Abstract
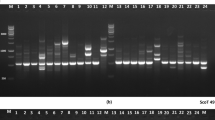
Genomes of 184 Sinorhizobium meliloti native isolates were studied to test the occurence of islands Sme21T, Sme19T, and Sme80S previously described in the model strain Rm1021. This analysis was conducted using PCR methodology involving specific primers. It was demonstrated that, in the examined geographically distinct populations of S. meliloti from the Northern Caucasus (NCG) and the Aral Sea region (PAG), the strains containing genomic islands were observed with similar frequency (0.55 and 0.57, respectively). Island Sme80S, denoted as an island of “environmental adaptivity,” was identified predominantly (frequency of 0.38) in genomes of strains which exhibited a lower level of salt tolerance and was isolated in PAG, a modern center of introgressive hybridization of alfalfa subjected to salinity. Island Sme21T designated as “ancestral” was observed in genomes of strains isolated in NCG, the primary center of host-plant biodiversity, 10-fold more often than in strains from PAG. An island Sme19T, which predominantly carries genes encoding transposases, was observed in genomes of strains in both populations with average frequency of 0.10. The analysis of linkage disequilibrium (LD) based on the assessment of probability for detection of different islands combinations in genomes revealed an independent inheritance of islands in salt-sensitive strains of various geographic origin. In contrast, the absence of this trend was noted in the majority of the examined combinations of salt-tolerant strains. It was concluded that the structure of chromosome in PAG strains which predominantly possessed a salt-sensitive phenotype was subjected to active recombinant processes, which could predetermine the intensity of microevolutionary processes in bacterial populations and facilitate an adaptation of bacteria in adverse environmental effect.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hacker, J. and Kaper, J.B., Pathogenicity islands and the evolution of microbes, Annu. Rev. Microbiol., 2000, vol. 54, pp. 641–679. doi 10.1146/annurev.micro.54.1.641
Dobrindt, U., Hochhut, B., Hentschel, U., and Hacker, J., Genomic islands in pathogenic and environmental microorganisms, Nat. Rev. Microbiol., 2004, vol. 2, no. 5, pp. 414–424. doi 10.1038/nrmicro884
Kaneko, T., Nakmura, Y., Sato, S., et al., Complete genome structure of the nitrogen-fixing symbiotic bacterium Mesorhizobium loti, DNA Res., 2000, vol. 7, no. 6, pp. 331–338. doi 10.1093/dnares/7.6.331
Kaneko, T., Nakamura, Y., Sato, S., et al., Complete genomic sequence of nitrogen-fixing symbiotic bacterium Bradyrhizobium japonicum USDA110, DNA Res., 2002, vol. 9, no. 6, pp. 189–197. doi 10.1093/dnares/9.6.189
Langille, M.G.I., Hsiao, W.W.L., and Brinkman, F.S.L., Detection of genomic islands using bioinformatics approaches, Nat. Rev. Microbiol., 2010, vol. 8, no. 5, pp. 373–382. doi 10.1038/nrmicro2350
Hacker, J., Blum-Oehler, G., Muehldorfer, I., and Tschaepe, H., Pathogenicity islands of virulent bacteria: structure, function and impact on microbial evolution, Mol. Microbiol., 1997, vol. 23, no. 6, pp. 1089–1097. doi 10.1046/j.1365-2958.1997.3101672.x
Fouts, D.E., Phage_Finder: automated identification and classification of prophage regions in complete bacterial genome sequences, Nucleic Acids Res., 2006, vol. 34, no. 20, pp. 5839–5851. doi 10.1093/nar/gkl732
Middendorf, B., Hochhut, B., Leipold, K., et al., Instability of pathogenicity islands in uropathogenic Escherichia coli 536, J. Bacteriol., 2004, vol. 186, no. 10, pp. 3086–3096. doi 10.1128/JB.186.10.3086-3096.2004
Juhas, M., van der Meer, J.R., Gaillard, M., et al., Genomic islands: tools of bacterial horizontal gene transfer and evolution, FEMS Microbiol. Rev., 2009, vol. 33, no. 2, pp. 376–393. doi 10.1111/j.1574-6976. 2008.00136.x
Capela, D., Barloy-Hubler, F., Gouzy, J., et al., Analysis of the chromosome sequence of the legume symbiont Sinorhizobium meliloti strain 1021, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 2001, vol. 98, no. 17, pp. 9877–9882. doi 10.1073/pnas.161294398
Mantri, Y. and Williams, K.P., Islander: a database of integrative islands in prokaryotic genomes, the associated integrases and their DNA site specificities, Nucleic Acids Res., 2004, vol. 32, D.55–D.58. doi 10.1093/nar/gkh059
Roumiantseva, M.L., Muntyan, V.S., and Simarov, B.V., Genomic islands of bacteria: structure and the functional analysis, in VIS’ezd VOGiS i assotsiirovannye geneticheskie simpoziumy (6th Congress of the Vavilov Society of Geneticists and Breeders and the Associated Genetic Symposia), Rostov on Don, 2014, p. 188.
Ferrieres, L., Francez-Charlot, A., Gouzy, J., et al., FixJ-regulated genes evolved through promoter duplication in Sinorhizobium meliloti, Microbiology, 2004, vol. 150, no. 7, pp. 2335–2345. doi 10.1099/mic.0.27081-0
Dzyubenko, N.I., Malyshev, L.L., and Rakovskaya, N.V., Mobilization of the genetic diversity of wild relatives of cultivated plants in the North Caucasus, in Geneticheskie resursy kul’turnykh rastenii (Genetic Resources of Cultivated Plants) (Proc. Int. Theor. Pract. Conf.), St. Petersburg, 2001, pp. 29–31.
Dzyubenko, N.I., Dzyubenko, E.A., and Khusainov, S.Kh., Methodical bases of expedition search and collection of salt-tolerant populations of wild species of leguminous plants in the zone of ecological disaster of the North Aral Sea area, in Geneticheskie resursy kul’turnykh rastenii (Genetic Resources of Cultivated Plants) (Proc. Int. Theor. Pract. Conf.), St. Petersburg, 2001, pp. 27–28.
Ibragimova, M.V., Roumiantseva, M.L., Onishchuk, O.P., et. al, Symbiosis between the root-nodule bacterium Sinorhizobium meliloti and alfalfa (Medicago sativa) under salinization conditions, Microbiology (Moscow), 2006, vol. 75, no. 1, pp. 71–81. doi 10.1134/S0026261706010140
Biondi, E.G., Pilli, E., Giuntini, E., et al., Genetic relationship of Sinorhizobium meliloti and Sinorhizobium medicae strains isolated from Caucasian region, FEMS Microbiol. Lett., 2003, vol. 220, no. 2, pp. 207–213. doi 10.1016/s0378-1097(03)00098-3
Roumiantseva, M.L., Genetic resources of nodule bacteria (review), Russ. J. Genet., 2009, vol. 45, no. 9, pp. 1013–1026. doi 10.1134/s2079059711020079
Ivanov, A.I., Lyutserna (Alfalfa), Moscow: Kolos, 1980.
Kust, G.S., Desertification and the evolution of arid areas (exemplified by the Aral Sea region), Extended Abstract of Doctoral (Biol.) Dissertation, Mosk. Gos. Univ., Moscow, 1993.
Roumiantseva, M.L., Muntyan, V.S., Mengoni, A., and Simarov, B.V., ITS-polymorphism of salt-tolerant and salt-sensitive native isolates of Sinorhizobium meliloti— symbionts of alfalfa, clover and fenugreek plants, Russ. J. Genet., 2014, vol. 50, no. 4, pp. 348–359. doi 10.1134/S1022795414040103
Maniatis, T., Fritsch, E.F., and Sambrook, J., Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual, Cold Spring Harbor: Cold Spring Harbor Lab., 1982.
Roumiantseva, M.L., Simarov, B.V., Onishchuk, O.P., et al., Biologicheskoe raznoobrazie klubenkovykh bakteriy v ekosistemakh i agrotsenozakh: teoreticheskie osnovy i metody (Biological Diversity of Root Nodule Bacteria in Ecosystems and Agrocenoses), Roumiantseva, M.L. and Simarov, B.V., Eds., St. Petersburg: Vserossiyskiy Nauchno-Issledovatel’skiy Institut Selskokhoziaystvennoy Mikrobiologii Rossiyskoy Akademii Selskokhoziaystvennykh Nauk, 2011.
Belova, V.S., Krol, L., Andronov, E.E., et al., Comparative genomics of Sinorhizobium meliloti/S. medicae isolates native to gene centers of alfalfa, in Applied and Fundamental Aspects of Responses, Signaling and Developmental Process in the Root-Microbe Systems (Abstracts of Postgraduate Course and Meeting of the Research Consortium on Evolution of Plant–Microbe Interactions), St.-Petersburg, 2007, p. 39.
Andronov, E.E., Climate change, salinization and soil microbial community adaptive evolution, in Adaptation to Climate Change in the Baltic Sea Region: Contributions from Plant and Microbial Biotechnology, Mikkeli, 2010, O11.
Hammer, O., Harper, D.A.T., and Ryan, P.D., PAST: Paleontological statistics software package for education and data analysis, Palaeontol. Electron., 2001, vol. 4, no. 1. http://palaeo-electronica.org/2001_1/past/issue1_01.htm
Excoffier, L. and Lischer, H.E.L., Arlequin suite ver 3.5: a new series of programs to perform population genetics analyses under Linux and Windows, Mol. Ecol. Res., 2010, vol. 10, pp. 564–567. doi 10.1111/j.1755-0998.2010.02847.x
Schwarz, H., Stichprobenverfahren: ein Leitfaden zur Anwendung statistischer Methoden zur Bewertung, München: R. Oldenbourg, 1975.
Roumiantseva, M.L. and Muntyan, V.S., Root nodule bacteria Sinorhizobium meliloti: tolerance to salinity and bacterial genetic determinants, Microbiology (Moscow), 2015, vol. 84, no. 3, pp. 303–318. doi 10.1134/S0026261715030170
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © V.S. Muntyan, M.E. Cherkasova, E.E. Andronov, B.V. Simarov, M.L. Roumiantseva, 2016, published in Genetika, 2016, Vol. 52, No. 10, pp. 1126–1133.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Muntyan, V.S., Cherkasova, M.E., Andronov, E.E. et al. Occurrence of islands in genomes of Sinorhizobium meliloti native isolates. Russ J Genet 52, 1015–1022 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1134/S102279541608010X
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S102279541608010X