC; 2000. p. 35–78.
Law D, Krill SL, Schmitt EA, Fort JJ, Qiu Y, Wang W et al. Physicochemical considerations in the preparation of amorphous ritonavir-poly (ethylene glycol) 8000 solid dispersions. J Pharm Sci. 2000;90:1015–25. doi:10.1002/jps.1054.
Pignatello R, Ferro M, Guidi GD, Salemi G, Vandelli MA, Guccione S et al. Preparation, characterisation and photosensitivity studies of solid dispersions of diflunisal and Eudragit RS100 and RL100. Int J Pharm. 2001;218:27–42. doi:10.1016/S0378-5173(01)00597-X.
Babu GVM, Prasad DS, Murthy KVR. Evaluation of modified gum karaya as carrier for the dissolution enhancement of poorly water-soluble drug Nimodipine. Int J Pharm. 2002;234:1–17. doi:10.1016/S0378-5173(01)00925-5.
Hancock BC, Zografi G. Characteristics and significance of the amorphous state in pharmaceutical systems. J Pharm Sci. 1997;86:1–12. doi:10.1021/js9601896.
Gowariker VR, Viswanathan NV, Sreedhar J. Polymer science. New Delhi: New Age; 1986. p. 150–79.
Serajuddin ATM. Solid dispersion of poorly water-soluble drugs: early promises, subsequent problems, and recent breakthroughs. J Pharm Sci. 1999;88:1058–66. doi:10.1021/js980403l.
Barker SA, Yap SP, Yuen KH, McCoy CP, Murphy JR, Craig DQM. An investigation in to structure and bioavailability of α-tocopherol in Gelucire 44/14. J Control Release. 2003;91:477–88. doi:10.1016/S0168-3659(03)00261-X.
Nilüfer Y, Aysegül K, Yalçın Ö, Ayhan S, Sibel AÖ, Tamer B. Enhanced bioavailability of piroxicam using Gelucire 44/14 and Labrasol: in vitro and in vivo evaluation. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2003;56:453–9. doi:10.1016/S0939-6411(03)00142-5.
Ozkan Y, Doganay N, Dikmen N, Isimer A. Enhanced release of solid dispersions of etodolac in polyethylene glycol. Farmaco. 2000;55:433–8.
Damian F, Blaton N, Naesens L, Balzarini J, Kinget R, Augustijns P et al. Physicochemical characterization of solid dispersions of the antiviral agent UC-781 with polyethylene glycol 6000 and Gelucire 44/14. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2000;10:311–22. doi:10.1016/S0928-0987(00)00084-1.
Kanaze FI, Kokkalou E, Niopas I, Georgarakis M, Stergiou A, Bikiaris D. Novel drug delivery systems for flavonoid compounds with enhanced solubility based on solid dispersions with polyvinylpyrolidone and polyethyleneglycol. J Appl Polym Sci. 2006;102:460–71. doi:10.1002/app. 24200.
Sekar V, Kestens D, Spinosa-Guzman S. The effect of different meal types on the pharmacokinetics of Darunavir (TMC114)/Ritonavir in HIV-Negative Healthy Volunteers. J Clin Pharmacol. 2007;47:479–84.
Acknowledgments
The authors are thankful to Department of Science and Technology, Government of India for financial assistance to this project (SR/FT/L-28/2006)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sinha, S., Ali, M., Baboota, S. et al. Solid Dispersion as an Approach for Bioavailability Enhancement of Poorly Water-Soluble Drug Ritonavir. AAPS PharmSciTech 11, 518–527 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1208/s12249-010-9404-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1208/s12249-010-9404-1