Abstract
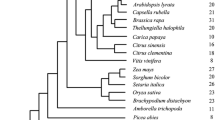
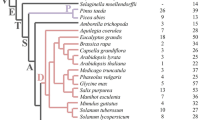
The tryptophan biosynthesis pathway is universal for the majority of known organisms, although it is absent in animals and some eubacteria. This pathway is conserved in plants, although various species differ in the number of paralogs of the enzymes involved in it. In this work, the possible role of the changes in the number of tryptophan biosynthesis enzymes paralogs in the course of evolution was analyzed. Towards this, the paralogs of the enzymes in tryptophan biosynthesis pathways were identified in plant species with fully sequenced genomes, and the relationship between the number of paralogs and the organismal complexity was assessed. It was demonstrated that organismal complexity statistically correlates with the number of tryptophan biosynthesis enzymes homologs, both with the total number of homologs and with the number of homologs for three of six enzymes, namely, ASA/ASB, PAI, and IGPS. This relationship may be accounted for by the increase in the organismal complexity and the number of tryptophan biosynthesis enzymes’ homologs being the mechanism of evolutionary adaptation to the varying conditions of the terrestrial environment in plants.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Van Bel, M., Proost, S., Wischnitzki, E., et al., Dissecting plant genomes with the PLAZA comparative genomics platform, Plant Physiol., 2012, Vol. 158, No. 2, pp. 590–600.
Bohlmann, J., DeLuca, V., Eilert, U., and Martin, W., Purification and cDNA cloning of anthranilate synthase from Ruta graveolens: modes of expression and properties of native and recombinant enzymes, Plant J., 1995, Vol. 7, No. 3, pp. 491–501.
Feliner, G.N. and Rossello, J.A., Concerted Evolution of Multigene and Homoelogous Recombination Families. Plant Genome Diversity, Wein: Springer, 2012.
Huson, D.H. and Bryant, D., Application of phylogenetic networks in evolutionary studies, Mol Biol Evol., 2006, Vol. 23, No. 2, pp. 254–267.
Kartel’, N.A., Makeeva, E.N., and Mezenko, A.M., Genetika = Genetics: entsiklopedicheskii slovar’ (Genetics = Genetics: Encyclopedic Dictionary), Minsk: Belarus Navuka, 2011.
Katoh, K. and Toh, H., Recent developments in the MAFFT multiple sequence alignment program, Brief Bioinform., 2008, Vol. 9, No. 4, pp. 286–298.
Kolchanov, N.A., Suslov, V.V., and Gunbin, K.V., Modeling of biological evolution: genetic regulatory system and coding of biological organization, Inform. Vestnik VOGIS, 2004, Vol. 8, No. 2, pp. 86–99.
Lamesch, P., Berardini, T.Z., Li, D., et al., The Arabidopsis information resource (TAIR): improved gene annotation and new tools, Nucleic Acids Res., 2012, vol. 40, pp. D1202–D1210.
Lang, D., Weiche, B., Timmerhaus, G., et al., Genomewide phylogenetic comparative analysis of plant transcriptional regulation: a timeline of loss, gain, expansion, and correlation with complexity, Genome Biol. Evol., 2010, Vol. 19, No. 2, pp. 488–503.
Last, R.L., Bissinger, P.H., Mahoney, D.J., et al., Tryptophan mutants in arabidopsis: the consequences of duplicated tryptophan synthase beta genes, Plant Cell, 1991, Vol. 3, No. 4, pp. 345–358.
Marchler-Bauer, A., Zheng, C., Chitsaz, F., et al., CDD: conserved domains and protein three-dimensional structure, Nucleic Acids Res., 2013, vol. 41, pp. D348–D352.
Niyogi, K.K. and Fink, G.R., Two anthranilate synthase genes in Arabidopsis: defense-related regulation of the tryptophan pathway, Plant Cell, 1992, Vol. 4, No. 6, pp. 721–733.
Radwanski, E.R. and Last, R.L., Tryptophan biosynthesis and metabolism: biochemical and molecular genetics, Plant Cell, 1995, Vol. 7, pp. 921–934.
Richardson, A.O. and Palmer, J.D., Horizontal gene transfer in plants, J. Exp. Bot., 2007, Vol. 58, No. 1, pp. 1–9.
Teichmann, S.A. and Babu, M.M., Gene regulatory network growth by duplication, Nat. Genet., 2004, Vol. 36, No. 5, pp. 492–496.
Tozawa, Y., Hasegawa, H., Terakawa, T., and Wakasa, K., Characterization of rice anthranilate synthase alphasubunit genes OASA1 and OASA2. Tryptophan accumulation in transgenic rice expressing a feedbackinsensitive mutant of OASA1, Plant Physiol., 2001, Vol. 126, No. 4, pp. 1493–1506.
Vogel, C. and Chothia, C., Protein family expansions and biological complexity, PLoS Comput. Biol., 2006, vol. 2, no. 5, p. e48.
Zhao, Y., Auxin biosynthesis: a simple two-step pathway converts tryptophan to indole-3-acetic acid in plants, Mol. Plant, 2012, vol. 5, no. 2 P, pp. 334–338.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © I.I. Turnaev, I.R. Akberdin, V.V. Suslov, D.A. Afonnikov, 2014, published in Vavilovskii Zhurnal Genetiki i Selektsii, 2014, Vol. 18, No. 4/2, pp. 1032–1038.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Turnaev, I.I., Akberdin, I.R., Suslov, V.V. et al. The number of homologs of some enzymes involved in tryptophan biosynthesis is correlated to the proportion of proteins associated with transcription in plants. Russ J Genet Appl Res 5, 308–312 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1134/S2079059715030193
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S2079059715030193