Abstract
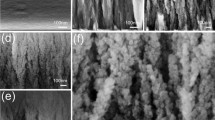
Silicon clusters were produced by sputtering of a p-doped Si target and aggregation of the Si atoms in an argon gas atmosphere. The clusters were deposited in ultra high vacuum onto either (i) carbon transmission electron microscope (TEM) grids or (ii) a liquid nitrogen cooled finger on which a thick layer of ice was co-deposited during the exposure to the cluster beam. The ice layer containing the clusters was melted to form a liquid sample which showed luminescence peaking at 421 nm when excited at 307.5 nm. The luminescence is attributed to electron-hole recombination in oxygen deficient defects in the Si–SiO2 interface region. TEM images of the nanoparticles deposited on the carbon grids show spherical particles with diameters ranging from 4 to 50 nm, flake-like structures or nanotube-like shapes. Grids with higher deposited densities reveal clusters that are agglomerated into chains, TEM images of the dried liquid sample show a network of fibres indicating that growth into fibres is further promoted when the clusters gain mobility in the melted ice.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
L.T. Canham, Appl. Phys. Lett. 57, 1046 (1990)
A. Cullis, L. Canham, Nature 353, 335 (1991)
A. Cullis, L. Canham, P. Calcott, J. Appl. Phys. 82, 909 (1997)
T. Shimizu-Iwayama, S. Nakao, K. Saitoh, N. Itoh, J. Phys. Cond. Mat. 6, 601 (1994)
D. Zhang et al., Appl. Phys. Lett. 65, 2684 (1994)
L. Pavesi et al., Nature 408, 440 (2000)
L. Pavesi, J. Phys. C 15, 1169 (2003)
A.J. Kenyon, Semicond. Sci. Technol. 20, 65 (2005)
D. Yu et al., Appl. Phys. Lett. 73, 3076 (1998)
F. Huisken, B. Kohn, V. Paillard, Appl. Phys. Lett. 74, 3776 (1999)
F. Huisken, G. Ledoux, O. Guillois, C. Reynaud, Adv. Mat. 14, 1861 (2002)
G. Ledoux et al., Phys. Rev. B 62, 15942 (2000)
M. Han et al., Eur. Phys. J. D 24, 269 (2003)
S. Pratontep et al., Rev. Sci. Instrum. 76, 045103 (2005)
K. Wegner, P. Piseri, H. Tafreshi, P. Milani, J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 39, R439 (2006)
M. Ehbrecht, F. Huisken, Phys. Rev. B 59, 2975 (1999)
M.A. Hoffmann et al., Eur. Phys. J. D 16, 9 (2001)
T. Laarmann, H. Wabnitz, K. Von Haeften, T. Möller, J. Chem. Phys. 128, 014502 (2008)
P. Montano et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 56, 2076 (1986)
M. Riedler et al., Phys. Rev. B 64, 245419 (2001)
H. Haberland, M. Karrais, M. Mall, Z. Phys. D 20, 413 (1991)
N. Shang et al., Nanotechnology 17, 3215 (2006)
H. Nishikawa et al., Phys. Rev. B 45, 586 (1992)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
von Haeften, K., Binns, C., Brewer, A. et al. A novel approach towards the production of luminescent silicon nanoparticles: sputtering, gas aggregation and co-deposition with H2O. Eur. Phys. J. D 52, 11–14 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjd/e2009-00024-x
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epjd/e2009-00024-x