Abstract
Background
Exendin-4, an exogenous glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor (GLP-1R) agonist, protects the heart from ischemia/reperfusion injury. However, the mechanisms for this protection are poorly understood. Caveolae, sarcolemmal invaginations, and caveolins, scaffolding proteins in caveolae, localize molecules involved in cardiac protection. We tested the hypothesis that caveolae and caveolins are essential for exendin-4 induced cardiac protection using in vitro and in vivo studies in control and caveolin-3 (Cav-3) knockout mice (Cav-3 KO).
Methods
Myocytes were treated with exendin-4 and then incubated with methyl-β-cyclodextrin (MβCD) to disrupt caveolae formation. This was then followed by simulated ischemia/reperfusion (SI/R). In addition, cardiac protection in vivo was assessed by measuring infarct size and cardiac troponin levels.
Results
Exendin-4 protected cardiac myocytes (CM) from SI/R [35.6 ± 12.6% vs. 64.4 ± 18.0% cell death, P = 0.034] and apoptosis but this protection was abolished by MβCD (71.8 ± 10.8% cell death, P = 0.004). Furthermore, Cav-3/GLP-1R co-localization was observed and membrane fractionation by sucrose density gradient centrifugation of CM treated with MβCD + exendin-4 revealed that buoyant (caveolae enriched) fractions decreased Cav-3 compared to CM treated with exendin-4 exclusively. Furthermore, exendin-4 induced a reduction in infarct size and cardiac troponin relative to control (infarct size: 25.1 ± 8.2% vs. 41.4 ± 4.1%, P < 0.001; troponin: 36.9 ± 14.2 vs. 101.1 ± 22.3 ng/ml, P < 0.001). However, exendin-4 induced cardiac protection was abolished in Cav-3 KO mice (infarct size: 43.0 ± 6.4%, P < 0.001; troponin: 96.8 ± 26.6 ng/ml, P = 0.001).
Conclusions
We conclude that caveolae and caveolin-3 are critical for exendin-4 induced protection of the heart from ischemia/reperfusion injury.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) is an intestinal hormone secreted in a nutrient-dependent manner that stimulates insulin secretion and inhibits glucagon secretion and gastric emptying, resulting in reduced post-prandial hyperglycemia [1]. GLP-1 acts upon the GLP-1 receptor (GLP-1R), which belongs to the family of G-protein-coupled receptor (GPCRs) [2]. This receptor is abundantly expressed in the gastrointestinal tract, but has also been detected in the central nervous system, heart, vascular smooth muscle cells, endothelial cells, and macrophages [3],[4]. Recently, GLP-1 has been shown to reduce an infarct size in both in vitro and in vivo animal models of cardiac ischemia/reperfusion injury [5]-[7] and exendin-4 (Ex-4), an exogenous GLP-1R agonist isolated form the Gila monster lizard [8], has reported to have very similar effects [4],[9],[10].
Caveolae are small flask-like invaginations of sarcolemmal membrane that are enriched in lipids. Caveolin-3 (Cav-3) is the principal protein component of caveolae and can interact with a number of signaling molecules including G protein, receptor tyrosine kinases, and GPCRs via caveolin-binding motif [11]-[13]. In our previous studies, we have shown that both caveolae and Cav-3 were essential in cardiac protection against ischemia/reperfusion in the animal model [14]-[17]. However, studies addressing the plasma-membrane localization of GLP-1R are not fully known and the impact of caveolae and Cav-3 on GLP-1-induced cardiac protection has not been investigated. Therefore, we hypothesized that both caveolae and Cav-3 are a critical component of GLP-1-induced cardiac protection and that coordination of protective signaling is dependent on the co-localization of Cav-3 and GLP-1R.
Material and methods
All animals were treated in compliance with the Guidelines for Proper Conduct of Animal Experiment and Related Activities (Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan) and the protocols, which was assigned to ARRIVE guidelines [18], approved by the Animal Care and Use Committee at the University of Tokushima. Male Wistar rats (12-14 weeks old, 250-300 g body weight) and male C57BL/6 mice (8-10 weeks old, 21-25 g body weight) were purchased from Japan SLC, and Cav-3 KO mice (8-10 weeks old, 21-25 g body weight) were created as reported previously [19]. The animals were kept on a 12 hour light dark cycle in a temperature and humidity-controlled room, and had ad lib access to food and water.
Preparation of Cardiac Myocytes (CM)
CM were isolated from adult male Wistar rats as described [20],[21]. In brief, hearts were retrograde perfused on a Langendorff apparatus and digested with collagenase (Worthington). Myocytes were plated in Medium 199 (4% fetal bovine serum and 1% penicillin/streptomycin) on laminin (2 μg/cm2)-coated plates for 1 h. Plating media was changed to serum-free media (1% bovine serum albumin) to remove non-myocytes and CM were incubated for 24 h at 37 C in 5% CO2.
Simulated ischemia/reperfusion (SI/R) in isolated cardiac myocytes
CM were plated on laminin-coated 12-well plates, and simulated ischemia was induced by replacing the air content with a 95% N2 and 5% CO2 gas mixture at 2 L/min in a chamber and by replacing the media to glucose-free media for 60 min. This was then followed by 60 min of reperfusion by replacing the media with normal maintenance media and by incubating the cells with 21% O2 and 5% CO2[16]. CM were exposed to 0.3 nM or 3.0 nM Ex-4, a GLP-1R agonist, for 1 h prior to SI/R. Cell death was quantified by counting trypan blue-stained cells with results expressed as a percentage of total cells counted. Cells were counted (3 random fields per well) using ImageJ software to determine percent cell death. To determine the impact of caveolae on cardiac protection, methyl-β-cyclodextrin (MβCD) was used as described [16]. CM were incubated under maintenance media (control conditions) or in the presence of MβCD (1 mM) for 1 h before SI/R.
Depolarization of the mitochondrial membrane
To analyze mitochondrial membrane potential, we used the JC-1 dye (MitoPT JC-1, ImmunoChemistry Technologies, Bloomington, MN), which shifts the fluorescence emission from red (580 nm) to green (488 nm) as mitochondrial membrane is depolarized. After SI/R, as described above, myocytes were incubated with JC-1 for 20 min at 37 C, and cellular fluorescence was determined by a fluorescence microscope (Leica TCS NT, Heidelberg, Germany). Data are assessed by comparing the ratios of red/green.
Gene expression analyses
Total RNA was extracted from CM using RNeasy Plus Universal Mini Kits (QIAGEN, Valencia, CA). Total RNA (1 g) was reverse-transcribed to cDNA in a final volume of 20 μL using the Primescript RT Reagent kit (Takara, Shiga, Japan). Real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR) was performed in a final volume of 10 μL containing 50 ng of the cDNA template and primers using a StepOnePlus Real-Time PCR System (Life Technologies, Carlsbad, CA). To determine the effect on apoptosis gene expression, we measured the expression of the BH3-interacting domain death agonist (BID), Bcl-2-associated death promoter (BAD), Caspase-3, Caspase-8, and Caspase-9, and Bcl-2 associated X protein (BAX) genes. To determine the effect on anti-apoptosis gene expression, we measured the expression of the B-cell lymphoma 2 (BCL-2) and inhibitor of apoptosis 1 (IAP-1) genes.
Immunofluorescence
CM were fixed with paraformaldehyde, incubated with 100 mM glycine, permeabilized in 0.1% buffered Triton X-100, and blocked with 1% bovine serum albumin, phosphate-buffered saline, and 0.05% Tween. Samples were then incubated with primary antibody (GLP-1R and caveolins-3, Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Santa Cruz, CA) (1:100) in 1% bovine serum albumin, phosphate-buffered saline, and 0.05% Tween for 24 h. Excess antibody was removed, and samples were incubated with fluorescein Alexa-conjugated secondary antibodies (1:250) for 1 h. To remove excess secondary antibody, samples were washed with phosphate-buffered saline/0.1% Tween and samples were mounted in UltraCruz (Santa Cruz Bioctechnology) for microscopy imaging. Fluorescent images of cell sections excited at 488 and 560 nm were captured using a confocal laser scanning microscope (Leica TCS NT, Heidelberg, Germany) equipped with an argon-krypton laser source. Images were taken at 400 × magnification and were assessed quantitatively by Image-Pro Plus (Media Cybernetics, Silver Spring, MD).
Sucrose density fractionation
Whole left ventricles or myocytes were used for sucrose density membrane fractions as reported previously [22]. Briefly, approximately 1 ml of lysate was mixed with 1 ml of 80% sucrose in 25 mM MES and 150 mM NaCl (MES buffered saline, MBS, pH 6.5) to form 40% sucrose and loaded at the bottom of an ultracentrifuge tube. A discontinuous sucrose gradient was generated by layering 6 ml of 35% sucrose prepared in MBS followed by 4 ml of 5% sucrose in MBS. The gradient was centrifuged at 175,000 g using a P70AT2 rotor (Hitachi Koki Co.) for 3 h at 4 C. After centrifugation, samples were removed in 1 ml aliquots to yield 12 fractions. We defined fraction 4 6 as buoyant membrane fractions enriched in caveolae and proteins associated with caveolae. Fraction 9-12 were defined as nonbuoyant fractions.
Immunoprecipitation
Immunoprecipitation was performed using Protein A Sepharose CL-4B (GE Healthcare) as described previously [23]. Buoyant fraction samples were incubated with primary antibody (GLP-1R and caveolins-3, Santa Cruz Biotechnology) for 3 h at 4 C, immune-precipitated overnight with protein-agarose at 4 C, and then centrifuged for 5 min at 13,000 g. Protein-agarose pellets were washed 3 times. Wash buffer was removed and sample buffer was added, and then boiled for 5 min at 95 C for immunoblotting.
Immunoblot analysis
Proteins were separated by SDS-PAGE 10% polyacrylamide precast gels (Bio-Rad Laboratories) and transferred to a polyvinylidene diflouride membrane by electroelution. Membranes were blocked in PBS containing 2.0% nonfat dry milk and incubated with primary antibody overnight (GLP-1R and caveolins-3, Santa Cruz Biotechnology; GAPDH, Santa Cruz Biotechnology and Cell Signaling Technology) and at 4 C. Bound primary antibodies were visualized using secondary antibodies (Santa Cruz Biotechnology) conjugated with horseradish peroxidase from Santa Cruz Biotechnology and ECL reagent from GE Healthcare [24]. All displayed bands migrated at the appropriate size, as determined by comparison to molecular weight standards (Santa Cruz Biotechnology).
Ischemia/reperfusion protocol and experimental groups
C57BL/6 mice and Cav-3 knockout (Cav-3 KO) micewere anesthetized with pentobarbital sodium (80 mg/kg ip) and mechanically ventilated by using a pressure-controlled ventilator (TOPO Ventilator, Kent Scientific) as described before [25]. Core temperature was maintained with a heating pad and ECG leads were placed to record heart rate. The hemodynamic effects were measured through the right carotid artery cannulation with a 1.4 F Mikro-tip pressure transducer (Model SPR-671, Millar Instruments), which was connected to an amplifier (Model TC-510, Millar Instruments) for determination of heart rate, arterial blood pressure, and rate pressure product as previous before [26]. After thoracotomy, baseline was established, and mice were randomly assigned to experimental protocols. Lethal ischemia was produced by occluding the left coronary artery with a 7-0 silk suture on a taper BV-1 needle (Ethicon) for 30 min. After 30 min of occlusion, the ligature was released and the heart was reperfused for 2 h. After reperfusion, mice were heparinized, and the coronary artery was again occluded. The area at risk (AAR) was determined by staining with 1% Evans blue (Sigma). The heart was immediately excised and placed into 1% agarose and allowed to harden. Once hardened, the heart was cut into 1.0-mm slices (McIlwain tissue chopper; Brinkmann Instruments). Each slice of left ventricle (LV) was then counterstained with 2,3,5,-triphenyltetrazolium chloride (Sigma). After overnight storage in 10% formaldehyde, slices were weighed and visualized under a microscope (SZ61-TR, Olympus) equipped with a charge coupled device camera (DXM 1200 F, Nikon). The images were analyzed (Image-Pro Plus, Media Cybernetics), and AAR and infarct size (IS) was determined by planimetry as previously described [27],[28]. Cardiac troponin I levels in the serum were measured using a High Sensitivity Mouse Cardiac Troponin-I ELISA Kit (Life Diagnostics).
Statistical analysis
Statistical analyses were performed by one-way and two-way ANOVA for repeated measures, followed by Bonferroni post-hoc test. All data are expressed as mean ± SD. Statistical significance was defined as P < 0.05.
Results
Experimental animals
The animals’ health status was monitored throughout the experiments by a health surveillance program. A total of 98 animals were used in the experiments described here (35 animals for in vitro simulated ischemia/reperfusion, 23 for immunofluorescence and immunoblot analyses, and 40 for in vivo ischemia/reperfusion experiments). Five mice died shortly after ischemia/reperfusion because of fatal cardiac arrhythmia in the in vivo experiments (control, 1; Ex-4 administration, 2; Cav-3 KO control, 1; Cav-3 KO Ex-4 administration, 1).
Exendin-4 induces cardiac protection in CM
CM were administered with various concentration of Ex-4 and then SI/R (Figure 1A). Administration of 0.3 nM and 3.0 nM Ex-4 before SI/R decreased cell death when compared to SI/R alone (47.4 ± 9.9%, and 35.6 ± 12.6% and 64.4 ± 18.0% cell death, respectively, n = 5 per each groups; Figure 1B).
Effects of exendin-4 on simulated ischemia/reperfusion (SI/R) of cardiac myocytes. (A) Cardiac myocytes were rod-shaped and treated with various concentration of exendin-4 prior to exposure to SI/R. (B) Cell death was determined by trypan blue staining. Optimal protection was observed at 3.0 nM exendin-4. Group sizes are indicated on the individual bars in parentheses.
MβCD abolish exendin-4 induced cardiac protection
CM were incubated with 1% BSA with 0.1% penicillin/streptomycin (Control) or in control media along with 3.0 nM Ex-4, and/or then incubated with 1 mM MβCD (Figure 2A). In the present study, the protective effect of Ex-4 was abolished in CM with MβCD (35.6 ± 12.6% [n = 4] and 71.8 ± 10.8% [n = 5] cell death, respectively; P = 0.004). Additionally, we observed no significant increase in basal cell death with the various treatments (Figure 2B).
In vitro assessment of the role of caveolae in exendin-4 (Ex-4) induced cardiac protection. (A) Summary illustration of in vitro experimental groups. (B) Cardiac myocytes exposed to simulated ischemia/reperfusion (SI/R) were exposed to experimental procedures outlined in A. Cell death was determined by trypan blue staining. Cardiac myocytes under control conditions (Control) had minimal cell death. Methyl-β-cyclodextrin (MβCD) abolished the Ex-4 induced cardiac protection effect. Group sizes are indicated on the individual bars in parentheses. (C) Apoptotic changes were measured by investigating mitochondrial membrane potential using JC-1 after SI/R. The excitation rate (red/green) indicates changes within the mitochondrial membrane potential. *P < 0.001 vs. SI/R, SIR + Ex-4, SI/R with MβCD, and SI/R + Ex-4 with MβCD. #P < 0.05 vs. Control, SI/R + Ex-4, and Control with MβCD. n = 4 per each group. (D) Real-time polymerase chain reaction analysis of pro-apoptotic and anti-apoptotic gene expression after re-oxygenation. n = 4 per each group.
To test whether Ex-4 inhibited apoptosis by modifying the mitochondrial membrane potential during reperfusion injury, we measured a membrane potential-sensitive dye, 5,5’,6,6’-tetrachloro-1,1’,3,3’-tetraethylbenzamidazolocarbocyanin iodide (JC-1). As shown in Figure 2C, Ex-4 inhibited reduction of mitochondrial membrane potential that occurred in the re-oxygenated cells expressing SI/R suggesting inhibition of apoptosis. This was further confirmed as Ex-4 decreased pro-apoptic and increased anti-apoptotic gene expression (Figure 2D; n = 4 per each groups).
Co-localization between GLP-1R and Cav-3, and MβCD alter caveolins expression
Immunofluorescence microscopy showed that Cav-3 co-localizes with GLP-1R on the surface of the CM (Figure 3A). Co-immunoprecipitation experiments using cardiac lysates and antibodies to Cav-3 and GLP-1R provided further evidence for the interaction of these proteins (Figure 3B). Expression of Cav-3 in buoyant caveolar fractions (fractions 4-6) was significantly increased after administration of Ex-4 as compared with control mice, and Ex-4 induced migration of Cav-3 from non-buoyant to buoyant fraction was eliminated by MβCD (Figure 4).
Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor (GLP-1R) localization with caveolins or caveolae. (A) Immunofluorescence analysis of the expression and colocalization of caveolin-3 (Cav-3) and GLP-1R in cardiac myocytes. Fluorescent secondary antibodies were used to determine Cav-3 (green) and GLP-1R (red) localization, and strong colocalization (merged images, yellow) were observed on the cell surface membrane. Bar length = 10 μm. (B) The colocalization was confirmed by immunoprecipitation (IP). Immunoblot (IB) analysis detected Cav-3 and GLP-1R in Cav-3 and GLP-1R IP of cell lysates. Supernatants (SUP) from which the immunoprecipitates were generated were stained for GAPDH as loading controls.
Lysed and fractionated hearts on sucrose density gradient. Fractions were collected and probed for caveolin-3 (Cav-3). We defined fractions 4-6 as buoyant membrane fractions enriched in caveolae and proteins associated with caveolae; fractions 9-12 were defined as nonbuoyant fractions, noncaveolar membranes. Fraction 7-8 were considered a transition zone and were not analyzed. Significant localization of Cav-3 in buoyant fractions was observed in the groups treated with exendin-4 (Ex-4), whereas control and methyl-μ-cyclodextrin (MβCD)-treated with Ex-4 cells showed no effects on Cav-3 localization. Group sizes are indicated on the individual bars in parentheses.
Caveolin-3 is required for exendin-4 induced cardiac protection
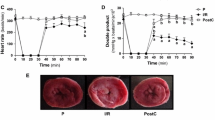
To assess the role of Cav-3 in the protection from ischemia/reperfusion injury, we treated C57BL/6 wild-type mice or Cav-3 KO mice with Ex-4 administration, and then exposed the mice to ischemia/reperfusion (Figure 5A). We found no significant differences between groups in pre-occlusion heart rate, blood pressure, or rate pressure product with and without Ex-4 (Table 1). The ability of Ex-4 to protect from ischemia/reperfusion injury was abolished in Cav-3 KO mice compared to wild-type animals (43.0 ± 6.4% [n = 8] and 25.1 ± 8.2% [n = 7] IS/AAR, P < 0.001) even though there was a similar AAR in all groups of animals (Figure 5B). Cardiac troponin I (cTnI) levels were significantly attenuated by Ex-4 treatment in wild-type mice compared to control mice subjected to ischemia/reperfusion (36.9 ± 14.2 and 101.1 ± 22.3 ng/ml, P < 0.001); however, GLP-1 failed to reduce cTnI in Cav-3 KO mice and a level similar to control Cav-3 KO mice was observed (103.4 ± 38.4 and 96.8 ± 26.6 ng/ml, Figure 5C).
Caveolin-3 expression and reduction in infarct size. Mice underwent 30-min coronary artery occlusion followed by 2-h reperfusion after 24-h recovery from pretreatment with oxygen (Control) or exendin-4 (Ex-4) in wild-type and caveolin-3 knockout (Cav-3 KO) mice. (A) In vivo Ex-4 induced cardiac protection protocol. (B) Area at risk was calculated as a percentage of the left ventricle and revealed no significant differences between all groups. Ex-4 induced cardiac protection was abolished Cav-3 KO mice, as shown by no significant decrease in percent infarct size / area at risk when compared to control Cav-3 KO; however, a significant decrease in infarct size was observed between wild-type Ex-4 and Cav-3 KO Ex-4. (C) Cardiac troponin I, a marker of myocardial damage also revealed a significant decrease in Ex-4 treated control mice, but no effect in Cav-3 KO mice. Group sizes are indicated on the individual bars in parentheses. *P < 0.001 compared with Cav-3 KO pretreated with Ex-4.
Discussion
In the current study, treatment with MβCD, an agent that has been shown to decrease the number of caveolae, produced an attenuation of Ex-4 (GLP-1R agonist) induced cardiac protection in in vitro models. Additionally, consistent with these findings, we observed that Ex-4 induced cardiac protection cannot be elicited in Cav-3 KO mice, indicating that the presence of caveolae (dependent on Cav-3 expression) is essential for myocardial protection in the in vivo mouse models. This is the first study to investigate the role of caveolins or caveolae in Ex-4 induced cardiac protection.
GLP-1 cardioprotection
Nutrient-responsive intestinal hormones including GLP-1 are rapidly metabolized by enzyme dipeptidyl-peptidase-4 (DPP-4) to generate an N-terminally truncated metabolite GLP-1 (9-36) [1],[29]. Previous studies have demonstrated that the cardioprotective effect of exogenous GLP-1 were attributed to GLP-1R activation and subsequent recruitment of numerous intracellular signaling pathways involving protein kinase B, extracellular regulated kinases, p70S6K, and 5’ adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase as well as downstream phosphorylation and inhibition of the pro-apoptotic protein BAD [5],[6],[30]. Hausenloy et al. also showed that chronic treatment with DPP-4 inhibitors reduce infarct size via the GLP-1R-protein kinase A pathway, in a glucose dependent manner in vivo rat models and confirmed the cardioprotective action of the endogenous intact GLP-1 on ischemia/reperfusion injury [31]. Moreover, Bao et al. [32] revealed that the long acting GLP-1R agonist could provide more sustained cardioprotective effect in the setting of acute myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury than the short-acting Ex-4.
GLP-1 and the caveolin-dependent pathway
Caveolae, cholesterol and sphingolipid enriched invaginations of plasma membrane play a role physiological functions and vital to cardiac protective mechanisms. Caveolae and caveolins have been shown to play a fundamental role in the phenomenon of myocardial protection against ischemia/reperfusion injury [11]-[13]. In the present study, we investigated that wild-type mice treated with GLP-1 analogue, Ex-4, were protected against ischemia/reperfusion injury in vivo, whereas Cav-3 KO mice were not. In addition, Ex-4 protected isolated CM from hypoxia-induced cell death in vitro and had profound effects on membrane microdomains of CM. Our previous studies also revealed that Cav-3 KO mice, which decrease the number of myocardial caveolae, lose the ability to undergo cardioprotection from ischemia/reperfusion injury both in vitro and in vivo models [14]-[17]. Although there has been little evidence regarding the relationship between caveolae, caveolins and GLP-1R within the heart, other organ systems including human embryonic kidney (HEK) 293 cells and pancreatic β cells [33],[34]. Syme et al. demonstrated that GLP-1 receptor interacts with Cav-1 in an association that is necessary for receptor trafficking to the cell membrane and signaling activity in HEK 293 cells [33]. Furthermore, Yang et al. demonstrated that activation peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor β/σ protects pancreatic β cells from apoptosis by upregulating the expression of GLP-1R, and sterol regulatory element binding protein-1c/Cav-1 pathway regulates GLP-1R expression [34].
In the present study, we showed that that GLP-1R interacted with Cav-3 and that the administration of Ex-4 led to cardiac protection. Caveolins can interact with a series of signaling molecules, including GPCRs via caveolin-binding motifs and may act as a molecular chaperone for GPCRs [12],[13]. Overexpression of a dominant-negative form of Cav-1 or mutations within the Cav-1 binding domain of the GLP-1R attenuated GLP-1 binding and GLP-1R expression at the membrane [33]. Collectively, these data implicate that caveolae and caveolins are essential for GLP-1 induced cardiac protection by mediating the GLP-1R.
Hemodynamic effects of GLP-1
GLP-1 has been shown to increase blood pressure and heart rate in rats [35],[36] although others failed to demonstrate any hemodynamic changes in the porcine models [37],[38] and human studies [39]-[42]. In addition, Bose et al. investigated that the effects of GLP-1 infusion in rats subjected to 30 min ischemia and 120 min of reperfusion and observed that GLP-1 had no hemodynamic differences in their in vivo and ex vivo experimental models [5],[30],[43]. The hemodynamic effects of Ex-4 were also assessed in the animal models, in which dose-dependent increases in mean arterial pressure and heart rate were noted in rats [44]. In our in vivo studies, however, there were not any hemodynamic changes among the groups at the pre-occlusion time. This may be due to the dose and the timing of administration, Gardiner et al. showed that at a dose of 25 ng/kg i.v., Ex-4 had little effect, but at higher concentrations (250 ng/kg) significant tachycardia and pressor effects were noted for 60 min [44]. As the dose and time period used for cardiac protection in mice are not known, we selected the dosage and time of administration for Ex-4 based on the reports of Gardiner et al. to prevent any hemodynamic differences during pre-occlusion (250 ng/kg i.v. at 60 min before occlusion) [44]. Furthermore, GLP-1 has been shown to have central nervous effects on the control of blood pressure and heart rate [45]; however, this mechanism can be avoided in the in vitro setting. In our in vitro mouse models, we used 3.0 nM Ex-4 concentration, consistent with previous study by Ban et al. in which 3.0 nM Ex-4 protect against after ischemia/reperfusion in isolated mouse hearts [4],[10].
Study limitations
There are several limitations in the present study. First, we evaluated the GLP-1R dependent effects of Ex-4 in experiments that investigated ischemia/reperfusion injury. Recent studies suggest that GLP-1 (9-36), the metabolite that is generated by DPP-4 and 1000-fold lower affinity to GLP-1R [46], also improve LV contractile function and post-ischemic myocardial injury [47]. Furthermore, GLP-1R knockout mice have lower heart rate and blood pressure with an increase in cardiac mass and GLP-1 has been shown to protect perfused hearts from rodents lacking GLP-1R from ischemia [4]. These findings suggest that GLP-1 and its metabolite GLP-1 (9-36) may be capable of exerting GLP-1 receptor-independent pathways on the cardiovascular system [10]. Second, Cav-3 KO mice have a variety of deleterious phenotypes (i.e., muscle degeneration, insulin resistance, and progressive cardiomyopathy with age) that may affect outcome after ischemia/reperfusion injury [19],[48],[49].
Clinical implications
As a regulator of glucose homeostasis, an exogenous GLP-1 analogue or potentiating endogenous GLP-1 by DPP-4 inhibitors show promise for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) associated with cardiovascular disease. Moreover, there have been several clinical trials using GLP-1 as a therapy for cardiovascular disease in human subjects. Exenatide, an exogenous GLP-1 analogue, was found to be more beneficial than the other current regimens (DPP-4 inhibitors, insulin or tiazolidinediones), in reaching therapeutic goals recommended by the American Diabetes Association in the treatment of T2DM, which is also promising in the reduction of other co-morbidities such as cardiovascular risk [50]. Lonborg et al. [51] has shown that exenatide resulted in an increased salvage index among ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction patients with hyperglycemia and normoglycemia. Interestingly, endogenous circulating GLP-1 level was found to be increased in patients with high cardiovascular risk, suggesting it represents a contra-regulatory response in states of increased metabolic risk [52].
Conclusions
In conclusion, the current results demonstrate that GLP-1R co-localized with caveolae and caveolins-3 are essential for the cardiac protection induced by exendin-4 from ischemia/reperfusion injury.
Authors’ contributions
Conceived and designed the experiments: YMT, RT. Performed the experiments: YMT, RT, EH, YS, AS. Analyzed the data: EH, KT. Drafting of the manuscript and critically revising the manuscript: YMT, EH. Extensive review and editing of manuscript: YI, UY, KT. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Abbreviations
- GLP-1R:
-
Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor
- Cav-3:
-
Caveolin-3
- Cav-3 KO:
-
Caveolins-3 knockout
- MβCD:
-
Methyl-β-cyclodextrin
- SI/R:
-
Simulated ischemia/reperfusion
- CM:
-
Cardiac myocytes
- GLP-1:
-
Glucagon-like peptide-1
- GPCRs:
-
G-protein-coupled receptor
- Ex-4:
-
Exendin-4
- LV:
-
Left ventricle
- AAR:
-
Area at risk
- IS:
-
Infarct size
- cTnI:
-
Cardiac troponin I
- DPP-4:
-
Dipeptidyl-peptidase-4
- HEK:
-
Human embryonic kidney
- T2DM:
-
Type 2 diabetes mellitus
References
Drucker DJ: The biology of incretin hormones. Cell Metab. 2006, 3 (3): 153-165. 10.1016/j.cmet.2006.01.004.
Davidson MH: Cardiovascular effects of glucagonlike peptide-1 agonists. Am J Cardiol. 2011, 108 (3 Suppl): 33B-41B. 10.1016/j.amjcard.2011.03.046.
Baggio LL, Drucker DJ: Biology of incretins: GLP-1 and GIP. Gastroenterology. 2007, 132 (6): 2131-2157. 10.1053/j.gastro.2007.03.054.
Ban K, Noyan-Ashraf MH, Hoefer J, Bolz SS, Drucker DJ, Husain M: Cardioprotective and vasodilatory actions of glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor are mediated through both glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor-dependent and -independent pathways. Circulation. 2008, 117 (18): 2340-2350. 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.107.739938.
Bose AK, Mocanu MM, Carr RD, Brand CL, Yellon DM: Glucagon-like peptide 1 can directly protect the heart against ischemia/reperfusion injury. Diabetes. 2005, 54 (1): 146-151. 10.2337/diabetes.54.1.146.
Noyan-Ashraf MH, Momen MA, Ban K, Sadi AM, Zhou YQ, Riazi AM, Baggio LL, Henkelman RM, Husain M, Drucker DJ: GLP-1R agonist liraglutide activates cytoprotective pathways and improves outcomes after experimental myocardial infarction in mice. Diabetes. 2009, 58 (4): 975-983. 10.2337/db08-1193.
Timmers L, Henriques JP, de Kleijn DP, Devries JH, Kemperman H, Steendijk P, Verlaan CW, Kerver M, Piek JJ, Doevendans PA, Pasterkamp G, Hoefer IE: Exenatide reduces infarct size and improves cardiac function in a porcine model of ischemia and reperfusion injury. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2009, 53 (6): 501-510. 10.1016/j.jacc.2008.10.033.
Eng J, Kleinman WA, Singh L, Singh G, Raufman JP: Isolation and characterization of exendin-4, an exendin-3 analogue, from Heloderma suspectum venom. Further evidence for an exendin receptor on dispersed acini from guinea pig pancreas. J Biol Chem. 1992, 267 (11): 7402-7405.
Sonne DP, Engstrom T, Treiman M: Protective effects of GLP-1 analogues exendin-4 and GLP-1(9-36) amide against ischemia-reperfusion injury in rat heart. Regul Pept. 2008, 146 (1-3): 243-249. 10.1016/j.regpep.2007.10.001.
Ban K, Kim KH, Cho CK, Sauve M, Diamandis EP, Backx PH, Drucker DJ, Husain M: Glucagon-like peptide (GLP)-1(9-36) amide-mediated cytoprotection is blocked by exendin (9-39) yet does not require the known GLP-1 receptor. Endocrinology. 2010, 151 (4): 1520-1531. 10.1210/en.2009-1197.
Stary CM, Tsutsumi YM, Patel PM, Head BP, Patel HH, Roth DM: Caveolins: targeting pro-survival signaling in the heart and brain. Front Physiol. 2012, 3: 393-10.3389/fphys.2012.00393.
Insel PA, Head BP, Ostrom RS, Patel HH, Swaney JS, Tang CM, Roth DM: Caveolae and lipid rafts: G protein-coupled receptor signaling microdomains in cardiac myocytes. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2005, 1047: 166-172. 10.1196/annals.1341.015.
Patel HH, Murray F, Insel PA: G-protein-coupled receptor-signaling components in membrane raft and caveolae microdomains. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2008, 186: 167-184. 10.1007/978-3-540-72843-6_7.
Tsutsumi YM, Horikawa YT, Jennings MM, Kidd MW, Niesman IR, Yokoyama U, Head BP, Hagiwara Y, Ishikawa Y, Miyanohara A, Patel PM, Insel PA, Patel HH, Roth DM: Cardiac-specific overexpression of caveolin-3 induces endogenous cardiac protection by mimicking ischemic preconditioning. Circulation. 2008, 118 (19): 1979-1988. 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.108.788331.
Horikawa YT, Patel HH, Tsutsumi YM, Jennings MM, Kidd MW, Hagiwara Y, Ishikawa Y, Insel PA, Roth DM: Caveolin-3 expression and caveolae are required for isoflurane-induced cardiac protection from hypoxia and ischemia/reperfusion injury. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2008, 44 (1): 123-130. 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2007.10.003.
Tsutsumi YM, Kawaraguchi Y, Horikawa YT, Niesman IR, Kidd MW, Chin-Lee B, Head BP, Patel PM, Roth DM, Patel HH: Role of caveolin-3 and glucose transporter-4 in isoflurane-induced delayed cardiac protection. Anesthesiology. 2010, 112 (5): 1136-1145. 10.1097/ALN.0b013e3181d3d624.
Tsutsumi YM, Kawaraguchi Y, Niesman IR, Patel HH, Roth DM: Opioid-induced preconditioning is dependent on caveolin-3 expression. Anesth Analg. 2010, 111 (5): 1117-1121. 10.1213/ANE.0b013e3181f3351a.
Kilkenny C, Browne WJ, Cuthill IC, Emerson M, Altman DG: Improving bioscience research reporting: the ARRIVE guidelines for reporting animal research. PLoS Biol. 2010, 8 (6): e1000412-10.1371/journal.pbio.1000412.
Hagiwara Y, Sasaoka T, Araishi K, Imamura M, Yorifuji H, Nonaka I, Ozawa E, Kikuchi T: Caveolin-3 deficiency causes muscle degeneration in mice. Hum Mol Genet. 2000, 9 (20): 3047-3054. 10.1093/hmg/9.20.3047.
Tsutsumi Y, Oshita S, Kitahata H, Kuroda Y, Kawano T, Nakaya Y: Blockade of adenosine triphosphate-sensitive potassium channels by thiamylal in rat ventricular myocytes. Anesthesiology. 2000, 92 (4): 1154-1159. 10.1097/00000542-200004000-00034.
Kawano T, Oshita S, Tsutsumi Y, Tomiyama Y, Kitahata H, Kuroda Y, Takahashi A, Nakaya Y: Clinically relevant concentrations of propofol have no effect on adenosine triphosphate-sensitive potassium channels in rat ventricular myocytes. Anesthesiology. 2002, 96 (6): 1472-1477. 10.1097/00000542-200206000-00029.
Patel HH, Tsutsumi YM, Head BP, Niesman IR, Jennings M, Horikawa Y, Huang D, Moreno AL, Patel PM, Insel PA, Roth DM: Mechanisms of cardiac protection from ischemia/reperfusion injury: a role for caveolae and caveolin-1. FASEB J. 2007, 21 (7): 1565-1574. 10.1096/fj.06-7719com.
Tsutsumi YM, Tsutsumi R, Horikawa YT, Sakai Y, Hamaguchi E, Ishikawa Y, Yokoyama U, Kasai A, Kambe N, Tanaka K: Geranylgeranylacetone protects the heart via caveolae and caveolin-3. Life Sci. 2014, 101 (1-2): 43-48. 10.1016/j.lfs.2014.02.019.
Tsutsumi YM, Tsutsumi R, Mawatari K, Nakaya Y, Kinoshita M, Tanaka K, Oshita S: Compound K, a metabolite of ginsenosides, induces cardiac protection mediated nitric oxide via Akt/PI3K pathway. Life Sci. 2011, 88 (15-V16): 725-729. 10.1016/j.lfs.2011.02.011.
Tsutsumi YM, Patel HH, Lai NC, Takahashi T, Head BP, Roth DM: Isoflurane produces sustained cardiac protection after ischemia-reperfusion injury in mice. Anesthesiology. 2006, 104 (3): 495-502. 10.1097/00000542-200603000-00017.
Hirose K, Tsutsumi YM, Tsutsumi R, Shono M, Katayama E, Kinoshita M, Tanaka K, Oshita S: Role of the O-linked beta-N-acetylglucosamine in the cardioprotection induced by isoflurane. Anesthesiology. 2011, 115 (5): 955-962. 10.1097/ALN.0b013e31822fcede.
Tsutsumi YM, Patel HH, Huang D, Roth DM: Role of 12-lipoxygenase in volatile anesthetic-induced delayed preconditioning in mice. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2006, 291 (2): H979-H983. 10.1152/ajpheart.00266.2006.
Tsutsumi YM, Yokoyama T, Horikawa Y, Roth DM, Patel HH: Reactive oxygen species trigger ischemic and pharmacological postconditioning: In vivo and in vitro characterization. Life Sci. 2007, 81 (15): 1223-1227. 10.1016/j.lfs.2007.08.031.
Green BD, Flatt PR, Bailey CJ: Dipeptidyl peptidase IV (DPP IV) inhibitors: A newly emerging drug class for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. Diab Vasc Dis Res. 2006, 3 (3): 159-165. 10.3132/dvdr.2006.024.
Bose AK, Mocanu MM, Carr RD, Yellon DM: Myocardial ischaemia-reperfusion injury is attenuated by intact glucagon like peptide-1 (GLP-1) in the in vitro rat heart and may involve the p70s6K pathway. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2007, 21 (4): 253-256. 10.1007/s10557-007-6030-6.
Hausenloy DJ, Whittington HJ, Wynne AM, Begum SS, Theodorou L, Riksen N, Mocanu MM, Yellon DM: Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors and GLP-1 reduce myocardial infarct size in a glucose-dependent manner. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2013, 12 (1): 154-10.1186/1475-2840-12-154.
Bao W, Holt LJ, Prince RD, Jones GX, Aravindhan K, Szapacs M, Barbour AM, Jolivette LJ, Lepore JJ, Willette RN, DeAngelis E, Jucker BM: Novel fusion of GLP-1 with a domain antibody to serum albumin prolongs protection against myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury in the rat. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2013, 12: 148-10.1186/1475-2840-12-148.
Syme CA, Zhang L, Bisello A: Caveolin-1 regulates cellular trafficking and function of the glucagon-like Peptide 1 receptor. Mol Endocrinol. 2006, 20 (12): 3400-3411. 10.1210/me.2006-0178.
Yang Y, Tong Y, Gong M, Lu Y, Wang C, Zhou M, Yang Q, Mao T, Tong N: Activation of PPARbeta/delta protects pancreatic beta cells from palmitate-induced apoptosis by upregulating the expression of GLP-1 receptor. Cell Signal. 2014, 26 (2): 268-278. 10.1016/j.cellsig.2013.11.019.
Yamamoto H, Lee CE, Marcus JN, Williams TD, Overton JM, Lopez ME, Hollenberg AN, Baggio L, Saper CB, Drucker DJ, Elmquist JK: Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor stimulation increases blood pressure and heart rate and activates autonomic regulatory neurons. J Clin Invest. 2002, 110 (1): 43-52. 10.1172/JCI0215595.
Gardiner SM, March JE, Kemp PA, Bennett T, Baker DJ: Possible involvement of GLP-1(9-36) in the regional haemodynamic effects of GLP-1(7-36) in conscious rats. Br J Pharmacol. 2010, 161 (1): 92-102. 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2010.00867.x.
Deacon CF, Pridal L, Klarskov L, Olesen M, Holst JJ: Glucagon-like peptide 1 undergoes differential tissue-specific metabolism in the anesthetized pig. Am J Physiol. 1996, 271 (3 Pt 1): E458-E464.
Kavianipour M, Ehlers MR, Malmberg K, Ronquist G, Ryden L, Wikstrom G, Gutniak M: Glucagon-like peptide-1 (7-36) amide prevents the accumulation of pyruvate and lactate in the ischemic and non-ischemic porcine myocardium. Peptides. 2003, 24 (4): 569-578. 10.1016/S0196-9781(03)00108-6.
Zander M, Madsbad S, Madsen JL, Holst JJ: Effect of 6-week course of glucagon-like peptide 1 on glycaemic control, insulin sensitivity, and beta-cell function in type 2 diabetes: a parallel-group study. Lancet. 2002, 359 (9309): 824-830. 10.1016/S0140-6736(02)07952-7.
Amori RE, Lau J, Pittas AG: Efficacy and safety of incretin therapy in type 2 diabetes: systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA. 2007, 298 (2): 194-206. 10.1001/jama.298.2.194.
Drucker DJ, Nauck MA: The incretin system: glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists and dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors in type 2 diabetes. Lancet. 2006, 368 (9548): 1696-1705. 10.1016/S0140-6736(06)69705-5.
Inzucchi SE, McGuire DK: New drugs for the treatment of diabetes: part II: Incretin-based therapy and beyond. Circulation. 2008, 117 (4): 574-584. 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.107.735795.
Bose AK, Mocanu MM, Carr RD, Yellon DM: Glucagon like peptide-1 is protective against myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury when given either as a preconditioning mimetic or at reperfusion in an isolated rat heart model. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2005, 19 (1): 9-11. 10.1007/s10557-005-6892-4.
Gardiner SM, March JE, Kemp PA, Bennett T: Mesenteric vasoconstriction and hindquarters vasodilatation accompany the pressor actions of exendin-4 in conscious rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2006, 316 (2): 852-859. 10.1124/jpet.105.093104.
Barragan JM, Eng J, Rodriguez R, Blazquez E: Neural contribution to the effect of glucagon-like peptide-1-(7-36) amide on arterial blood pressure in rats. Am J Physiol. 1999, 277 (5 Pt 1): E784-E791.
Deacon CF: Circulation and degradation of GIP and GLP-1. Horm Metab Res. 2004, 36 (11-12): 761-765. 10.1055/s-2004-826160.
Nikolaidis LA, Elahi D, Shen YT, Shannon RP: Active metabolite of GLP-1 mediates myocardial glucose uptake and improves left ventricular performance in conscious dogs with dilated cardiomyopathy. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2005, 289 (6): H2401-H2408. 10.1152/ajpheart.00347.2005.
Woodman SE, Park DS, Cohen AW, Cheung MW, Chandra M, Shirani J, Tang B, Jelicks LA, Kitsis RN, Christ GJ, Factor SM, Tanowitz HB, Lisanti MP: Caveolin-3 knock-out mice develop a progressive cardiomyopathy and show hyperactivation of the p42/44 MAPK cascade. J Biol Chem. 2002, 277 (41): 38988-38997. 10.1074/jbc.M205511200.
Oshikawa J, Otsu K, Toya Y, Tsunematsu T, Hankins R, Kawabe J, Minamisawa S, Umemura S, Hagiwara Y, Ishikawa Y: Insulin resistance in skeletal muscles of caveolin-3-null mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004, 101 (34): 12670-12675. 10.1073/pnas.0402053101.
Meloni AR, DeYoung MB, Han J, Best JH, Grimm M: Treatment of patients with type 2 diabetes with exenatide once weekly versus oral glucose-lowering medications or insulin glargine: achievement of glycemic and cardiovascular goals. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2013, 12: 48-10.1186/1475-2840-12-48.
Lonborg J, Vejlstrup N, Kelbaek H, Nepper-Christensen L, Jorgensen E, Helqvist S, Holmvang L, Saunamaki K, Botker HE, Kim WY, Clemmensen P, Treiman M, Engstorm T: Impact of acute hyperglycemia on myocardial infarct size, area at risk, and salvage in patients with STEMI and the association with exenatide treatment: results from a randomized study. Diabetes. 2014, 63 (7): 2474-2485. 10.2337/db13-1849.
Piotrowski K, Becker M, Zugwurst J, Biller-Friedmann I, Spoettl G, Greif M, Leber AW, Becker A, Laubender RP, Lebherz C, Goeke B, Marx N, Parhofer KG, Lehrke M: Circulating concentrations of GLP-1 are associated with coronary atherosclerosis in humans. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2013, 12: 117-10.1186/1475-2840-12-117.
Acknowledgments
The project was supported by JSPS KAKENHI numbers 24592300, 25462405, and 60161486 from Japan Society for the Promotion of Science, Tokyo.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Authors’ original submitted files for images
Below are the links to the authors’ original submitted files for images.
Rights and permissions
This article is published under an open access license. Please check the 'Copyright Information' section either on this page or in the PDF for details of this license and what re-use is permitted. If your intended use exceeds what is permitted by the license or if you are unable to locate the licence and re-use information, please contact the Rights and Permissions team.
About this article
Cite this article
Tsutsumi, Y.M., Tsutsumi, R., Hamaguchi, E. et al. Exendin-4 ameliorates cardiac ischemia/reperfusion injury via caveolae and caveolins-3. Cardiovasc Diabetol 13, 132 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12933-014-0132-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12933-014-0132-9