Abstract
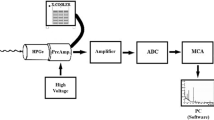
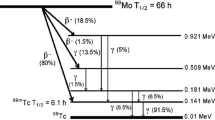
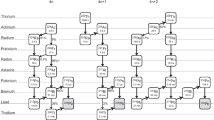
It is widely acknowledged that the 178m2Hf nuclide is the most suitable substance to study the decay characteristic of the isomer induced by low-energy X-ray. In order to conduct the experiment on the induced gamma emission, the research group has started producing the 178m2Hf nuclide based on the 176Yb(α, 2n)178m2Hf reaction. After the chemical purification is conducted, the sample is prepared and used in Shanghai Synchrotron Radiation Facility. During the production of isomer, the natural metal Yb target is got through magnetron sputtering. Bombarded by α particles about 27 MeV, the 178m2Hf nuclide reaches about 1012. Yb target prepared in this way is most suitable for the production of 178m2Hf nuclide in the CS30 cyclotron. There are various nuclides in the irradiated target and the main long-lived nuclides are 173Lu, 172Lu, 175Hf, 172Hf and 65Zn. The chemical separation of 178m2Hf is studied and its process is monitored by radioactive tracer. The above result shows that decontamination factors of Zn and Lu are 105 and 103, respectively, and the yield of hafnium is 69%. Under the protection of vacuum filtration technology, the purified 178m2Hf isomers are entirely transferred to the surface of filter paper, in order to form the sample which satisfies requirements of X-ray triggering the 178m2Hf isomer decay experiment in Shanghai Synchrotron Radiation Facility in the future.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
C.B. Collins et al., Phys. Rev. C 42, 1813 (1990).
C.B. Collins et al., Phys. Rev. C 37, 2267 (1988).
S. Olariu, Agata Olariu, Phys. Rev. C 58, 333 (1998).
C.B. Collins et al., Laser Phys. 9, 8 (1999).
C.B. Collins et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 83, 695 (1999).
C.B. Collins et al., Phys. At. Nucl. 63, 2067 (2000).
C.B. Collins, F. Davanloo, A.C. Rusu, M.C. Iosif, N.C. Zoita, D.T. Camase, J.M. Hicks, S.A. Karamian et al., Phys. Rev. C 61, 054305 (2000).
C.B. Collins et al., Hyperfine Interact. 135, 51 (2001).
C.B. Collins et al., Radiat. Phys. Chem. 71, 619 (2004).
C.B. Collins et al., Laser Phys. Lett. 2, 162 (2005).
C.B. Collins et al., Laser Phys. 14, 154 (2004).
C.B. Collins et al., Europhys. Lett. 57, 677 (2002).
P. McDaniel et al., Sandia Report SAND2007 2690, 1 (2008).
I. Ahmad et al., Phys. Rev. C 67, 041305 (2003).
I. Ahmad et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 87, 072503 (2001).
J.J. Carroll et al., Hyperfine Interact. 143, 37 (2002).
H.E. Roberts et al., Hyperfine Interact. 143, 111 (2002).
Yu.Ts. Oganessian et al., Hyperfine Interact. 107, 129 (1997).
S.A. Karamian et al., Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. A 530, 463 (2004).
S.A. Karamian et al., Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. A 489, 448 (2002).
S.A. Karamian et al., Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. A 530, 609 (2004).
Obrien HA, Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. B 40-41, 1126 (1989).
Karamian et al., Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. A 600, 488 (2009).
Yu.Ts. Oganessian et al., J. Phys. G 18, 393 (1992).
J.F. Ziegler, J.P. Biersack, U. Littmark, The Stopping and Range of Ions in Matter (Pergamon, New York, 1985).
Nuclear Navigator, Version 3.4, June 2000. Nuclear Navigator was developed for OTEC by Battelle Memorial Institute.
I. Ahmad et al., Phys. Rev. C 71, 024311 (2005).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by N. Alamanos
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, T., TaoJiang, Ze, R. et al. Preparation of the 178m2Hf isomer used in the induced gamma decay experiment by X-ray from synchrotron radiation facility. Eur. Phys. J. A 48, 149 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1140/epja/i2012-12149-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epja/i2012-12149-7