Abstract
Background
X-linked Adrenal Hypoplasia Congenita (AHC) is a rare cause of primary adrenal insufficiency due to mutations in the NR0B1 gene, causing a loss of function of the nuclear receptor protein DAX-1. Adrenal insufficiency usually appears in the first 2 months of life, but can sometimes emerge during childhood. Hypogonadotropic Hypogonadism is often associated later in life and patients may develop azoospermia. We describe an unusual onset of AHC started with isolated hypoaldosteronism as first and only sign of the disease.
Case presentation
A 18-days-old newborn presented with failure to thrive and feeding difficulties. Blood tests showed severe hyponatremia, hyperkalemia and hypochloremia. Renin was found over the measurable range and aldosterone was low whereas cortisol level was normal with a slightly increased ACTH. In the suspicion of Primary Hypoaldosteronism, correction of plasmatic electrolytes and replacement therapy with Fludrocortisone were promptly started. The subsequent evidence of low plasmatic and urinary cortisol and increased ACTH required the start of Hydrocortisone replacement therapy and it defined a clinical picture of adrenal insufficiency. Genetic analysis demonstrated a novel mutation in the DAX-1 gene leading to the diagnosis of AHC.
Conclusions
AHC onset may involve the aldosterone production itself, miming an isolated defect of aldosterone synthesis. NR0B1/DAX-1 mutations should be considered in male infants presenting with isolated hypoaldosteronism as first sign of adrenal insufficiency.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
X-linked Adrenal Hypoplasia Congenita (AHC; OMIM #300200) is a congenital disorder characterized by adrenal insufficiency, often associated with hypogonadotropic hypogonadism. The first case, described in 1948, was a male who died at 33 days of life for adrenal crisis with salt wasting [1]. The estimated incidence is 1 in 12,500 births. AHC results from mutations in the NR0B1/DAX-1 gene, a nuclear receptor located on the X-chromosome (Xp21) and expressed in adrenal cortex, gonads, hypothalamus and pituitary gland. DAX-1 regulates adrenal and reproductive differentiation and function, although its role is not completely clear [2]. DAX-1 mutations are usually associated with primary adrenal failure, hypogonadotropic hypogonadism and impaired spermatogenesis (oligospermia or azoospermia are typically present) although uncommon phenotypes, different clinical features and different age of onset have been described [2, 3]. More than 100 pathogenic mutations of DAX-1 are known, together with deletions of the exons or of the entire gene, most of which are located at the carboxyl-terminal of the protein and are nonsense or frameshift missense mutations. We present a newborn with isolated hypoaldosteronism as first sign of AHC caused by a novel mutation (c.848_849delinsCC) of DAX-1 gene [4].
Case presentation
The male 18-days-old Caucasian newborn was admitted to our department for ineffective breastfeeding and failure to thrive. He was born at term from spontaneous delivery, small for gestational age to non-consanguineous parents [5]. Pregnancy was uneventful except for a delayed intrauterine growth restriction detected during the last month of gestation. External genitalia were of normal appearance, prepubertal, with testicular volumes of 1 ml. Blood tests showed a severe hyponatremia (Na + 110 mEq/l; NR 136–146 mEq/l), hyperkalemia (K+ 7.5 mEq/l; NR 3.5–5.30 mEq/l), hypochloremia (Cl- 81 mEq/l; NR 97–110 mEq/l) and metabolic acidosis with increased lactate. Glycemia was within the normal range for age (68 mg/dl); urinary sodium loss was also detected (Natriuria 16 mEq/l).
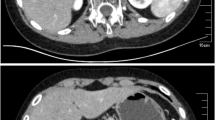
Endocrinological tests revealed low plasmatic aldosterone levels (38.6 pg/ml; NR 50–300 pg/ml), dramatic increased renin (44,100 μU/ml; NR 4.4–46.1), elevated levels of adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH, 91.4 pg/ml NR 4,3–52) and normal plasmatic cortisol (13.7 μg/dl NR 6.7–22.6). Skin pigmentation was normal except for mild pigmentation of the external genitalia. Neonatal screening for 17-OH-progesterone was within the normal range. Electrolytes replacement first intravenous and then oral, and therapy with Fludrocortisone (50 μg/die) and salt integration were started with normalization of clinical and hormonal conditions. Treatment revealed to be effective and the newborn started growing properly, with normal electrolytes. Cerebral ultrasounds and cerebral magnetic resonance (MRI) were normal, as well as the elettrocardiogram (ECG) and chest X-rays. Abdominal MRI showed normal size of the adrenal glands. A diagnosis of Primary Hypoaldosteronism was entertained and genetic analysis of the CYP11B2 gene (encoding aldosynthase) was requested.
During the follow up after the first 5 months of life, ACTH levels started increasing again although there was a good treatment compliance, normal electrolytes, good weight and length gain and slightly low basal cortisol levels, within the normal range for age (Table 1).
At 9 months of age the result of the CYP11B2 gene sequencing did not show any mutation. The parents refused to accomplish a short synacthen test (SST), however basal ACTH was 300 pg/ml and 24-h urine collection pointed out low levels of urinary cortisol (20 μg/24 h, NR 58–403 μg/24 h) with normal Na/K urinary ratio. Moreover, normal serum 17-OH-progesterone was found, ruling out the hypothesis of congenital adrenal hyperplasia (CAH).
Luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) were found, respectively, of 1 IU/l and 2.2 IU/l, and Testosterone of 0.2 ng/ml, being to the highest levels of the normal range for age.
A diagnosis of adrenal insufficiency was made and replacement therapy with Hydrocortisone (10 mg/m2/day), joint to already in use Fludrocortisone therapy (100 μg/day) and salt integration, was started. An abnormal development of adrenal glands rather than an enzymatic defect was hypothesized. Adrenal antibodies and very long chain fatty acids (VLCFA) were negative. DNA analysis performed by Sanger sequencing identified a novel in frame indel mutation in the NROB1 gene (c.848_849delinsCC or p.(Gln283Pro)), confirming the diagnosis of AHC. As expected the same mutation was carried by the mother as hemizygous (see Fig. 1).
Partial chromatograms showing the novel NR0B1 /DAX-1 mutation. Base change c.848_849delinsCC leading to the missense mutation p.(Gln283Pro). The reference sequence is in highlighted in red. The proband’s DNA sequence is above, the mother’s DNA sequence in the middle and a healthy control’s sequence underneath
Discussion
We describe the case of a newborn presenting with unspecific symptoms and silent family history, in which AHC started with an isolated mineralocorticoid deficiency, leading to the initial hypothesis of primary hypoaldosteronism treated with fludrocortisone. The negative results of CYP11B2 genetic analysis and the tightened endocrinological follow-up allowed to discover the secondary development of glucocorticoid deficiency, although parents refused to perform a SST, and a prompt supplementation therapy with hydrocortisone was started before any adrenal crisis. The initial presentation of pathogenic DAX-1 mutations is often a combination of mineral and glucocorticoid deficiency but, especially during the neonatal period, it is known how aldosterone deficiency may precede cortisol deficiency at onset, confounding the initial diagnosis. The reason of this peculiar clinical appearance is still unknown, and recent studies failed to establish a genotype phenotype correlation in patients with NR0B1 mutations [6].
Generally, healthy newborns exhibit a renal tubular immaturity at birth, with sodium wasting and impaired water reabsorption. Renal sodium reabsorption is mainly regulated by aldosterone, through the binding of its receptor, the mineralocorticoid receptor (MR), a transcription factor regulating the expression of several transporting proteins related to sodium homeostasis [7]. Soon after birth, changing from an intra-uterine aquatic environment to the out-womb/terrestrial one, a partial aldosterone resistance is well documented, with high plasma levels of aldosterone and renin, contrasting with biological signs of functional hypoaldosteronism (as hyponatremia, hyperkalemia and urinary sodium loss). The highest aldosterone levels detected in the cord blood at birth are consistent with the de novo synthesis in the fetal adrenal gland, given the very early expression of the aldosterone synthase gene starting from 13 gestational weeks [8]. This hormonal resistance could account for the weight loss observed during the first days of life and might be an adaptive phenomenon of the passage from the in utero to terrestrial life [9]. Nevertheless, the transient aldosterone resistance is associated with low MR renal presence at birth, followed by a significant increase in the postnatal period, with a complete renal tubular expression developed during the first year of life, contemporary to renal functional maturation [10]. It was demonstrated that high aldosterone levels soon after birth are required for the MR optimal up-regulation in the postnatal period, and it is therefore indispensable for sodium homeostasis [7]. Glucocorticoids are able to bind MR with the same affinity of mineralocorticoids, being a possible responsible for the development of MR during the first year of life even in cases of hypoaldosteronism. Moreover, basal cortisol levels at birth and during the first days/months of life may be normal in patients with AHC, sign of the possible adrenal transition from fetal to adult zone. In fact, several adrenal enzymes responsible for steroids synthesis of the fetus, are active since the very first weeks of gestation, and may lead to the development of an “adrenal reserve”, during the neonatal and perinatal period, responsible for the slow development of glucocorticoid deficiency symptoms.
It is important to bear in mind that in boys, once CAH has been ruled out, the most frequent cause of adrenal insufficiency in neonatal period are the DAX-1 mutations. In our case, CAH was excluded by normal 17-OH-progesterone levels at neonatal screening [11,12,13]. Afterwards, the DNA sequencing identified a novel in frame indel mutation in the NR0B1 gene and the diagnosis of AHC was made. An indel was identified with the deletion of two base-pair (bp) replaced by two cytosine in position 848_849. The sequence variants is designated according to the Human Genome Society recommendations (https://www.hgvs.org) using the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) reference sequences NM_000475.4, NP_000466.2 built on the GRCh37/hg19 and is NM_000475.4:c.848_849delinsCC or p.(Gln283Pro).
Pathogenicity prediction was performed in silico using several programs: Align-GVGD, Polyphen-2 and SIFT and the variant was predicted to be most likely pathogenic using Align-GVGD class, probably damaging, using Polyphen-2, deleterious using SIFT. The Grantham score that ranges from 0 to 215, was calculated to predict the effect of substitutions between amino acids based on chemical properties (i.e. polarity and molecular volume). Higher scores indicate greater differences between two amino acids and may indicate a stronger (negative) effect on protein structure and function. Physicochemical effect of this variation is important with a Grantham score of 76. Frequency databases (dbSNP, ESP, and gnomAD) were searched to determine if the variant had already been reported and it was not. It has not been found in 100 Caucasian healthy controls sequences. According to the ACMG/AMP standards Guidelines the variant is classified as pathogenic [14].
Since the first description of the NR0B1/DAX-1 mutation in 1994 as the etiology of AHC, several novel mutations have been discovered. Deletions, nonsense and frameshift mutations of the carboxyl-terminal domain seem to be the most common and are usually associated to clinical phenotypes. Structure-function studies suggest that mutations in the amino-terminal domain are compensated by the presence of redundant LXXLL motifs that allow DAX-1 interacting with other proteins, changing the normal nucleocytoplasmic ratio. Stuart et al. described an amino-terminal DAX-1 missense mutation causative of AHC associated with isolated mineralocorticoid deficiency [15].
The different causative mutations of DAX-1 can be responsible of the phenotypical variability, but different clinical features between patients of the same family, carrying the same mutations, indicate that environmental factors are involved and a detailed study of this disease also in presence of mild symptoms is essential to make a correct diagnosis and start a prompt therapy [16,17,18]. Table 2 summarizes some of the cases of DAX-1 mutation with initial isolated hypoaldosteronism and the main clinical and genetic characteristics described in literature [11,12,13, 15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24].
Replacement therapy with Hydrocortisone and Fludrocortisone guarantees an adequate growth of the DAX-1 patients. The only case in which growth failure was detected despite optimization of therapy and nutrition was a patient with AHC and growth hormone deficiency (GHD) [19]. This underlines the importance of a genetic diagnosis as soon as possible, especially in this case where an isolated mineralocorticoid deficiency was misleading the diagnosis with a treatment by fludrocortisone only. The precocious diagnosis allowed to add hydrocortisone and will improve the future management of patient’s puberty, as hypogonadotropic hypogonadism may appear, and above all possible spermatogonia conservation before azoospermia development.
Although AHC onset is usually within the first 2 months of life, later and insidious manifestations of symptoms may occur in childhood. Ten cases of new adult-onset AHC have been described and diagnosis was suspected observing the association of adrenal insufficiency and hypogonadotropic hypogonadism [20].
The onset of puberty is variable in AHC but boys usually fail to enter puberty, gonadotropins levels are low, testosterone level can be normal or low and GnRH stimulation is usually ineffective. Some patients present transient manifestation of secondary sex precocity, due to gonadotropin-independent precocious puberty, ACTH-dependent precocious puberty, and gonadotropin-dependent central precocious puberty [25, 26]. However, usually exogenous gonadotropins fail in stimulating a complete pubertal development because of a primary defect in spermatogenesis. In AHC patients, testicular biopsy demonstrates hypoplasia of Sertoli cells and oligo-azoospermia [3, 19, 20]. DAX-1 seems to increase the Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) expression in the presence of SF-1 in a dose-dependent manner, consequently decreased expression of DAX-1 could down-regulate GnRH secretion [27]. Thus, hormonal levels need to be monitored during the pubertal period and testosterone replacement therapy needs to be started, if puberty does not appear, to directly stimulate virilization.
Our patient shows levels of LH and FSH within the highest levels of normal range for 9 months of age, regular size of penis and testis, and mild high testosterone for age. We will follow up strictly his pubertal development, to avoid signs of precocious puberty, seen that the minipuberty profile seems delayed or longer than usual.
Conclusion
To summarize, this case highlights that in newborn and infant with suspicion of congenital primary hypoaldosteronism, glucocorticoid function should be carefully assessed, possibly through a SST, with sometimes an increase of ACTH level preceding the cortisol defect but guiding to X-linked AHC. The phenotypical presentation may be variable and this underlines the importance of genetic diagnosis this leads to the correct monitoring of the patient (puberty, sterility) and his family by identifying the potential girls that are carriers.
Availability of data and materials
Not Applicable.
Abbreviations
- ACTH:
-
Adrenocorticotropic hormone
- AHC:
-
Adrenal Hypoplasia Congenita
- CAH:
-
Congenital adrenal hyperplasia
- ECG:
-
Electrocardiogram
- FSH:
-
Follicle-stimulating hormone
- GHD:
-
Growth hormone deficiency
- GnRH:
-
Gonadotropin-releasing hormone
- LH:
-
Luteinizing hormone
- MR:
-
Mineralocorticoid receptor
- MRI:
-
Magnetic Resonance
- SST:
-
Short synacthen test
- VLCFA:
-
Very low chain fatty acids
References
Achermann JC, Meeks JJ, Jameson JL. X-linked adrenal hypoplasia Congenita and Dax-1. Endocrinologist. 2000;10:289–99.
Suntharalingham JP, Buonocore F, Duncan AJ, Achermann JC. DAX-1 (NR0B1) and steroidogenic factor-1 (SF-1, NR5A1) in human disease. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2015;29:607–19.
Unmesh Jadhav JLJ, Harris RM. Hypogonadotropic hypogonadism in subjects with DAX1 mutations. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2011;346:65–73.
Gagnier JJ, Kienle G, Altman DG, Moher D, Sox H, Riley D, et al. The CARE guidelines: consensus-based clinical case reporting guideline development. Glob Adv Health Med. 2013;2:38–43.
Bertino E, Spada E, Occhi L, Coscia A, Giuliani F, Gagliardi L, et al. Neonatal anthropometric charts: the Italian neonatal study compared with other European studies. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2010;51:353–61.
Lin L, Gu WX, Ozisik G, To WS, Owen CJ, Jameson JL, et al. Analysis of DAX1 (NR0B1) and steroidogenic factor-1 (NR5A1) in children and adults with primary adrenal failure: ten years’ experience. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2006;91:3048–54.
Martinerie L, Viengchareun S, Meduri G, Kim HS, Luther JM, Lombes M. Aldosterone postnatally, but not at birth, is required for optimal induction of renal mineralocorticoid receptor expression and sodium reabsorption. Endocrinology. 2011;152:2483–91.
Coulter CL, Jaffe RB. Functional maturation of the primate fetal adrenal in vivo: 3. Specific zonal localization and developmental regulation of CYP21A2 (P450c21) and CYP11B1/CYP11B2 (P450c11/aldosterone synthase) lead to integrated concept of zonal and temporal steroid biosynthesis. Endocrinology. 1998;139:5144–50.
Martinerie L, Munier M, Le Menuet D, Meduri G, Viengchareun S, Lombès M. The mineralocorticoid signaling pathway throughout development: expression, regulation and pathophysiological implications. Biochimie. 2013;95:148–57.
Martinerie L, Pussard E, Foix-L'Hélias L, Petit F, Cosson C, Boileau P, et al. Physiological partial aldosterone resistance in human newborns. Pediatr Res. 2009;66:323–8.
Evliyaoğlu O, Dokurel I, Bucak F, Özcabı B, Ercan O, Ceylaner S. Primary adrenal insufficiency caused by a novel mutation in DAX1 gene. J Clin Res Pediatr Endocrinol. 2013;5:55–7.
Abraham MB, Shetty VB, McKenzie F, Curran J. X-linked congenital adrenal hypoplasia with a novel NR0B1/DAX gene mutation. Indian Pediatr. 2016;53:529–31.
Wheeler B, George PM, Mackenzie K, Hunt P, Potter HC, Florkowski CM. Case report three cases of congenital adrenal hypoplasia with novel mutations in the ( NROB1 ) DAX-1 gene. Ann Clin Biochem. 2008;45(Pt 6):606–9.
Richards S, Aziz N, Bale S, Bick D, Das S, Gastier-Foster J, et al. Standards and guidelines for the interpretation of sequence variants: a joint consensus recommendation of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology. Genet Med. 2015;17:405–24.
Verrijn Stuart AA, Ozisik G, de Vroede MA, Giltay JC, Sinke RJ, Peterson TJ, et al. An amino-terminal DAX1 (NR0B1) missense mutation associated with isolated mineralocorticoid deficiency. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2007;92:755–61.
Calliari LE, Rocha MN, Monte O, Longui CA. Mild adrenal insufficiency due to a NR0B1 mutation in a boy presenting an association of hypogonadotropic hypogonadism, reduced final height and attention deficit disorder. Arq Bras Endocrinol Metabol. 2013;57:562–5.
Zhang Z, Feng Y, Ye D, Li CJ, Dong FQ, Tong Y. Clinical and molecular genetic analysis of a Chinese family with congenital X-linked adrenal hypoplasia caused by novel mutation 1268delA in the DAX-1 gene. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2015;16:963–8.
Ahmad I, Paterson WF, Lin L, Adlard P, Duncan P, Tolmie J. A novel missense mutation in Dax-1 with an unusual presentation of X-linked adrenal hypoplasia Congenita. Horm Res. 2007;68:32–7.
Chung ST, Chi CH, Haymond MW, Jeha GS. Infantile growth hormone deficiccency and X-linked adrenal hypoplasia congenita. Jacobs J Pediatr. 2015;1.
Kyriakakis N, Shonibare T, Kyaw-Tun J, Lynch J, Lagos CF, Achermann JC. Late-onset X-linked adrenal hypoplasia (DAX-1 , NR0B1): two new adult-onset cases from a single center. Pituitary. 2017;20:585–93.
Li N, Liu R, Zhang H, Yang J, Sun S, Zhang M, et al. Seven novel DAX1 mutations with loss of function identified in Chinese patients with congenital adrenal hypoplasia. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2010;95:E104–11.
Gerster K, Katschnig C, Wyss S, Kolly A, Sproll P, Biason-Lauber A, et al. A novel DAX-1 (NR0B1) mutation in a boy with X-linked adrenal hypoplasia congenita. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2017;30:1321–5.
Bizzarri C, Olivini N, Pedicelli S, Marini R, Giannone G, Cambiaso P, et al. Congenital primary adrenal insufficiency and selective aldosterone defects presenting as salt-wasting in infancy: a single center 10-year experience. Ital J Pediatr. 2016;42:73.
Al Amer AM, Al Rubaya KM, Alzahrani AS. Adrenal hypoplasia congenita in identical twins. Saudi Med J. 2019;40:87–92.
Landau Z, Hanukoglu A, Sack J, Goldstein N, Weintrob N, Eliakim A, et al. Clinical and genetic heterogeneity of congenital adrenal hypoplasia due to NR0B1 gene mutations. Clin Endocrinol. 2010;72:448–54.
Guzzetti C, Bizzarri C, Pisaneschi E, Mucciolo M, Bellacchio E, Ibba A, et al. Next-generation sequencing identifies different genetic defects in 2 patients with primary adrenal insufficiency and gonadotropin-independent precocious puberty. Horm Res Paediatr. 2018;90:203–11.
Okuhara K, Abe S, Kondo T, Fujita K, Koda N, Mochizuki H, et al. Four Japanese patients with adrenal hypoplasia Congenita and hypogonadotropic hypogonadism caused by DAX-1 gene mutations : mutant DAX-1 failed to repress steroidogenic acute regulatory protein ( StAR ) and luteinizing hormone β -subunit gene promoter activity. Endocr J. 2008;55:97–103.
Acknowledgements
Not Applicable.
Funding
The authors declare that they did not receive any funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Study conception and design – LI. Acquisition of data – SM, SC and EB. Analysis and interpretation of data – FR-B, LI, and PB. Drafting of manuscript – LL and BP. Critical revision – FR-B, LI and LL. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not Applicable.
Consent for publication
The parents gave informed written consent to study the infant and to publish the clinical case.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
About this article
Cite this article
Iughetti, L., Lucaccioni, L., Bruzzi, P. et al. Isolated hypoaldosteronism as first sign of X-linked adrenal hypoplasia congenita caused by a novel mutation in NR0B1/DAX-1 gene: a case report. BMC Med Genet 20, 98 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12881-019-0834-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12881-019-0834-7