Abstract
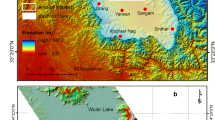
A comparative analysis of Western Siberia area images made from the SMOS satellite with a MIRAS radiometer at a frequency of 1.42 GHz at different times is performed. To validate and calibrate the satellite data, ground measurements of physical parameters of the underlying surface were conducted. As a test site, Kulunda Steppe situated in the steppe part of the Altay region was chosen. Using satellite and ground data, water-logging and swamped soils tending to salt and bitter-salt lakes were detected.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
E. Shanda, Physical Fundamentals of Remote Sensing (Berlin, Springer-Verlag, 1986).
U. Ris, Fundamentals of Remote Sensing (Tekhnosfera, Moscow, 2006) [in Russian].
S. Sorooshian, B. Imam, S. Mahani, and M. Whittaker, “Hydrologic sciences and water resources management issues in a changing world,” in Developments in Water Science (Elsevier, 2003), vol. 50, pp. 83–92.
A. N. Romanov and I. A. Sutorikhin, “Remote monitoring of ecologic state of supersaturated soils,” Atmos. Ocean. Opt. 19(11), 880–881 (2006).
V. L. Mironov and P. P. Bobrov, “Microwave radiometric sensing of soils,” Atmos. Ocean. Opt. 20(12), 1024–1026 (2007).
J.-P. Wigneron, M. Schwank, E. L. Baeza, Y. Kerr, N. Novello, C. Millan, C. Moisy, P. Richaume, A. Mialon, A. Al. Bitar, F. Cabot, H. Lawrence, D. Guyon, J.-C. Calvet, J. P. Grant, T. Casal, P. de Rosnay, K. Saleh, A. Mahmoodi, S. Delwart, and S. Mecklenburg, “First evaluation of the simultaneous SMOS and ELBARA-II observations in the Mediterranean region,” Remote Sens. Environ. 124(9), 26–37 (2012).
G. B. Brassington and P. Divakaran, “The theoretical impact of remotely sensed sea surface salinity observations in a multi-variate assimilation system,” Ocean Model. 27(1–2), 70–81 (2009).
A. E. Basharinov, A. S. Gurvich, and S. T. Egorov, Radio Thermal Radiation of the Earth as a Planet (Nauka, Moscow, 1974) [in Russian].
L. M. Mitnik, Radiative Parameters of Water Surface. Ser. Oceanology (review) (Inform. Tsentr, Obninsk, 1978) [in Russian].
N. M. Tseitlin, Antenna Technique and Radio Astronomy (Sov. Radio, Moscow, 1976) [in Russian].
A. N. Romanov, Dielectric and Radio Radiative Properties of Salted Soils in the Microwave Range (Izd-vo Altaiskogo Un-ta, Barnaul, 2002).
N. I. Bazilevich, Geochemistry of Natrium Salinized Soils (Nauka, Moscow, 1965) [in Russian].
A. N. Romanov, Doctoral Dissertation in Engineering (Barnaul, 2004).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © A.N. Romanov, I.V. Khvostov, V.E. Pavlov, Yu.I. Vinokurov, 2014, published in Optika Atmosfery i Okeana.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Romanov, A.N., Khvostov, I.V., Pavlov, V.E. et al. Remote monitoring of wetland areas of Western Siberia using SMOS (ESA) data. Atmos Ocean Opt 27, 313–316 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1024856014040150
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1024856014040150