Abstract
Background
Despite the large body of research on racial/ethnic disparities in health, there are limited data on health disparities in Caribbean origin populations. This review aims to analyze and synthesize published literature on the disparities in diabetes mellitus (DM) and its complications among Afro-Caribbean populations.
Methods
A detailed protocol, including a comprehensive search strategy, was developed and used to identify potentially relevant studies. Identified studies were then screened for eligibility using pre-specified inclusion and exclusion criteria. An extraction form was developed to chart data and collate study characteristics including methods and main findings. Charted information was tagged by disparity indicators and thematic analysis performed. Disparity indicators evaluated include ethnicity, sex, age, socioeconomic status, disability and geographic location. Gaps in the literature were identified and extrapolated into a gap map.
Results
A total of 1009 diabetes related articles/manuscripts, published between 1972 and 2013, were identified and screened. Forty-three studies met inclusion criteria for detailed analysis. Most studies were conducted in the United Kingdom, Trinidad and Tobago and Jamaica, and used a cross-sectional study design. Overall, studies reported a higher prevalence of DM among Caribbean Blacks compared to West African Blacks and Caucasians but lower when compared to South Asian origin groups. Morbidity from diabetes-related complications was highest in persons with low socioeconomic status. Gap analysis showed limited research data reporting diabetes incidence by sex and socioeconomic status. No published literature was found on disability status or sexual orientation as it relates to diabetes burden or complications. Prevalence and morbidity were the most frequently reported outcomes.
Conclusion
Literature on diabetes health disparities in Caribbean origin populations is limited. Future research should address these knowledge gaps and develop approaches to reduce them.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
In 1995, the global prevalence of diabetes mellitus (DM) in adults was estimated to be 4.0% and projected to rise to 5.4% by the year 2025 [1]. However by 2011, the International Diabetes Federation (IDF) estimated the global prevalence of diabetes mellitus to be 8.3% and projected a rise to 9.9% by 2030. In absolute numbers, this translates to 366 million persons with diabetes mellitus in 2011 which will rise to 552 million people by 2030. Eighty percent of those with diabetes live in low and middle income countries [2]. In the Caribbean, the overall prevalence of diabetes mellitus is estimated to be approximately 9% [3] and is responsible for 13.8% of all deaths among adults in the region [2]. Diabetes mellitus is therefore one of the major public health challenges for the Caribbean in the twenty-first century.
Researchers have found that patterns in allocation of resources and differential access to care directly influence health in population sub-groups [4]. This has led to the emergence of the study of these differences or health disparities as a major focus of research and public health policy over the last two decades. These changes in focus are reflected in policies such as the in the United States Healthy People 2010/2020, aimed at eliminating health disparities [5,6] as well as the World Health Organization World Conference on Social Determinants of Health in 2011 resulting in a political declaration and commitment for the implementation of the social determinants of health approach to reduce health disparities [7].
The literature defines health disparities as “the variation or differences in health status resulting from the distribution of the effects of health determinants between and among different population groups” [8]. In addition health disparities imply a social disadvantage among population-subgroups as it relates to a particular health outcome such, as morbidity, mortality or access to care. These health disparities can occur by gender race or ethnicity, education or income, disability, living in rural localities or sexual orientation (disparity indicators) [9].Through measurement of the indicators of health, the degree of disparity can be characterized by absolute and relative differences in measures of occurrence captured as proportions, rates and ratios (disparity measures).
The Caribbean is a geographically diverse region and its citizens live both inside and outside of the region. It includes islands in the Caribbean Sea, but for the purpose of this paper was expanded to include some South and Central American countries (Guyana, Suriname, and Belize) and islands in the Atlantic (Turks and Caicos Islands) which through strong historical, political, and social links and are part of the Caribbean Community (CARICOM). The Caribbean population is predominantly of African descent, but includes an admixture of peoples representing South Asians, Chinese, Europeans, and people from the Middle East. The racial admixture varies between countries; for example, in Jamaica and Barbados over 90% of the population is of African descent while in Trinidad and Tobago and Guyana over 50% of the population are of South Asian origin or mixed ethnicity.
There is a paucity of information on disparities in diabetes mellitus within populations of Afro-Caribbean ethnicity. Scoping reviews have emerged as a method which “aims to rapidly map the key concepts underpinning a research area and the main sources and types of evidence available. It can be undertaken as stand-alone projects, especially where an area is complex or has not been reviewed comprehensively before” [10]. The scoping review is one method of knowledge synthesis which differs from other types of literature reviews in that it addresses broader topics, while a systematic review focuses on specific questions on a relatively narrow range of quality assessed studies. Like the systematic review but unlike other traditional literature reviews, the scoping review employs a systematic replicable approach which includes a search strategy to reduce bias.
This scoping review aimed to summarize the published studies on disparities in diabetes mellitus in Afro-Caribbean populations in order to identify gaps in the available literature as well as characterize the factors which might explain the disparities observed.
The specific objectives were:
-
1.
To review and synthesize the published evidence on health disparities in diabetes mellitus among Afro-Caribbean origin populations
-
2.
To evaluate the effect of health disparities on outcomes including incidence and prevalence of diabetes type1 and 2, micro-vascular or macro-vascular complications of diabetes, and mortality related to diabetes mellitus
-
3.
To identify which health disparity indicators are more frequently reported among Caribbean populations and identify gaps in the literature on health disparities in diabetes mellitus.
Methods
A scoping review was undertaken in accordance with the framework published by Arksey and O’Malley [11].
Inclusion criteria
Studies that reported on diabetes mellitus and the effect which health disparities had on Caribbean populations were examined. Disparity indicators included were: age, sex, ethnicity/race, geographic location, sexual orientation, disability status and socioeconomic status. Disability status was defined as a physical or mental permanent inability to carry out routine function, and socioeconomic status was measured by occupation, education, income, or household amenities. Study participants had to be adults 18 years or older, of Caribbean origin, living in CARICOM or Caribbean immigrant populations living outside of the Caribbean. The complete list of included countries is shown in Appendix 1. Outcomes assessed included incidence and prevalence of diabetes, micro-vascular or macro-vascular complications of diabetes, mortality related to diabetes mellitus and utilization and access to health services among persons with diabetes.
Exclusion criteria
We excluded studies which did not report on an Afro-Caribbean population or immigrant populations of Caribbean descent alone or as a comparator group with other populations (e.g. African American, UK-Africans). Studies reporting only on diabetes control (e.g. blood glucose levels or glycosylated haemoglobin) and studies which grouped Afro-Caribbean populations with other ethnic groups e.g. West African or Latin American so that separate effects could not be determined were also excluded. We also excluded studies in which the less than 18 year old age group could not be separated from those older than 18 years of age.
Types of outcome measures
Both absolute and relative differences in measures of occurrence estimated as proportions rates and ratios were extracted as well as any qualitative information found.
Search strategy
A comprehensive search strategy was developed in consultation with a library and information science specialist. The search was designed to retrieve all articles combining the concepts of ‘Caribbean region’ , ‘African ancestry’ and ‘black Caribbean ethnicity’ with specific chronic diseases, and social determinants of health, health disparities, or health inequity in relevant bibliographic databases. The following databases were searched:
-
Ovid MEDLINE(R) <1946 to June 20, 2013>)
-
Ovid MEDLINE(R) In-Process & Other Non-Indexed Citations <1946 to June 20, 2013>)
-
CENTRAL via Cochrane Library (February 2013)
-
LILACS
-
PsycINFO 1806 to June 2013.
For conference proceedings, theses, dissertations and other grey literature the following databases were searched:
-
Science Citation Index Expanded (SCI-EXPANDED) --1992-present
-
Social Sciences Citation Index (SSCI) --1992-present
-
Arts & Humanities Citation Index (A&HCI) --1992-present
-
Conference Proceedings Citation Index- Science (CPCI-S) --1992-present
-
Conference Proceedings Citation Index- Social Science & Humanities (CPCI-SSH) --1992-present
-
Proquest: Theses and Dissertation 1990-present.
The search was conducted without a study design filter in order to retrieve qualitative as well as quantitative papers. The search was limited to the English language.
Screening and charting
Duplicated articles were identified and removed from the database prior to screening. The titles and abstracts of articles identified by the search strategy were independently screened for relevance by two review authors according to the inclusion and exclusion criteria described above. Citations were managed using EndNote X5 and Microsoft Excel. Discrepancies between review authors were resolved through discussion and, where necessary, by consultation with a third review author. Studies meeting the criteria outlined were charted using a standard study extraction form with domains as listed in Appendix 2. Textual data were charted using Microsoft Excel. The charting approach was akin to a ‘narrative review’ [12] to include detailed information of population characteristics according to identified indicators of health disparities. Reported study quality and limitations of each included study were also charted.
Data synthesis
The synthesis of the charted data was conducted on two levels as suggested by Arskey and O’Malley [11]. Firstly, a numerical analysis was conducted to determine the extent, nature and distribution of the studies included in the review. The included studies were used to create tables and charts, mapping the distribution of studies according to geographic location; study design; publication year; outcome measures used to quantify disease occurrence; and disparity indicators and outcome. This process subsequently informed the approach to identifying main areas of research and the development of gap maps. Secondly, textual data charted in excel were organized thematically, according to the disparity indicators. The review findings were then organized into categories which combined diabetes related outcomes and disparity indicators.
Results
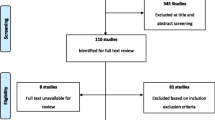
One thousand and nine (1009) published studies on diabetes and health disparities were identified from the search. After title and abstract screening of these references 196 studies met the criteria for full text review, from which 43 studies were selected for final analysis. Details of the screening and study selection process are shown in Figure 1. Table 1 shows the characteristics of the included studies including study design, country of origin, setting, and quality and limitations of included studies. Figure 2 summarizes the distribution of included studies with regards to the disparity measures addressed and the type of diabetes related outcome.
Prevalence and incidence of diabetes in Afro-Caribbean populations
Seventeen papers reported on the prevalence of diabetes mellitus by ethnicity [15,16,18,20,22,23,25,31,32,38,40-42,47,49-51] Overall, the prevalence of diabetes was higher among Afro-Caribbean populations when compared to other African ethnic groups [25,41,42], except in one study where the prevalence among Black Africans (11%) was higher in comparison to Afro-Caribbean (7%) (Table 2) [23]. Markus et al. reported a significantly higher prevalence of diabetes in Afro-Caribbean (45.1%) vs. African (30.8%) ethnic groups among patients with a history of stroke [41]. The prevalence of diabetes in the Afro-Caribbean groups were notably higher in comparison to Caucasians as reported by 13 studies [15,20,22,23,25,32,38,40,42,47,49-51]. However, only 6 of these studies showed any statistically significantly difference (Table 1). The baseline populations in which these prevalence estimates were reported varied widely from the general population to those with heart failure or hypertension. When Afro-Caribbean groups were compared to Asians, the results were mixed, [31] Gill showed the prevalence of diabetes was higher in Afro-Caribbeans (31% vs. 26%; p < 0.05) and in contrast Goyal [32] reported a higher prevalence in South Asians (27.5% vs. 15.6%; p < 0.05).
Only one study reported on incident diabetes by ethnicity [43] The authors found that there was a higher incidence of diabetes in Indo-Trinidadian men compared to Afro-Trinidadian men but not for women.
Age and Sex differences in diabetes
Four studies reported on the prevalence of diabetes by age groups. Overall, the prevalence of diabetes increased with age across all ethnic groups and social indicators [18,28,36,54]. In age groups < 35 the prevalence was ~2% and in those >65 years it ranged between 10 and 16%.
Eleven papers investigated the sex differences in the prevalence of diabetes [18,23,25,28-30,34,36,42,44,54], of which 6 noted a higher prevalence among women compared to men which ranged between 9.3 - 14% vs. 6.4-9.8% respectively [23,28-30,36,54]. One study evaluated the burden of diabetes among immigrants in Canada and reported higher prevalence of newly diagnosed diabetes among men (10.0%) compared to women (9.3%) [25]. This difference was not statistically significant. Four studies noted no sex differences in diabetes prevalence [18,34,42,44].
Only one study was found which reported sex differences in incident diabetes and found that sex was not a significant predictor of incident diabetes [52].
Socioeconomic inequalities and diabetes
Few studies addressed socioeconomic status and diabetes. Among the studies reviewed we found that the prevalence of diabetes was higher among persons with lower incomes and lower educational attainment. This trend in the prevalence of diabetes was similar across the Caribbean [18,36].
Our search found no studies addressing the prevalence of diabetes using other indicators of disparity, such as, geographical location, rural vs. urban distribution or by disability status among the Afro-Caribbean ethnic group (see Figure 3).
Diabetes mortality in Afro-Caribbean populations
Three studies reported on mortality attributable to diabetes of which one noted ethnic differences between Afro-Caribbeans and UK Caucasians [21,44,53]. Chaturvedi investigated the differences in morbidity and mortality due to non-insulin dependent diabetes in Afro-Caribbeans and Europeans and found that Afro-Caribbean’s had lower (HR 0.42 (0.24, 0.76, p < 0.05) all-cause mortality compared with the Europeans [21]. Molokhia reported that there was a higher rate of mortality attributable to diabetes in women (22.1%) when compared to men (5.8%) [44].
Disparities in diabetes complications
Twelve studies investigated disparities in micro-vascular and macro-vascular complications among persons with diabetes [13,14,19,24,27,33,34,37,39,40,45,46,48]. The micro-vascular complications included retinopathy, nephropathy as well as peripheral sensory neuropathy or was not individually specified in the papers reviewed. Studies reporting on macro-vascular complications specified diabetic foot amputations only.
Afro-Caribbeans had a higher prevalence of micro-vascular complications related to diabetes when compared to South Asians and Caucasians in the United Kingdom [19,27,37]. In one study it results were mixed depending on the method of testing for the peripheral sensory neuropathy [13] and in another study that compared Afro-Caribbeans to Caucasians the neuropathy was lower (23 ± 4 vs. 35 ± 3 p = 0.03) though nephropathy (14 ± 3 vs. 11 ± 2 p = 0.6) and retinopathy (24 ± 4 vs. 20 ± 3 p = 0.4) were higher respectively [39]. Overall macro-vascular complications related to diabetes was lower in the Afro-Caribbean populations compared to Caucasians [13,19,39] but comparable to the South-Asian ethnic group [13,19]. Within the Caribbean, the rates of amputation however were found to be higher in Afro-Trinidadians compared to Indo-Trinidadians [34].
With regard to age and sex differences in diabetes complications, one hospital-based cross sectional study among persons with amputation in Jamaica found that older males had higher rates of below knee amputation [24]. In the same study, women were found to have significantly better quality of life and function scores than men as measured by the SF-36 [24]. In another study Leske et al. reported that although the prevalence of diabetic retinopathy varied by age, an increase with age was only evident in women [40].
Inequalities in healthcare utilization and access and diabetes complications
There were very little published data in this area. One study found that there were significant differences in the burden of diabetes complications in the Caribbean population with higher levels of morbidity and lower healthcare utilization in those of lower socioeconomic status [33]. Morbidity from diabetes was greater in groups with lower educational attainment. Private health care was used less frequently by persons in the lower social groups. In another paper [37], Gulliford’s group found that in comparing the Afro-Caribbean, Caucasian, African and other Black ethnic groups, there was notable socioeconomic inequality in sight threatening diabetic retinopathy.
Place of residence: urban rural differences
There remains a dearth of published information on the influence of place of residence on diabetes mellitus (see Figure 3). Of the studies found, most were carried out in urban areas and among those which included rural dwellers; the authors did not present data on differences in disease outcome by place of residence.
Disparity indicators and knowledge gaps
The most frequently reported disparity indicators among the afro-Caribbean population in this review were ethnicity and sex (Figure 3). Among studies reporting on ethnic disparities, the majority examined the prevalence of diabetes (19) and its complications (13). With the exception of incidence of diabetes, sex differences were explored by 15 studies across the other disparity measures, the bulk of which were prevalence studies. Very few studies reported on socioeconomic status and age by the disparity measure, while no study was found to examine indicators such as geographic location and disability status (Figure 4). Of note, very few indicators were investigated in terms of incidence, and mortality from diabetes.
Discussion
This review presents an in-depth outline of the scope of the published literature relating to the investigation of disparities in diabetes mellitus in the Caribbean and the Caribbean Diaspora. The review was based on a comprehensive search of the literature and as such should capture the full range of available studies on health disparities in the Caribbean. We acknowledge however that it is possible that some relevant studies may have been missed from this review, as the search strategy, although iterative and broad, was restricted only to studies published in English which may exclude literature published in the Spanish and French speaking Caribbean as well as those from Caribbean immigrant populations published in languages other than English.
Most of the studies were done in urban settings on Afro-Caribbean immigrants to the United Kingdom over a forty year period from 1972–2012. The comparison groups were mainly Afro-Caribbean vs. Caucasians and Afro-Caribbean vs. South Asians. Very few studies published in English were found which compared Afro-Caribbeans to Latin American populations and none of the studies compared Afro-Caribbean to African American populations. The lack of comparison with the African American population was mainly due to the fact that the categories of race provided by the U.S. Office of Management and Budget and used by the Census Bureau do not disaggregate the Black/African American to allow for comparisons using subset groups such as African-Caribbean population, and would account for no studies comparing the Afro-American population with the Afro-Caribbean Population [56].
Overall it can be said that, the prevalence of diabetes mellitus was higher within the Afro-Caribbean population when compared to Caucasian or other African populations but lower when compared to South Asian populations which were the main groups of comparison. The prevalence of diabetes is higher in women when compared to men and higher in people of lower SES when measured by education and or income. In addition, the morbidity and mortality from diabetes was higher in lower SES groups which also reflected accessibility of health care. The prevalence of the micro-vascular complications related to diabetes mellitus is higher in people of Afro-Caribbean descent when compared to other ethnic groups but when the macro-vascular complications were considered the results were mixed across the ethnic groups.
Although disparities in diabetes mellitus as it relates to disability were of interest, no studies on this area were found.
It must be noted that there was a wide range of study types looking at different populations of persons with diabetes so many of the comparisons were difficult and inferences had to be made.
Conclusions
We have found that while a number of studies have been published exploring health disparities in relation to diabetes mellitus, the literature on diabetes health disparities in Caribbean origin populations is limited, in particular as it relates to studies conducted within the Caribbean. There were no studies comparing Afro-Caribbean with African American populations. Such studies would help in understanding the mechanisms underlying health disparities among minority population in the United States and the influence of factors such as self-governance, discriminations and variations in health care systems on health disparities. Future research should address these knowledge gaps and approaches to reduce them as we seek to reduce health disparities and improve health for all social and ethnic groups.
References
King H, Aubert RE, Herman WH. Global burden of diabetes, 1995–2025: prevalence, numerical estimates, and projections. Diabetes Care. 1998;21(9):1414–31.
International_Diabetes_Federation. IDF Diabetes Atlas. In: International Diabetes Federation. 5th ed. 2011.
Ferguson T, Tulloch-Reid M, Wilks R. The epidemiology of diabetes mellitus in Jamaica and the Caribbean: a historical review. West Indian Med J. 2010;59:259–64.
Nelson A. Unequal treatment: confronting racial and ethnic disparities in health care. J Natl Med Assoc. 2002;94(8):666–8.
Marwick C. Healthy People 2010 initiative launched. JAMA. 2000;283(8):989–90.
Koh HK, Piotrowski JJ, Kumanyika S, Fielding JE. Healthy people: a 2020 vision for the social determinants approach. Health Educ Behav. 2011;38(6):551–7.
Rio Political Declaration on Social Determinants of Health. [http://www.who.int/sdhconference/declaration/en/index.html]
Hayward K, Colman R, Pannozzo L. Health Disparities Indicators. In: Background Report For Developing Health Disparities Indicators in Canada, GPI Atlantic. 2008.
Carter-Pokras O, Baquet C. What is a “health disparity”? Public Health Rep (Washington, DC:1974). 2002;117(5):426–34.
Mays N, Roberts E, Popay J. Synthesising research evidence. In: Studying the organisation and delivery of health services: Research methods. 2001. p. 188–220.
Arksey H, O’Malley L. Scoping studies: towards a methodological framework. Int J Soc Res Methodol. 2005;8(1):19–32.
Pawson R. Evidence-based policy: in search of a method. Evaluation. 2002;8(2):157–81.
Abbott CA, Garrow AP, Carrington AL, Morris J, Van Ross ER, Boulton AJ, et al. Foot ulcer risk is lower in South-Asian and african-Caribbean compared with European diabetic patients in the U.K.: the North-West diabetes foot care study. Diabetes Care. 2005;28(8):1869–75.
Abbott CA, Malik RA, van Ross ERE, Kulkarni J, Boulton AJM. Prevalence and characteristics of painful diabetic neuropathy in a large community-based diabetic population in the U.K. Diabetes Care. 2011;34(10):2220–4.
Admiraal WM, van Valkengoed IGM, L de Munter JS, Stronks K, Hoekstra JBL, Holleman F. The association of physical inactivity with Type 2 diabetes among different ethnic groups. Diabet Med. 2011;28(6):668–72.
Agyemang C, Kunst AE, Bhopal R, Anujuo K, Zaninotto P, Nazroo J, et al. Diabetes prevalence in populations of South Asian Indian and African origins: a comparison of England and the Netherlands. Epidemiology. 2011;22(4):563–7.
Babwah F, Baksh S, Blake L, Cupid-Thuesday J, Hosein I, Sookhai A, et al. The role of gender in compliance and attendance at an outpatient clinic for type 2 diabetes mellitus in Trinidad. Pan Am J Public Health. 2006;19(2):79–84.
Barcelo A, Pelaez M, Rodriguez-Wong L, Pastor-Valero M. The prevalence of diagnosed diabetes among the elderly of seven cities in Latin America and the Caribbean: The Health Wellbeing and Aging (SABE) Project. J Aging Health. 2006;18(2):224–39.
Baskar V, Kamalakannan D, Holland MR, Singh BM. Does ethnic origin have an independent impact on hypertension and diabetic complications? Diabetes Obes Metab. 2006;8(2):214–9.
Cappuccio FP, Cook DG, Atkinson RW, Strazzullo P. Prevalence, detection, and management of cardiovascular risk factors in different ethnic groups in south London. Heart. 1997;78(6):555–63.
Chaturvedi N, Jarrett J, Morrish N, Keen H, Fuller JH. Differences in mortality and morbidity in African Caribbean and European people with non-insulin dependent diabetes mellitus: results of 20 year follow up of a London cohort of a multinational study. BMJ. 1996;313(7061):848–52.
Conway DSG, Lip GYH. Ethnicity in relation to atrial fibrillation and stroke (the West Birmingham Stroke Project). Am J Cardiol. 2003;92(12):1476–9.
Cooper RS, Rotimi CN, Kaufman JS, Owoaje EE, Fraser H, Forrester T, et al. Prevalence of NIDDM among populations of the African diaspora. Diabetes Care. 1997;20(3):343–8.
Cox PSL, Williams SKP, Weaver SR. Life after lower extremity amputation in diabetics. West Indian Med J. 2011;60(5):536–40.
Creatore MI, Booth GL, Manuel DG, Moineddin R, Glazier RH. Diabetes screening among immigrants: a population-based urban cohort study. Diabetes Care. 2012;35(4):754–61.
Cruickshank JK, Beevers DG, Osbourne VL, Haynes RA, Corlett JC, Selby S. Heart attack, stroke, diabetes, and hypertension in West Indians, Asians, and whites in Birmingham, England. Br Med J. 1980;281(6248):1108.
Cruickshank JK, Alleyne SA. Black West Indian and matched white diabetics in Britain compared with diabetics in Jamaica: body mass, blood pressure, and vascular disease. Diabetes Care. 1987;10(2):170–9.
Eldemire D, Hagley K. Diabetes mellitus in the Jamaican elderly. West Indian Med J. 1996;45(3):82–4.
Ferguson TS, Francis DK, Tulloch-Reid MK, Younger NOM, McFarlane SR, Wilks RJ. An update on the burden of cardiovascular disease risk factors in Jamaica: findings from the Jamaica Health and Lifestyle Survey 2007–2008. West Indian Med J. 2011;60(4):422–8.
Florey CV, McDonald H, McDonald J, Miall WE. The prevalence of diabetes in a rural population of Jamaican adults. Int J Epidemiol. 1972;1(2):157–66.
Gill PS, Calvert M, Davis R, Davies MK, Freemantle N, Lip GYH. Prevalence of heart failure and atrial fibrillation in minority ethnic subjects: the Ethnic-Echocardiographic Heart of England Screening Study (E-ECHOES). PLoS ONE [Electronic Resource]. 2011;6(11):e26710.
Goyal D, Tayebjee M, Lip GYH, MacFadyen RJ. South Asian or Afro-Caribbean ethnicity is not associated with altered 1 min heart rate recovery estimates in suspected coronary artery disease patients. Int J Cardiol. 2007;114(2):261–4.
Gulliford MC, Ariyanayagam-Baksh SM, Bickram L, Picou D, Mahabir D. Social environment, morbidity and use of health care among people with diabetes mellitus in Trinidad. Int J Epidemiol. 1997;26(3):620–7.
Gulliford MC, Mahabir D. Social inequalities in morbidity from diabetes mellitus in public primary care clinics in Trinidad and Tobago. Soc Sci Med. 1998;46(1):137–44.
Gulliford MC, Mahabir D. Utilisation of private care by public primary care clinic attenders with diabetes: relationship to health status and social factors. Soc Sci Med. 2001;53(8):1045–56.
Gulliford MC, Mahabir D, Rocke B. Diabetes-related inequalities in health status and financial barriers to health care access in a population-based study. Diabet Med. 2004;21(1):45–51.
Gulliford MC, Dodhia H, Chamley M, McCormick K, Mohamed M, Naithani S, et al. Socio-economic and ethnic inequalities in diabetes retinal screening. Diabet Med. 2010;27(3):282–8.
Khattar RS, Swales JD, Senior R, Lahiri A. Racial variation in cardiovascular morbidity and mortality in essential hypertension. Heart. 2000;83(3):267–71.
Leggetter S, Chaturvedi N, Fuller JH, Edmonds ME. Ethnicity and risk of diabetes-related lower extremity amputation: a population-based, case–control study of African Caribbeans and Europeans in the United kingdom. Arch Intern Med. 2002;162(1):73–8.
Leske MC, Wu SY, Hyman L, Li X, Hennis A, Connell AM, et al. Diabetic retinopathy in a black population: the Barbados Eye Study. [Erratum appears in Ophthalmology 2000 Mar;107(3):412]. Ophthalmology. 1999;106(10):1893–9.
Markus HS, Khan U, Birns J, Evans A, Kalra L, Rudd AG, et al. Differences in stroke subtypes between black and white patients with stroke: the South London Ethnicity and Stroke Study. Circulation. 2007;116(19):2157–64.
Mbanya JC, Cruickshank JK, Forrester T, Balkau B, Ngogang JY, Riste L, et al. Standardized comparison of glucose intolerance in west African-origin populations of rural and urban Cameroon, Jamaica, and Caribbean migrants to Britain. Diabetes Care. 1999;22(3):434–40.
Miller GJ, Maude GH, Beckles GL. Incidence of hypertension and non-insulin dependent diabetes mellitus and associated risk factors in a rapidly developing Caribbean community: the St James survey, Trinidad. J Epidemiol Community Health. 1996;50(5):497–504.
Molokhia M, Nitsch D, Patrick AL, McKeigue P. 30 Year patterns of mortality in Tobago, West Indies, 1976–2005: impact of glucose intolerance and alcohol intake. PLoS ONE [Electronic Resource]. 2011;6(1):e14588.
Mungrue K, Ramdial S, Barran A, Lorinda B, Bridgelal A, Gildharie S, et al. The epidemiology of end stage renal disease at a centre in Trinidad. West Indian Med J. 2011;60(5):553–6.
Prasad S, Singh S, Duncan N, Cairns TDH, Griffith M, Hakim N, et al. Ethnicity and survival on dialysis in west London. Kidney Int. 2004;66(6):2416–21.
Riste L, Khan F, Cruickshank K. High prevalence of type 2 diabetes in all ethnic groups, including Europeans, in a British inner city: relative poverty, history, inactivity, or 21st century Europe? Diabetes Care. 2001;24(8):1377–83.
Sedgwick JE, Pearce AJ, Gulliford MC. Evaluation of equity in diabetes health care in relation to African and Caribbean ethnicity. Ethnicity & health. 2003;8(2):121–33.
Shantsila E, Wrigley B, Shantsila A, Tapp LD, Blann AD, Gill PS, et al. Ethnic differences in macro-vascular and micro-vascular function in systolic heart failure. Circ Heart Fail. 2011;4(6):754–62.
Sharp A, Tapp R, Francis DP, McG Thom SA, Hughes AD, Stanton AV, et al. Ethnicity and left ventricular diastolic function in hypertension an ASCOT (Anglo-Scandinavian Cardiac Outcomes Trial) substudy. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2008;52(12):1015–21.
Sosin MD, Patel JV, Bhatia GS, Hughes EA, Davis RC, Lip GYH. Effects of white European, African Caribbean and South Asian ethnicity on homocysteine levels in patients with systolic heart failure. Int J Cardiol. 2008;129(1):69–75.
Sargeant LA, Bennett FI, Forrester TE, Cooper RS, Wilks RJ. Predicting incident diabetes in Jamaica: the role of anthropometry. Obes Res. 2002;10(8):792–8.
Ethnicity and cardiovascular disease. The incidence of myocardial infarction in white, South Asian, and Afro-Caribbean patients with type 2 diabetes (U.K. Prospective Diabetes Study 32). Diabetes care. 1998;21(8):1271-7.
Wilks R, Rotimi C, Bennett F, McFarlane-Anderson N, Kaufman JS, Anderson SG, et al. Diabetes in the Caribbean: results of a population survey from Spanish Town, Jamaica. Diabet Med. 1999;16(10):875–83.
Wilks R, Bennett F, Forrester T, McFarlane-Anderson N. Chronic diseases: the new epidemic. West Indian Med J. 1998;47 Suppl 4:40–4.
Jones NA, Bullock JJ. Understanding Who Reported Multiple Races in the U.S. Decennial Census: Results From Census 2000 and the 2010 Census. Fam Relat. 2013;62(1):5–16.
Acknowledgements
The project described was supported by Grant Number U24MD006959 from the National Institute on Minority Health and Health Disparities (NIMHD), United State of America. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Institute on Minority Health and Health Disparities or the National Institutes of Health (NIH), United States of America.
The authors wish to acknowledge the contribution of Ms. Tamara Rader, Library Scientist of the University of Ottawa, Ontario, Canada, for her assistance with the preliminary data search.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Corresponding author
Additional information
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Authors’ contributions
NRB: Developed the protocol; conducted screening and data extraction; led analysis and interpretation of data; drafted manuscript, critically revising for intellectual content and approved final version. DKF: Developed the protocol; conducted screening and data extraction; led analysis and interpretation of data; drafted manuscript, critically revising for intellectual content and approved final version. TSF: Developed the protocol; participated in analysis and interpretation of data; critically revised for intellectual content and approved final version. RJW: Conceptualized the project; developed the protocol; participated in analysis and interpretation of data; critically revised for intellectual content and approved final version. AJH: Conceptualized the project; developed the protocol; participated in analysis and interpretation of data; critically revised for intellectual content and approved final version. ENH: Conceptualized the project; critically revising for intellectual content, approved final version. MYM: Conceptualized the project; critically revising for intellectual content, approved final version. LWS: Conceptualized the project; critically revising for intellectual content; approved final version. Members of the USCAHDR Group (AB, IH, CH, AH, LW, NYC): Contributed to the development of the protocol, critically revising for intellectual content, approved final version. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Authors’ information
Members of the USCAHDR Group are: Bennett NR, Bidulescu A, Ferguson TS, Francis DK, Hambleton IR, Harris EN, Hassell C, Hennis AJM, MacLeish MY, Sullivan LW, Wilks RJ, Williams L, and Younger-Coleman NO.
Rights and permissions
This article is published under an open access license. Please check the 'Copyright Information' section either on this page or in the PDF for details of this license and what re-use is permitted. If your intended use exceeds what is permitted by the license or if you are unable to locate the licence and re-use information, please contact the Rights and Permissions team.
About this article
Cite this article
Bennett, N.R., Francis, D.K., Ferguson, T.S. et al. Disparities in diabetes mellitus among Caribbean populations: a scoping review. Int J Equity Health 14, 23 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12939-015-0149-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12939-015-0149-z