Abstract
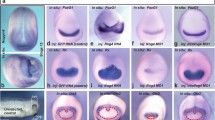
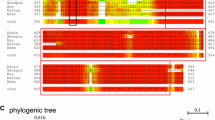
Noggin proteins are important regulators of the early development of the vertebrate neural system. Previously, it has been traditionally thought that vertebrates have only one noggin gene (Noggin1), whose main function is the inhibition of BMP signaling pathway during the formation of dorsoventral polarity in embryos. Then other proteins of this family were discovered, and the studies of Noggin2 protein showed that noggin proteins also participate in the modulation of Nodal/Activin and Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathways in the early development of amphibian head structures. The purpose of this study is to investigate the properties of another noggin protein, Noggin4. We proved that Noggin4 plays an important role in the formation of head structure in clawed frog, since it inhibits the activity of Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway. At the same time, unlike Noggin1 and Noggin2, Noggin4 does not inhibit the activity of TGF-beta signaling pathways (BMP and Nodal/Activin).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bayramov, A.V., Eroshkin, F.M., Martynova, N.Y., et al., Novel functions of Noggin proteins: inhibition of Activin/Nodal and Wnt signaling, Development, 2011, vol. 138, pp. 5345–5356.
Borodulin, A.V., Eroshkin, F.M., Bayramov, A.V., et al., Noggin4 expression during chick embryonic development, Int. J. Dev. Biol., 2013, vol. 56, pp. 403–406.
Eroshkin, F.M., Ermakova, G.V., Bayramov, A.V., et al., Multiple Noggins in vertebrate genome: cloning and expression of noggin2 and noggin4 in Xenopus laevis, Gene Expr. Patterns, 2006, vol. 6, pp. 180–186.
Fletcher, R.B., Watson, A.L., and Harland, R.M., Expression of Xenopus tropicalis Noggin1 and Noggin2 in early development: two Noggin genes in a tetrapod, Gene Expr. Patterns, 2004, vol. 5, pp. 225–230.
Graff, J.M., Thies, R.S., Song, J.J., et al., Studies with a Xenopus BMP receptor suggest that ventral mesoderminducing signals override dorsal signals in vivo, Cell, 1994, vol. 79, pp. 169–179.
Groppe, J., Greenwald, J., Wiater, E., Rodriguez-Leon, J., et al., Structural basis of bmp signalling inhibition by the cystine knot protein Noggin, Nature, 2002, vol. 420, pp. 636–642.
Harland, R.M., In situ hybridization: an improved wholemount method for Xenopus embryos, Methods Cell Biol., 1991, vol. 36, pp. 685–695.
Hikasa, H., Ezan, J., Itoh, K., Li, X., et al., Regulation of TCF3 by Wnt-dependent phosphorylation during vertebrate axis specification, Dev. Cell, 2010, vol. 19, pp. 521–532.
Niehrs, C., Head in the Wnt: the molecular nature of Spemann’s head organizer, Trends Genet., 1999, vol. 15, pp. 314–319.
Nieuwkoop, P.D. and Faber, J., Normal table of Xenopus laevis, Amsterdam: North Holland, 1967.
Piccolo, S., Agius, E., Leyns, L., et al., The head inducer Cerberus is a multifunctional antagonist of Nodal, BMP and Wnt signals, Nature, 1999, vol. 397, pp. 707–710.
Pierreux, C.E., Nicolas, F.J., and Hill, C.S., Transforming growth factor beta-independent shuttling of Smad4 between the cytoplasm and nucleus, Mol. Cell. Biol., 2000, vol. 20, pp. 9041–9054.
Smith, W.C. and Harland, R.M., Expression cloning of Noggin, a new dorsalizing factor localized to the Spemann organizer in Xenopus embryos, Cell, 1992, vol. 70, pp. 829–840.
Yuan, G., Yang, G., Zheng, Y., et al., The non-canonical BMP and Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathways orchestrate early tooth development, Development, 2015, vol. 142, no. 1, pp. 128–139.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © A.V. Bayramov, F.M. Eroshkin, A.V. Borodulin, N.Yu. Martynova, G.V. Ermakova, A.G. Zaraisky, 2016, published in Ontogenez, 2016, Vol. 47, No. 4, pp. 229–234.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bayramov, A.V., Eroshkin, F.M., Borodulin, A.V. et al. Secreted protein Noggin4 participates in the formation of forebrain structures in Xenopus laevis by inhibiting the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway. Russ J Dev Biol 47, 202–206 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1062360416040020
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1062360416040020