Abstract
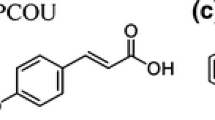
Heterogeneous photocatalytic degradation of many organic pollutants, such as phenol and phenol derivatives, may be optimised if the catalyst surface saturation and the appearance and accumulation of non-photocatalytically degradable intermediates is avoided. It has been shown that under certain concentration threshold the highest degradation efficiencies are achieved. Over these concentrations, degradation rates become constant owing to the limited catalyst surface. By the dosage of the contaminant, currently in an aqueous solution, the process may be optimised, thus avoiding the formation of inert intermediates which may be more toxic than the parental compound. The effect of dosage on the photocatalytic degradation of phenol and phenol derivatives, such as salicylic acid and 4-aminophenol has been studied. Comparatively notably higher efficiencies have been obtained compared to those of the high initial single dose experiments (non-dosage), for which high initial concentrations of the organics resulted in the catalysts poisoning. Degussa P-25 and its combination with 13% (w/w) activated carbon, namely AC−TiO2, have been used as catalysts. Almost complete degradations are achieved at low dosage rates (1–2 pmm/min). At higher dosage rates, different processes such as catalyst poisoning predominate, resulting in lower degradation efficiencies.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
V. Auguliaro, E. Davì, L. Palmisano, M. Schiavello and A. Sclafani, Appl. Catal. 65, 101 (1990).
D. Chen and A. K. Ray, Appl. Catal. B: Environ. 23, 143 (1999).
J. Villaseñor, P. Reyes and G. Pecchi, Catal. Today 76, 121 (2002).
H. Chung, W. Yizhong and T. Hongxiao, Chemosphere 41, 1205 (2000).
J. Grzechulska and A. Waldemar-Morawski, Appl. Catal. B: Environ. 46, 415 (2003).
G. Colón, M. C. Hidalgo and J. A. Navío, Appl. Catal. B: Environ. 45, 39 (2003).
S. Parra J. Olivero, L. Pacheco and C. Pulgarin, Appl. Catal. B: Environ. 43, 293 (2003).
G. Colón, M. C. Hidalgo, M. Macías, J. A. Navío and J. M. Doña, Appl. Catal. B: Environ. 43, 163 (2003).
D. M. Alfano, D. Bahnemann, A. E. Cassano, R. Dillert and R. Goslich, Catal. Today 58, 199 (2000).
J. Blanco Gálvez and S. Malato Rodríguez, Tecnología de Fotocatálisis Solar. Instituto de Estudios Almerienses de la Diputación de Almería, CIEMAT, Almería (1996).
M. Schiavello (Ed.), Heterogeneous Photocatalysis, Wiley, Chichester (1997).
A. Fujisima, T. N. Rao and D. A. Tryk, J. Photochem. Photobiol. C: Photochem. Rev. 1, 1 (2000).
A. M. Peiró, J. A. Ayllón, J. Peral and X. Doménech, Appl. Catal B: Environ. 30, 359 (2001).
J. Peral, J. Casado and J. Doménech, J. Photochem. Photobiol. A: Chem. 44, 209 (1988).
K. Okamoto, Y. Yamamoto, H. Tanaka and A. Itaya, Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 58, 2015 (1985).
J. A. Herrera Melián, J. M. Doña Rodríguez, A. Viera Suárez, E. Tello Rendón, C. Valdés do Campo, J. Araña Mesa and J. Pérez Peña, Water Res. 34, 3967 (2000).
J. Araña, E. Tello Rendón, J. M. Doña Rodríguez, C. Valdés do Campo, J. A. Herrera Melián, O. González Díaz and J. Pérez Peña, Water Sci. Technol. 44, 229 (2001).
K. Wang, Y. Hsieh, M. Chou and C. Chang, Appl. Catal. B: Environ. 21, 1 (1999).
E. Leyva, E. Moctezuma, M. G. Ruíz and L. Torres-Martínez, Catal. Today 40, 367 (1998).
J. Araña, E. Tello Rendón, J. M. Doña Rodríguez, C. Valdés do Campo, J. A. Herrera Melián, O. González Díaz and J. Pérez Peña, Appl. Catal. B: Environ. 30, 1 (2001).
J. M. Herrmann, Catal. Today 53, 115 (1999).
J. Araña, J. M. Doña-Rodriguez, E. Tello-Rendón, C. Garriga i Cabo, O. González Díaz, J. A. Herrera Melián, J. Pérez Peña, G. Colón and J. A. Navío, Appl. Catal. B: Environ. 44, 161 (2003).
J. Araña, J. M. Doña-Rodriguez, E. Tello-Rendón, C. Garriga i Cabo, O. González Díaz, J. A. Herrera Melián, J. Pérez Peña, G. Colón and J. A. Navío, Appl. Catal. B: Environ. 44, 153 (2003).
N. Serpone and A. Salinaro, Pure Appl. Chem. 71, 303 (1999).
A. Salinaro, A. V. Emeline, J. Zhao, H. Hidaka, V. K. Ryabchuk and N. Serpone, Pure Appl. Chem. 71, 321 (1999).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Doña, J.M., Garriga, C., Araña, J. et al. The effect of dosage on the photocatalytic degradation of organic pollutants. Res. Chem. Intermed. 33, 351–358 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1163/156856707779238676
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1163/156856707779238676