Abstract
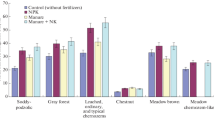
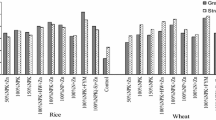
The influence of crop rotation systems with different portions of nitrogen-fixing crops, intermediate crops, and organic fertilizers on the enzymatic activity and humus content of soils in organic farming was studied. The highest activity of the urease and invertase enzymes was determined in the soil under the crop rotation with 43% nitrogen-fixing crops and with perennial grasses applied twice per rotation. The application of manure and the growing of intermediate crops for green fertilizers did not provide any significant increase in the content of humus. The activity of urease slightly correlated with the humus content (r = 0.30 at the significance level of 0.05 and r = 0.39 at the significance level of 0.01).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
L. N. Aleksandrova,Soil Organic Matter and the Processes of Its Transformation (Nauka, Leningrad, 1980) [in Russian].
E. K. Blagoveshchenskaya and T. L. Trishina, “Green Manure in Modern Farming,” Zemledelie, No. 5, 36–37 (1987).
V. P. Volynskaya, “The Use of Sweet Clover as Green Manure Crop,” Zemledelie, No. 6, 20–21 (1997).
N. A. Voronkova and O. F. Khamova, “Agroecological Assessment of the Influence of Precursors on Fertility of Leached Chernozems and on the Yield of Summer Wheat,” Vestn. Altaisk. Gos. Agrarn. Univ., No. 5, 24–29 (2009).
L. A. Karyagina, “Microbiological Basis of Improving Soil Fertility,” in Science and Technology (Minsk, 1983) [in Russian].
T. N. Kulakovskaya and L. M. Stefankina, “The Relationship between the Indices of the Biological Activity, Humus Content, and Crop Yields on a Loamy Sandy Soddy-Podzolic Soil,” Abstr. of the V Congress of the All-Union Microbiol. Soc. (Yerevan, 1975), p. 75 [in Russian].
R. S. Kutuzova, L. B. Sirota, O. V. Orlova, and N. I. Vorobev, “Microbial Community and the Analysis of Microbiological Processes in Soddy-Podzolic Soil,” Eur. Soil Sci. 34(3), 286–297 (2001).
V. G. Loshakov, Yu. D. Ivanov, and Yu. N. Sinikh, “Productivity of Cereal Crop Rotations upon the Use of Green Manure,” Dokl. Timiryazevsk. Sel’skokhoz. Akad., No. 3, 3–20 (1997).
V. I. Loshakov, V. T. Emtsev, L. K. Nitse, et al., “Biological Activity of Soils in a Crop Rotation with the Use of Afterharvest Residues as a Fertilizer,” Izv. Timiryazevsk. Sel’skokhoz. Akad., No. 4, 10–17 (1986).
Yu. K. Novoselov, V. V. Rudoman, and T. S. Brazhnikova, “Intermediate Cabbage Crops as Green Manure,” Zemledelie, No. 2, 20 (1998).
A. Svirskene, “Microbiological and Biochemical Indicators of Anthropogenic Impacts on Soils,” Eur. Soil Sci. 36(2), 192–200 (2003).
V. I. Soroko, G. V. Pirogovskaya, A. M. Rusalovich, et al., Soils and Their Fertility on the Turn of the Century. Book 2. Actual Problems of Soil Fertility under Modern Conditions (Minsk, 2001) [in Russian].
A. I. Chunderova, Extended Abstract of Candidate’s Dissertation in Agriculture (Tallinn, 1973).
M. M. Abdallahi and A. N’Dayegamiye, “Effects of Green Manures on Soil Physical and Biological Properties and on Wheat Yields and N Uptake,” Can. J. Soil Sci. 80, 81–89 (2000).
A. Arlauskienė, S. Maikštenienė, and A. Šlepetienė, “The Effect of Catch Crops and Straw on Spring Barley Nitrogen Nutrition and Soi Humus Composition,” Žemdirbystė-Agriculture. 96, 53–70 (2009).
A. K. Bandick and R. P. Dick, “Field Management Effects on Soil Enzyme Activities,” Soil Biol. Biochem. 31, 1471–1479 (1999).
V. Bogužas, Rudeninio žemės dirbimo ir tarpinių pasė-liu vaidmuo javų sėjomainoje. Daktaro disertacijos tezės (Akademija, Kaunas, 1993).
S. Goyal, M. M. Mishra, S. S. Dhankar, et al., “Microbial Biomass Turnover and Enzyme Activities Following the Application of Farmyard Manure to Fields Soil with and Without Previous Long-Term Applications,” Biol. Fertil. Soils 15, 60–64 (1993).
U. Hege and K. Offenberger, “Effect of Differentiated Mineral Fertilization and Organic Manuring on Yield, Product Quality and N Balance in the International Permanent Organic Nitrogen Experiment (IOSDV) Puch,” Archives Agron. Soil Sci. 52, 535–550 (2006).
V. Janušien, “Humuso kiekio ir kokybinės sudėties kitimas įvairaus humusingumo priesmėlio dirvožemyje,” Žemdirb. mokslo darbai, 80, 23–37 (2002).
G. Kahnt, Gründüngung (Frankfurt, 1981).
E. E. Kara and M. Penezoglu, “The Effect of Green Manuring on Soil Organic Content and Soil Biological Activity,” Anadolu 10, 73–86 (2000).
N. Mikhailovskaya and E. Tarasyuk, “Polyphenoloxidase and Peroxidase Activity in Luvisol Loamy Sand Soil,” in Dirvožemis tvarioje aplinkoje (Akademija, 2008), p. 47.
M. Nawrath, Einfluüngung (Stroh- und Gründüngung, Stallmist) auf Humusgehalt, Humusqualitat und Pflanzenertrag (Diss. Agrarwissenschaft Fachbereich (Gießen, 1998).
J. Pekarskas and D. Zakarauskaitė, “Dirvožemio biologinio aktyvumo ivertinimas ekologinėje ir intensyvioje žemdirbystės sistemose,” in Vadyba: mokslo tiriamieji darbai (Klaipėda), No. 2, 187–194 (2009).
D. Romanovskaja, “Įvairių organinių trąšų įtaka organinės medžiagos kaupimuisi ir mineralinio azoto dinamikai vel niniame jauriniame priesmėlio dirvožemyje,” Žemės ūkio mokslai 1, 3–10 (2001).
F. Schimner and R. Sonnleitner, “Bodenokologie: Mikrobiologie Und Bodenenzymatik,” in Bodenbewirtschaftung, Dungung und Rekultivierung (Berlin, 1996).
G. E. Siebeneicher, Handbuch fur den Biologischen Landbau: das Standartwerk fur alle Richtungen and Gebiete (Ulmer, Stuttgart, 1993).
A. Svirskienė, “Antropogeniniam poveikiui jautrių dirvožemio mikrobiologinio aktyvumo ir jo derlingumo indikatorių įvertinimas,” Ekologija, 3, 90–94 (1999).
A. Svirskien and A. Magyla, “Įvairios specializacijos sėjomain bei monokultūrų įtaka dirvožemio biologiniams aktyvumui,” in Žemdirbystė: mokslo darbai, Akademija 59, 3–13 (1997).
A. Svirskienė, A. Šlepetienė, and A. Bučienė, “Microbiological processes and humus quality while applying organic and mineral fertilizers,” in Ecological effects of microorganism action, mat. Int. Conf. (Vilnius, 1997).
A. Šlepetienė, Ilgalaikių agrotechnikos priemonių įtaka humuso kiekiui ir jo sudėčiai Lietuvos veleniniuose glejiškuose karbonatiniuose priemolio dirvožemiuose, Daktaro disertacijos santrauka (Dotnuva-Akademija, 1997).
M. Tejada, J. L. Gonzalez, A. M. Garcia-Martinez, and J. Parrado, “Effects of Different Green Manures on Soil Biological Properties and Maize Yield,” Biores. Technol. 99, 1758–1767 (2007).
C. TrasarCepeda, C. Leiras, F. GilSotres, and S. Seone, “Towards a Biochemical Quality Indexes for Soils. An Expression Relating Several Biological and Biochemical Properties,” Biol. Fertil. Soils, No. 26, 100–106 (1998).
L. Tripolskaja, Organinės trąšos ir jų poveikis aplinkai (Akademija, 2005).
R. Velička, Rapsai (Lutute, Kaunas, 2002).
D. Zakarauskaitė, K. Grigaliūnienė, and J. Kučinskas, et al., “Ilgalaikio tręšimo organin mis ir mineralinėmis trąšomis poveikis dirvožemio biologiniam aktyvumui,” Vagos: LŽŪU mokslo darbai, 68(21), 44 (2005).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Original Russian Text © A. Marcinkeviciene, V. Boguzas, S. Balnyte, R. Pupaliene, R. Velicka, 2013, published in Pochvovedenie, 2013, No. 2, pp. 219–225.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Marcinkeviciene, A., Boguzas, V., Balnyte, S. et al. Influence of crop rotation, intermediate crops, and organic fertilizers on the soil enzymatic activity and humus content in organic farming systems. Eurasian Soil Sc. 46, 198–203 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1064229313020105
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1064229313020105