Abstract
Background
Nanoparticles have a large number of surface atoms, which translates into a significant increase in the surface energy. Once introduced in a biological environment they tend to interact with proteins and form a protein corona shell. The aim of this study was to develop a novel, silver based, bio-nanocomposite for biological applications. Immunoglobulin G (IgG) molecule was chosen for the passivation of the silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) in order to avoid macrophage recognition of the synthesized structures.
Results
Monodisperse IgG-folinate functionalized silver nanoparticles were obtained, with sizes around 39 nm. UV–Vis and UATR-FT-IR spectroscopies were employed to confirm the successful functionalization of the silver nanoparticles. Atomic force microscopy and dynamic light scattering measurements gave information about the size and shape of the nanoparticles prior and after the passivation with IgG.
Conclusions
Immunoglobulin G formed a monolayer around the nanoparticles with the binding site seemingly in the Fc domain, leaving the two Fab regions available for antigen binding. To our knowledge, this is the first report of an IgG-folinate functionalized AgNP bionanostructure developed for biological applications.

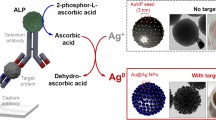
Graphical illustration for IgG-folinate silver nanoparticles functionalization steps
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
In the past few decades, metal nanoparticles have been developed for a variety of applications, such as biosensors, anti-bacterial agents, drug-delivery vehicles, contrast agents and so on. Silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) have attracted a lot of attention due to their ease of synthesis, chemical stability, good conductivity and antimicrobial properties [1–3].
A wide variety of methods for silver nanoparticle synthesis is available in literature, these include: chemical reduction, laser ablation, thermal decomposition and sonochemical synthesis [4–8]. A vastly utilized method for silver nanoparticle synthesis is the reduction of silver ions in a aqueous solution in the presence of a capping agent [9], such as citrate molecules which impart negative surface charges that prevent nanoparticle aggregation through repulsion forces [10].
Silver nanoparticles present a surface plasmon resonance band (SPR) derived from the collective oscillation of valence electrons under stimulation from incident light, this phenomenon is observed when the frequency of light photons matches the natural frequency of surface electrons oscillating against the restoring force [11]. The SPR band is sensitive to the nanoparticle size and shape and also to the properties of the surrounding medium [12].
Nanoparticles have a large number of surface atoms, which translates into a significant increase in the surface energy. A tendency to reduce their large surface energy by interacting with the surrounding components that contain donating or accepting sites has been observed [13]. Literature data shows that nanoparticles introduced in a biological environment tend to interact with proteins and form a protein corona shell [14]. The nature of the protein corona influences the extent and mechanism of nanoparticle cellular internalization [15, 16]. AgNPs that are stable enough to significantly restrict bacterial growth are challenging to prepare [17]. Thus, the passivation of nanoparticles, a technique that involves surface modification or coating with naturally-occurring molecules (such as serum abundant proteins or fatty acids) has to be taken into account when designing nanoparticles for life sciences applications [18, 19].
It has been showed that when the protein concentration is sufficient to cover the available silver nanoparticle surface, the protein molecules at the metal–water interface retain their native structure [20].
Silver has a well-documented toxic effect on lower organisms while a biological role in the human body has not yet been demonstrated [21]. Aueviriyavit et al. showed that AgNPs can cause acute cellular damage in Caco-2 (HTB-37) cells but only after treatment with relatively high amounts nanoparticles [22]. Several other studies show that AgNPs can cause apoptosis, DNA damage or cause oxidative stress, but interestingly toxicity levels reported vary greatly [17]. Thus, the AgNPs low toxicity in humans makes them excellent candidates for future silver based drugs in the fight against antibiotic-resistant bacteria [21]. Strong antibacterial activity of AgNPs was demonstrated at very low total concentrations of silver (<7 ppm) against several Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. The exact mechanism through which they present antimicrobial properties is yet to be elucidated [23].
Nanoparticles, due to their size, shape and surface chemistry are prone to interception by different defence components following entry into the body. For macrophage avoidance of nanoparticles several strategies that suppress the opsonisation processes can be undertaken. Thus, nanoparticle surface modification or coating with natural occurring complement inhibitors yield stealth or macrophage-avoiding nanoparticles [18].
Immunoglobulin G (IgG) is composed of four polypeptidic chains, two heavy and two light chains, linked through a disulphidic bond to give a ‘Y-shaped’ conformation. IgG has one Fc domain, which should be preferred in the adsorption onto the nanoparticle surface and two identical Fab domains responsible for antigen binding [24].
Calcium folinate (CF) is the salt form of folinic acid, a known drug used to combat the adverse effects of tetrahydrofolate reductase inhibitors [25].
The aim of this study was to develop a novel, silver based, bio-nanocomposite for biological applications. IgG molecule was chosen for the passivation of the AgNPs in order to avoid macrophage recognition of the synthesized structures. To our knowledge, this is the first report of an IgG-folinate functionalized AgNP bionanostructure developed for biological applications.
Results and discussions
The synthesis protocol used for obtaining the AgNP–IgG–CF bio-nanocomposite is presented in Fig. 1 and has three stages: in the first stage silver ions (Ag+) were reduced to metallic silver (Ag0) with the aid of sodium citrate; in the second stage IgG molecules were covalently coupled to the CF molecules and in the third stage silver nanoparticles were functionalized with the IgG–CF conjugate. The obtained functionalized nanoparticles in aqueous solution were kept at both room temperature (20 °C) and 4 °C for several weeks and did not present any agglomeration or sedimentation.
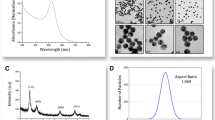
UV–Vis spectroscopy is a valuable technique in terms of size and morphology characterization of silver nanoparticle dispersions [26]. The UV–Vis spectra for the AgNP, IgG, IgG–CF and AgNP–IgG–CF samples are presented in Fig. 2. The citrate capped silver nanoparticles presented a surface plasmon resonance band (SPR) at 433 nm [27], while the IgG and the IgG–CF conjugate had a λmax centered at 284 nm. In the case of AgNP–IgG–CF bio-nanocomposite the UV–Vis spectra two absorbtion peaks can be observed. The first peak, situated at 432 nm, is attributed to the SPR band of silver nanoparticles [28–30], while the second peak, at 284 nm, is attributed to the IgG molecules [31] coupled to the surface of AgNPs in the functionalization step. Available literature data shows that the SPR profile of AgNPs is dependent to the protein concentration and the surrounding media [20].
Dynamic light scattering (DLS) measurements were performed in order to investigate the size of the citrate capped silver nanoparticles and IgG–CF functionalized AgNP. The DLS size distribution curves for the hydrodynamic diameters of AgNP and AgNP–IgG–CF samples are presented in Fig. 3. Both samples presented themselves as being monodisperse and stable at room temperature. For the AgNP a mean diameter of ~29 nm was registered, while the AgNP–IgG–CF had a mean hydrodynamic diameter of ~48 nm. The polydispersity index for the AgNP–IgG–CF sample was 0.283, indicating a narrow size range.
The typical dimensions reported in literature for IgG are approximately 14.5 nm × 8.5 nm × 4 nm [32], this corroborated with the DLS data, suggests that IgG has formed a monolayer on the surface of AgNPs during the functionalization step. Also the binding site of the immunoglobulin to the silver nanoparticle surface seems to be in the Fc domain, leaving the two Fab regions available for antigen binding.
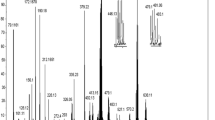
Attenuated total reflectance Fourier transform infra-red (ATR-FT-IR) spectroscopy is a straightforward technique that gives valuable information about the secondary structure of proteins [31]. Figure 4 depicts the IR spectra of (A) calcium folinate, (B) immunoglobulin G, (C) IgG–CF functionalized silver nanoparticles, (D) citrate capped silver nanoparticles and (E) IgG–CF conjugate. Figure 4f shows a comparison, in the 2500–1000 cm−1 region, between the IR spectra presented in Fig. 4a–e. In the case of the AgNP sample, the absorbtion bands at 1590 and 1370 cm−1 are attributed to the antisymmetric and, respectively symmetric stretching vibrations of COO− from citrate molecule present on the surface of silver nanoparticles [33, 34]. For the IgG and IgG–CF samples, the IR bands at 1635–1638 and 1534–1554 cm−1 correspond to the amide I band (which leads to stretching vibrations of the C=O bond of the amide) and, respectively to the amide II band (C–N stretching and N–H bending vibrations) from the IgG β-sheets [31, 35]. These absorption bands are also present in the final bio-nanocomposite at 1637 and 1534 cm−1, making the IR spectra of the IgG and AgNP–IgG–CF nearly identical. Thus, in the case of the AgNP–IgG–CF sample, the disappearance of the IR band attributed to citrate ions, corroborated with the appearance of IgG characteristic IR bands confirm the successful functionalization of silver nanoparticles with the IgG–CF conjugate.
Atomic force microscopy was conducted in order to further investigate the size and shape of the AgNP–IgG–CF bio-nanocomposite. Figure 5a is a 2D representation of a single AgNP–IgG–CF nanoparticle, while Fig. 5c is a 3D representation of the same bio-nanostructure. AFM data collected showed that AgNPs were spherical in shape and had a mean diameter of ~26 nm. The IgG–CF functionalized silver nanoparticles were ~39 nm in diameter. The difference between the DLS and AFM data regarding nanoparticle size can be attributed to the fact that the dynamic light scattering technique provides a hydrodynamic diameter of the nanoparticle and the associated solvation layers [36].
Experimental
Silver nitrate (AgNO3 99.9 %), sodium citrate (≥99 %), N-(3-Dimethylaminopropyl)-N′-ethylcarbodiimide hydrochloride (EDC) and N-Hydroxysuccinimide (NHS) were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich™ (Darmstadt, Germany) and were used without further purification. Immunoglobulin G (IgG) was purchased from Kedrion (Lucca, Italy) and was purified with the aid of Pierce® centrifugal concentrators with a 30 kDa molecular weight cut-off. Calcium folinate (CF) was purchased from Actavis (Romania). All glassware used was cleaned with aqua regia (HCl:HNO3, 3:1) prior to use.
Aqueous stable silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) were obtained by reducing silver ions in the presence of sodium citrate. Thus, 9 mg AgNO3 were dissolved in 50 mL H2O dist. and the solution was heated to boiling point. Next, 2 mL of sodium citrate (0.5 %) were quickly added under vigorous stirring and the reaction was allowed to continue until the solution reached a pale-yellow colour.
In order to covalently bind the immunoglobulin G with the calcium folinate, 3 mL IgG solution (5 mg/mL) were reacted with 1.5 mL EDC solution (30 mg/mL) and 1.5 mL NHS sol. (30 mg/mL) under continuous stirring for 20 min, at room temperature. Afterwards, 1 mL CF (3 mg/mL) was added and the reaction allowed to continue for another 30 min. For the purification of the IgG–CF conjugate, centrifugal concentrators with a molecular cut-off of 30 kDa were used at 4000 RPM for 60 min. The purified IgG–CF was re-eluted in 6 mL H2O dist. and 4 mL AgNP sol. were added under vigorous stirring, the reaction was allowed to continue at room temperature for 60 min. Finally, the obtained AgNP–IgG–CF bio-nanocomposite was separated by means of centrifugation at 13,200 RPM for 20 min and re-dispersion in H2O dist.
UV–Vis spectroscopy measurements were recorded with a Shimadzu UV-1800™ instrument. UV–Vis spectra were recorded for the AgNP, IgG, IgG–CF and AgNP–IgG–CF samples in the 800–200 nm range, with a spectral resolution of 0.5 nm. The OriginLab® 7.0 software was used for normalization of the registered spectra.
Dynamic light scattering (DLS) data was registered on a Zetasizer—Nano S90 instrument (Malvern Instruments, Westborough, UK) at 20 °C and a 90° diffraction angle; a refractive index of 0.20 and a material absorption of 3.980 were considered.
Universal attenuated total reflectance Fourier transform infra-red spectroscopy (UATR-FT-IR) measurements were performed on a Perkin-Elmer Spectrum Two® instrument equipped with a diamond ATR stage. All registered spectra were processed with the aid of the Spectrum 10™ software.
Atomic force microscopy (AFM) was conducted of a Workshop TT-AFM® instrument (AFMWorkshop, CA, USA), equipped with ACTA-SS cantilevers (AppNano, CA, USA) operated in vibrating mode. The samples were deposited on a mica substrate with the aid of a KLM® SCC spin-coater. The registered data was processed with the aid of the Gwyddion® 2.36 software.
Conclusions
Monodisperse IgG-folinate functionalized silver nanoparticles with sizes around 39 nm were obtained. UV–Vis and UATR-FT-IR spectroscopies were employed to confirm the successful functionalization of the silver nanoparticles. AFM and DLS measurements gave information about the size and shape of the nanoparticles prior and after the passivation with IgG. Immunoglobulin G formed a monolayer around the nanoparticles with the binding site seemingly in the Fc domain, leaving the two Fab regions available for antigen binding. To our knowledge, this is the first report of an IgG-folinate functionalized AgNP bionanostructure developed for biological applications. Further investigations are being carried out regarding the AgNP–IgG–CF interactions in biological systems.
Abbreviations
- AgNP:
-
silver nanoparticles
- CF:
-
calcium folinate
- IgG:
-
immunoglobulin G
- SPR:
-
surface plasmon resonance
- ATR-FT-IR spectroscopy:
-
attenuated total reflectance Fourier transform infra-red spectroscopy
- DLS:
-
dynamic light scattering
- AFM:
-
atomic force microscopy
References
Drake PL, Hazelwood KJ (2005) Exposure-related health effects of silver and silver compounds: a review. Ann Occup Hyg 49:575–585
Khodashenas B, Ghorbani HR (2015) Synthesis of silver nanoparticles with different shapes. Arab J Chem. doi:10.1016/j.arabjc.2014.12.014
Lansdown ABG (2006) Silver in health care: antimicrobial effects and safety in use. In: Burg G (ed) Biofunctional textiles and the skin, vol 33. Karger, Basel, pp 17–34
Lee PC, Meisel D (1982) Adsorbtion and surface-enhanced Raman of dyes on silver and gold sols. J Phys Chem 86:3391–3395
Ravindran A, Chandran P, Khan SS (2013) Biofunctionalized silver nanoparticles: advances and prospects. Colloids Surf B 105:342–352
Salkar RA, Jeevanadam P, Aruna ST, Koltypin Y, Gedanken A (1999) The sonochemical preparation of amorphous silver nanoparticles. J Mater Chem 9:1333–1335
Simakin AV, Voronov VV, Kirichenko NA, Shafeev GA (2004) Nanoparticles produced by laser ablation of solids in liquid environment. Appl Phys A 79:1127
Yang Y, Matsubara S, Xiong I (2007) Solvothermal synthesis of multiple shapes of silver nanoparticles and their SERS properties. J Phys Chem 111:9095–9104
Tudose M, Culita DC, Ionita P, Chifiriuc MC (2015) Silver nanoparticles embedded into silica functionalized with vitamins as biological active materials. Ceram Int 41:4460–4467
Larguinho M, Baptista P (2012) Gold and silver nanoparticles for clinical diagnostics—from genomics to proteomics. J Proteom 75:2811–2823
Moores A, Goettmann F (2006) The plasmon band in noble metal nanoparticles: an introduction to theory and applications. New J Chem 30:1121–1132
Liz-Marzan LM, Giersig M, Mulvaney P (1996) Synthesis of nanosized gold-silica core-shell particles. Langmuir 12:4329–4335
Abdelhamid HN, Wu HF (2015) Proteomics analysis of the mode of antibacterial action of nanoparticles and their interactions with proteins. TrAC Trends Anal Chem 65:30–46
Monopoli MP, Aberg C, Salvati A, Dawson KA (2012) Biomolecular coronas provide the biological identity of nanosized materials. Nat Nanotechnol 7:779–786
Karmali PP, Simberg D (2011) Interactions of nanoparticles with plasma proteins: implications on clearance and toxicity of drug delivery systems. Expert Opin Drug Deliv 8:343–357
Shang L, Nienhaus K, Nienhaus HU (2014) Engineered nanoparticles interacting with cells: size matters. J Nanobiotechnol 12:5–11
Karlsson HL, Toprak MS, Fadeel B (2014) Toxicity of Metal and metal oxide nanoparticles. In: Nordberg G, Fowler B, Nordberg M (eds) Handbook on the toxicology of metals, 4th edn. Academic Press, London, pp 75–112
Moghimi SM, Farhangrazi ZS (2013) Nanoparticles in medicine: nanoparticle engineering for macrophage targeting and nanoparticles that avoid macrophage recognition. In: Boraschi D, Duschl A (eds) Nanoparticles and the immune system: safety and effects. Academic Press, London, pp 77–89
Monteiro-Riviere NA, Samberg ME, Oldenburg SJ, Riviere JE (2013) Protein binding modulates the cellular uptake of silver nanoparticles into human cells: implications for in vitro to in vivo extrapolations? Toxicol Lett 220:286–293
Banerjee V, Das KP (2013) Interaction of silver nanoparticles with proteins: a characteristic protein concentration dependent profile of SPR signal. Colloids Surf B 111:71–79
Medici S, Peana M, Nurchi VM, Lachowicz JI, Crisponi G, Zoroddu MA (2015) Noble metals in medicine: latest advances. Coord Chem Rev 284:329–350
Aueviriyavit S, Phummiratch D, Maniratanachote R (2014) Mechanistic study on the biological effects of silver and gold nanoparticles in Caco-2 cells Induction of Nrf2/HO-1 pathway by high concentrations of silver nanoparticles. Toxicol Lett 224:73–83
Guzman M, Dille J, Godet S (2012) Synthesis and antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles against gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. Nanomed Nanotechnol Biol Med 8:37–45
Iafisco M, Varoni E, Foggia MD, Pietronave S, Fini M, Roveri N, Rimondini L, Prat M (2012) Conjugation of hydroxyapatite nanocrystals with human immunoglobulin G for nanomedical applications. Colloids Surf B 90:1–7
Folic acid, folinic acid, and calcium folinate. In: Aronson JK (ed) Meyler’s side effects of drugs—the international encyclopedia of adverse drug reactions and interactions, 15th edn. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 1432–1436
Liu J, Chang M-J, Gou X-C, Xu Z-G, Zhang H-L (2012) One-step synthesis of antibody-stabilized aqueous colloids of noble metal nanoparticles. Colloids Surf A 404:112–118
Dhanalakshmi L, Udayabhaskararao T, Pradeep T (2012) Conversion of double layer charge-stabilized Ag@citrate colloids to thiol passivated luminescent clusters. Chem Commun 48:859–861
Mohri N, Inoue M, Arai Y, Yoshikawa K (1995) Kinetic study on monolayer formation with 4-aminobenzenethiol on a gold surface. Langmuir 11:1612–1616
Ravindran A, Singh A, Raichur AM, Chandrasekaran N, Mukherjee A (2010) Studies on interaction of colloidal Ag nanoparticles with bovine serum albumin (BSA). Colloids Surf B 76:32–37
Shen X, Yuan Q, Liang H, Yan H, Xiwen H (2003) Hysteresis effects of the interaction between serum albumins and silver nanoparticles. Sci China (Ser B) 46:387–398
Arfat MY, Ashrat JM, Arif Z, Arif Z, Alam K (2014) Fine characterization of glycosylated human IgG by biochemical and biophysical methods. Int J Biol Macromol 69:408–415
Tan YH, Liu M, Nolting B, Go JG, Gervay-Hague J, Liu G (2008) A nanoengineering approach for investigation and regulation of protein immobilization. ACS Nano 2:2374–2384
Park J, Shumaker-Parry JS (2014) Structural study of citrate layers on gold nanoparticles: role of intermolecular interactions in stabilizing nanoparticles. J Am Chem Soc 136:1907–1921
Zou X, Ying E, Dong S (2006) Seed-mediated synthesis of branched gold nanoparticles with the assistance of citrate and their surface-enhanced Raman scattering proprieties. Nanotechnology 17:4758–4764
Pelton JT, McLean LR (2000) Spectroscopic methods for analysis of protein secondary structure. Anal Biochem 277:167–176
Mandal G, Bardhan M, Ganguly T (2010) Interaction of bovine serum albumin and albumin-gold nanoconjugates with l-aspartic. A spectroscopic approach. Colloids Surf B 81:178–184
Authors’ contributions
CTM performed the bio-functionalization and of AgNPs with IgG-CF and wrote various sections of the manuscript, TM performed UV–Vis and DLS measurements and the interpretation of results, FZ and CI designed the study, LM supervised the research and wrote various sections of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Acknowledgements
The present study was funded by projects numbers PN-II-PT-PCCA-2013-4-1553 and PN-II-PT-PCCA-2011-3.2-1289. This paper was published under the frame of European Social Fund, Human Resources Development Operational Programme 2007-2013, project no. POSDRU/159/1.5/S/138776.
Compliance with ethical guidelines
Competing interests The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
About this article
Cite this article
Matea, C.T., Mocan, T., Zaharie, F. et al. A novel immunoglobulin G monolayer silver bio-nanocomposite. Chemistry Central Journal 9, 55 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13065-015-0126-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13065-015-0126-z